Abstract
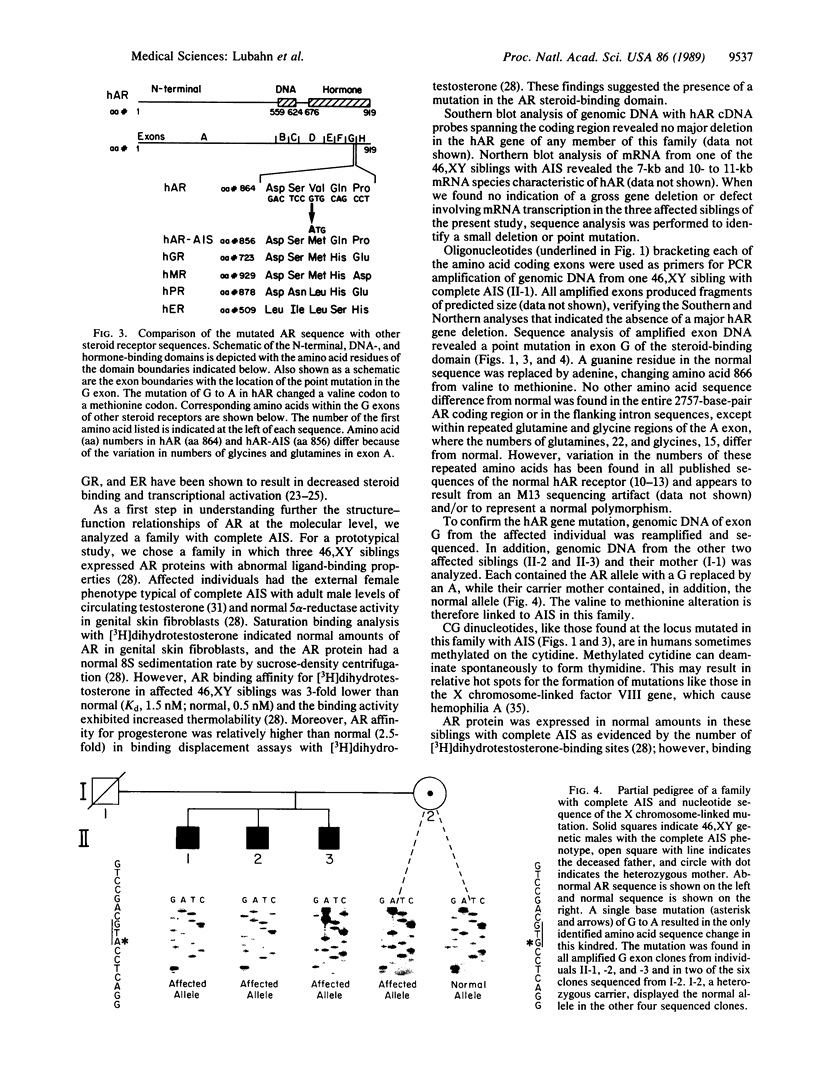
Androgens act through a receptor protein (AR) to mediate sex differentiation and development of the male phenotype. We have isolated the eight exons in the amino acid coding region of the AR gene from a human X chromosome library. Nucleotide sequences of the AR gene intron/exon boundaries were determined for use in designing synthetic oligonucleotide primers to bracket coding exons for amplification by the polymerase chain reaction. Genomic DNA was amplified from 46,XY phenotypic female siblings with complete androgen insensitivity syndrome. AR binding affinity for dihydrotestosterone in the affected siblings was lower than in normal males, but the binding capacity was normal. Sequence analysis of amplified exons demonstrated within the AR steroid-binding domain (exon G) a single guanine to adenine mutation, resulting in replacement of valine with methionine at amino acid residue 866. As expected, the carrier mother had both normal and mutant AR genes. Thus, a single point mutation in the steroid-binding domain of the AR gene correlated with the expression of an AR protein ineffective in stimulating male sexual development.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aiman J., Griffin J. E., Gazak J. M., Wilson J. D., MacDonald P. C. Androgen insensitivity as a cause of infertility in otherwise normal men. N Engl J Med. 1979 Feb 1;300(5):223–227. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197902013000503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amrhein J. A., Meyer W. J., 3rd, Jones H. W., Jr, Migeon C. J. Androgen insensitivity in man: evidence for genetic heterogeneity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Mar;73(3):891–894. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.3.891. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arriza J. L., Weinberger C., Cerelli G., Glaser T. M., Handelin B. L., Housman D. E., Evans R. M. Cloning of human mineralocorticoid receptor complementary DNA: structural and functional kinship with the glucocorticoid receptor. Science. 1987 Jul 17;237(4812):268–275. doi: 10.1126/science.3037703. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beato M. Gene regulation by steroid hormones. Cell. 1989 Feb 10;56(3):335–344. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90237-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breathnach R., Chambon P. Organization and expression of eucaryotic split genes coding for proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:349–383. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.002025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown T. R., Lubahn D. B., Wilson E. M., Joseph D. R., French F. S., Migeon C. J. Deletion of the steroid-binding domain of the human androgen receptor gene in one family with complete androgen insensitivity syndrome: evidence for further genetic heterogeneity in this syndrome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Nov;85(21):8151–8155. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.21.8151. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown T. R., Maes M., Rothwell S. W., Migeon C. J. Human complete androgen insensitivity with normal dihydrotestosterone receptor binding capacity in cultured genital skin fibroblasts: evidence for a qualitative abnormality of the receptor. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1982 Jul;55(1):61–69. doi: 10.1210/jcem-55-1-61. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang C. S., Kokontis J., Liao S. T. Molecular cloning of human and rat complementary DNA encoding androgen receptors. Science. 1988 Apr 15;240(4850):324–326. doi: 10.1126/science.3353726. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang C. S., Kokontis J., Liao S. T. Structural analysis of complementary DNA and amino acid sequences of human and rat androgen receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Oct;85(19):7211–7215. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.19.7211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dobson A. D., Conneely O. M., Beattie W., Maxwell B. L., Mak P., Tsai M. J., Schrader W. T., O'Malley B. W. Mutational analysis of the chicken progesterone receptor. J Biol Chem. 1989 Mar 5;264(7):4207–4211. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans R. M. The steroid and thyroid hormone receptor superfamily. Science. 1988 May 13;240(4854):889–895. doi: 10.1126/science.3283939. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faber P. W., Kuiper G. G., van Rooij H. C., van der Korput J. A., Brinkmann A. O., Trapman J. The N-terminal domain of the human androgen receptor is encoded by one, large exon. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1989 Feb;61(2):257–262. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(89)90137-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- French F. S., Van Wyk J. J., Baggett B., Easterling W. E., Talbert L. M., Johnston F. R., Forchielli E., Dey A. C. Further evidence of a target organ defect in the syndrome of testicular feminization. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1966 May;26(5):493–503. doi: 10.1210/jcem-26-5-493. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giguère V., Hollenberg S. M., Rosenfeld M. G., Evans R. M. Functional domains of the human glucocorticoid receptor. Cell. 1986 Aug 29;46(5):645–652. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90339-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottlieb B., Kaufman M., Pinsky L., Leboeuf G., Sotos J. F. Extracellular correction of the androgen-receptor transformation defect in two families with complete androgen resistance. J Steroid Biochem. 1987 Sep;28(3):279–284. doi: 10.1016/0022-4731(87)91019-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green S., Chambon P. Nuclear receptors enhance our understanding of transcription regulation. Trends Genet. 1988 Nov;4(11):309–314. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(88)90108-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huckaby C. S., Conneely O. M., Beattie W. G., Dobson A. D., Tsai M. J., O'Malley B. W. Structure of the chromosomal chicken progesterone receptor gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(23):8380–8384. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.23.8380. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes I. A., Evans B. A. Complete androgen insensitivity syndrome characterized by increased concentration of a normal androgen receptor in genital skin fibroblasts. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1986 Aug;63(2):309–315. doi: 10.1210/jcem-63-2-309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes M. R., Malloy P. J., Kieback D. G., Kesterson R. A., Pike J. W., Feldman D., O'Malley B. W. Point mutations in the human vitamin D receptor gene associated with hypocalcemic rickets. Science. 1988 Dec 23;242(4886):1702–1705. doi: 10.1126/science.2849209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumar V., Chambon P. The estrogen receptor binds tightly to its responsive element as a ligand-induced homodimer. Cell. 1988 Oct 7;55(1):145–156. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90017-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumar V., Green S., Stack G., Berry M., Jin J. R., Chambon P. Functional domains of the human estrogen receptor. Cell. 1987 Dec 24;51(6):941–951. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90581-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lubahn D. B., Joseph D. R., Sar M., Tan J., Higgs H. N., Larson R. E., French F. S., Wilson E. M. The human androgen receptor: complementary deoxyribonucleic acid cloning, sequence analysis and gene expression in prostate. Mol Endocrinol. 1988 Dec;2(12):1265–1275. doi: 10.1210/mend-2-12-1265. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lubahn D. B., Joseph D. R., Sullivan P. M., Willard H. F., French F. S., Wilson E. M. Cloning of human androgen receptor complementary DNA and localization to the X chromosome. Science. 1988 Apr 15;240(4850):327–330. doi: 10.1126/science.3353727. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mullis K., Faloona F., Scharf S., Saiki R., Horn G., Erlich H. Specific enzymatic amplification of DNA in vitro: the polymerase chain reaction. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1986;51(Pt 1):263–273. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1986.051.01.032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ponglikitmongkol M., Green S., Chambon P. Genomic organization of the human oestrogen receptor gene. EMBO J. 1988 Nov;7(11):3385–3388. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03211.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pratt W. B., Jolly D. J., Pratt D. V., Hollenberg S. M., Giguere V., Cadepond F. M., Schweizer-Groyer G., Catelli M. G., Evans R. M., Baulieu E. E. A region in the steroid binding domain determines formation of the non-DNA-binding, 9 S glucocorticoid receptor complex. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jan 5;263(1):267–273. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rivarola M. A., Saez J. M., Meyer W. J., Kenny F. M., Migeon C. J. Studies of androgens in the syndrome of male pseudohermaphroditism with testicular feminization. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1967 Mar;27(3):371–378. doi: 10.1210/jcem-27-3-371. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strickland A. L., French F. S. Absence of response to dihydrotestosterone in the syndrome of testicular feminization. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1969 Sep;29(9):1284–1286. doi: 10.1210/jcem-29-9-1284. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tilley W. D., Marcelli M., Wilson J. D., McPhaul M. J. Characterization and expression of a cDNA encoding the human androgen receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jan;86(1):327–331. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.1.327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trapman J., Klaassen P., Kuiper G. G., van der Korput J. A., Faber P. W., van Rooij H. C., Geurts van Kessel A., Voorhorst M. M., Mulder E., Brinkmann A. O. Cloning, structure and expression of a cDNA encoding the human androgen receptor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 May 31;153(1):241–248. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)81214-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai S. Y., Carlstedt-Duke J., Weigel N. L., Dahlman K., Gustafsson J. A., Tsai M. J., O'Malley B. W. Molecular interactions of steroid hormone receptor with its enhancer element: evidence for receptor dimer formation. Cell. 1988 Oct 21;55(2):361–369. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90059-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webster N. J., Green S., Jin J. R., Chambon P. The hormone-binding domains of the estrogen and glucocorticoid receptors contain an inducible transcription activation function. Cell. 1988 Jul 15;54(2):199–207. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90552-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Youssoufian H., Kazazian H. H., Jr, Phillips D. G., Aronis S., Tsiftis G., Brown V. A., Antonarakis S. E. Recurrent mutations in haemophilia A give evidence for CpG mutation hotspots. 1986 Nov 27-Dec 3Nature. 324(6095):380–382. doi: 10.1038/324380a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zahraoui A., Cuny G. Nucleotide sequence of the chicken proto-oncogene c-erbA corresponding to domain 1 of v-erbA. Eur J Biochem. 1987 Jul 1;166(1):63–69. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1987.tb13484.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




