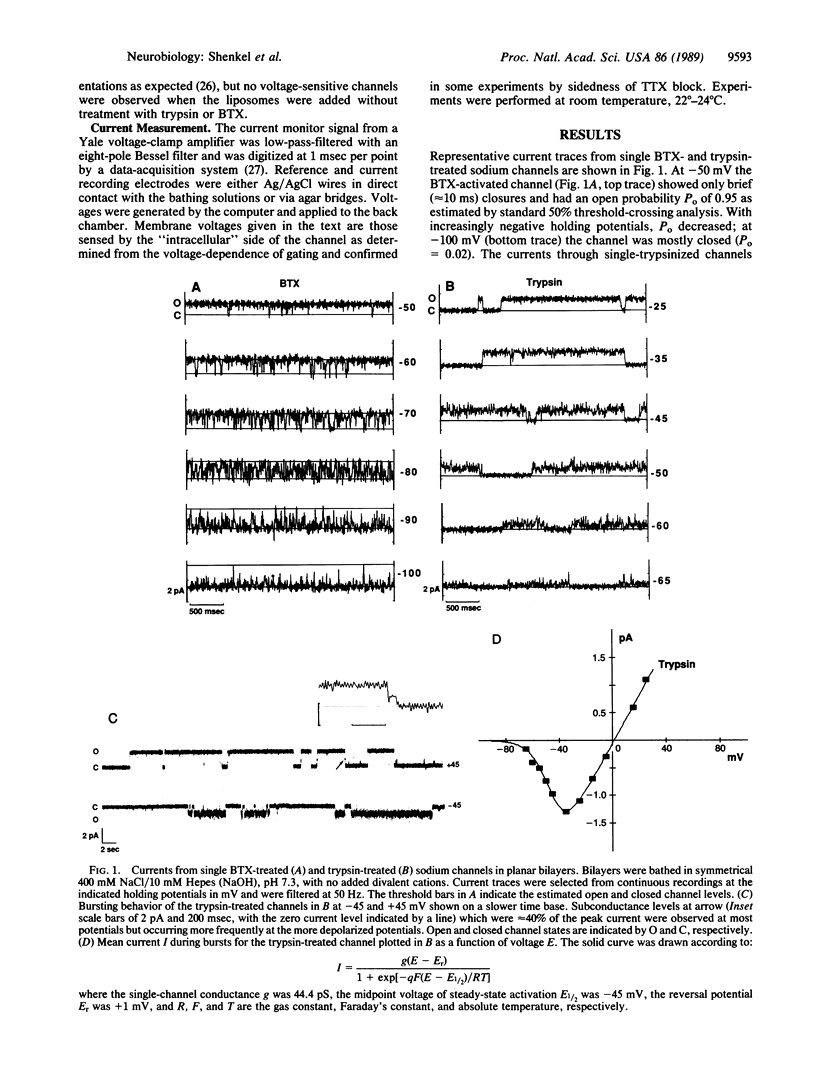
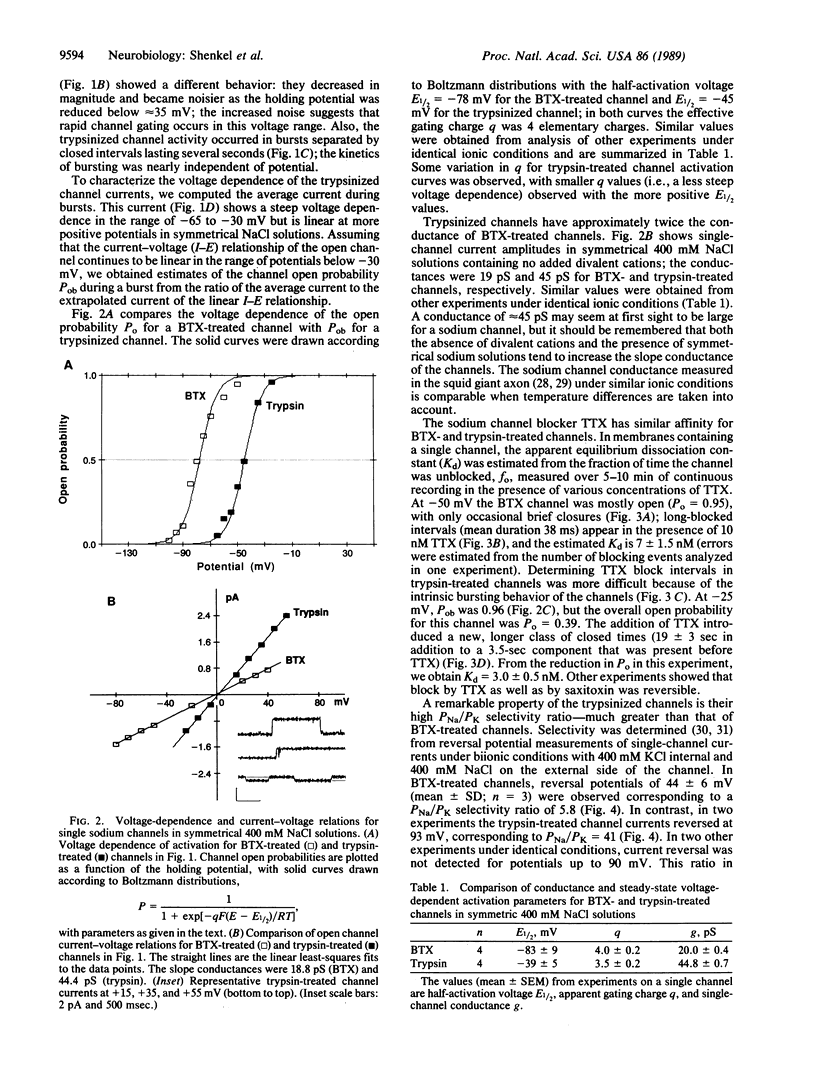
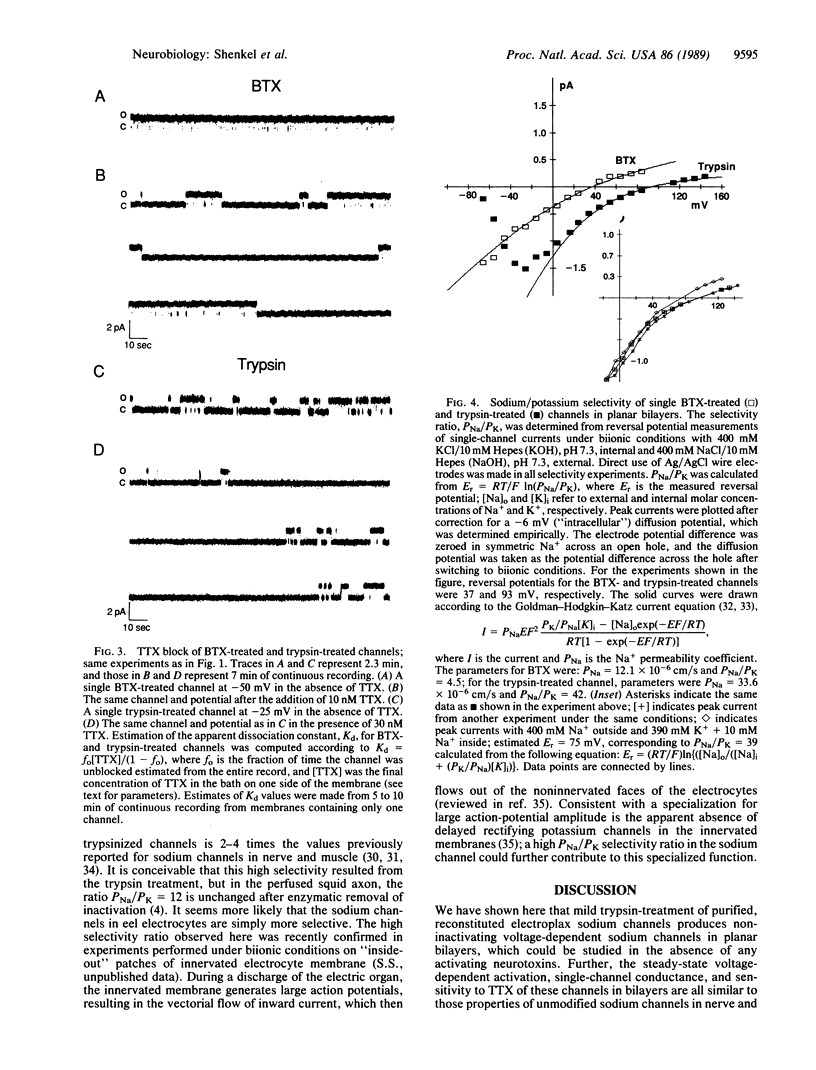
Abstract
A recent study showed that limited trypsin treatment of liposomes containing purified Electrophorus electricus sodium channels activates a sodium radiotracer flux. We now report that similarly treated sodium channels show voltage-gated, tetrodotoxin-sensitive and highly sodium-selective single-channel currents when incorporated into planar lipid membranes. The trypsinized channels opened repeatedly in bursts of several seconds duration, as would be expected for channels whose fast inactivation process had been removed. Furthermore, they have a higher conductance, different voltage-dependence of gating, and a remarkably higher selectivity (PNa/PK = 41) than sodium channels bound by batrachotoxin or other activating neurotoxins; these properties of the trypsinized channels are probably closer to those of channels in intact electrocytes.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Armstrong C. M., Bezanilla F., Rojas E. Destruction of sodium conductance inactivation in squid axons perfused with pronase. J Gen Physiol. 1973 Oct;62(4):375–391. doi: 10.1085/jgp.62.4.375. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Behrens M. I., Oberhauser A., Bezanilla F., Latorre R. Batrachotoxin-modified sodium channels from squid optic nerve in planar bilayers. Ion conduction and gating properties. J Gen Physiol. 1989 Jan;93(1):23–41. doi: 10.1085/jgp.93.1.23. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bezanilla F. Single sodium channels from the squid giant axon. Biophys J. 1987 Dec;52(6):1087–1090. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(87)83304-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell D. T. Ionic selectivity of the sodium channel of frog skeletal muscle. J Gen Physiol. 1976 Mar;67(3):295–307. doi: 10.1085/jgp.67.3.295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chandler W. K., Meves H. Voltage clamp experiments on internally perfused giant axons. J Physiol. 1965 Oct;180(4):788–820. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1965.sp007732. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen F. S., Zimmerberg J., Finkelstein A. Fusion of phospholipid vesicles with planar phospholipid bilayer membranes. II. Incorporation of a vesicular membrane marker into the planar membrane. J Gen Physiol. 1980 Mar;75(3):251–270. doi: 10.1085/jgp.75.3.251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper E. C., Tomiko S. A., Agnew W. S. Reconstituted voltage-sensitive sodium channel from Electrophorus electricus: chemical modifications that alter regulation of ion permeability. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Sep;84(17):6282–6286. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.17.6282. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eaton D. C., Brodwick M. S., Oxford G. S., Rudy B. Arginine-specific reagents remove sodium channel inactivation. Nature. 1978 Feb 2;271(5644):473–476. doi: 10.1038/271473a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furman R. E., Tanaka J. C., Mueller P., Barchi R. L. Voltage-dependent activation in purified reconstituted sodium channels from rabbit T-tubular membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jan;83(2):488–492. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.2.488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman D. E. POTENTIAL, IMPEDANCE, AND RECTIFICATION IN MEMBRANES. J Gen Physiol. 1943 Sep 20;27(1):37–60. doi: 10.1085/jgp.27.1.37. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green W. N., Weiss L. B., Andersen O. S. Batrachotoxin-modified sodium channels in planar lipid bilayers. Ion permeation and block. J Gen Physiol. 1987 Jun;89(6):841–872. doi: 10.1085/jgp.89.6.841. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., HUXLEY A. F. A quantitative description of membrane current and its application to conduction and excitation in nerve. J Physiol. 1952 Aug;117(4):500–544. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1952.sp004764. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., KATZ B. The effect of sodium ions on the electrical activity of giant axon of the squid. J Physiol. 1949 Mar 1;108(1):37–77. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1949.sp004310. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanke W., Boheim G., Barhanin J., Pauron D., Lazdunski M. Reconstitution of highly purified saxitoxin-sensitive Na+-channels into planar lipid bilayers. EMBO J. 1984 Mar;3(3):509–515. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01839.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartshorne R. P., Keller B. U., Talvenheimo J. A., Catterall W. A., Montal M. Functional reconstitution of the purified brain sodium channel in planar lipid bilayers. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(1):240–244. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.1.240. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hille B. The permeability of the sodium channel to metal cations in myelinated nerve. J Gen Physiol. 1972 Jun;59(6):637–658. doi: 10.1085/jgp.59.6.637. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horn R., Vandenberg C. A., Lange K. Statistical analysis of single sodium channels. Effects of N-bromoacetamide. Biophys J. 1984 Jan;45(1):323–335. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(84)84158-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khodorov B. I. Batrachotoxin as a tool to study voltage-sensitive sodium channels of excitable membranes. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 1985;45(2):57–148. doi: 10.1016/0079-6107(85)90005-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krueger B. K., Worley J. F., 3rd, French R. J. Single sodium channels from rat brain incorporated into planar lipid bilayer membranes. Nature. 1983 May 12;303(5913):172–175. doi: 10.1038/303172a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller C., Racker E. Ca++-induced fusion of fragmented sarcoplasmic reticulum with artificial planar bilayers. J Membr Biol. 1976;30(3):283–300. doi: 10.1007/BF01869673. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moczydlowski E., Garber S. S., Miller C. Batrachotoxin-activated Na+ channels in planar lipid bilayers. Competition of tetrodotoxin block by Na+. J Gen Physiol. 1984 Nov;84(5):665–686. doi: 10.1085/jgp.84.5.665. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niles W. D., Cohen F. S. Video fluorescence microscopy studies of phospholipid vesicle fusion with a planar phospholipid membrane. Nature of membrane-membrane interactions and detection of release of contents. J Gen Physiol. 1987 Nov;90(5):703–735. doi: 10.1085/jgp.90.5.703. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nonner W., Spalding B. C., Hille B. Low intracellular pH and chemical agents slow inactivation gating in sodium channels of muscle. Nature. 1980 Mar 27;284(5754):360–363. doi: 10.1038/284360a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oxford G. S., Wu C. H., Narahashi T. Removal of sodium channel inactivation in squid giant axons by n-bromoacetamide. J Gen Physiol. 1978 Mar;71(3):227–247. doi: 10.1085/jgp.71.3.227. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patlak J., Horn R. Effect of N-bromoacetamide on single sodium channel currents in excised membrane patches. J Gen Physiol. 1982 Mar;79(3):333–351. doi: 10.1085/jgp.79.3.333. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quandt F. N. Burst kinetics of sodium channels which lack fast inactivation in mouse neuroblastoma cells. J Physiol. 1987 Nov;392:563–585. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016797. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Recio-Pinto E., Duch D. S., Levinson S. R., Urban B. W. Purified and unpurified sodium channels from eel electroplax in planar lipid bilayers. J Gen Physiol. 1987 Sep;90(3):375–395. doi: 10.1085/jgp.90.3.375. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rojas E., Rudy B. Destruction of the sodium conductance inactivation by a specific protease in perfused nerve fibres from Loligo. J Physiol. 1976 Nov;262(2):501–531. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011608. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg R. L., Tomiko S. A., Agnew W. S. Reconstitution of neurotoxin-modulated ion transport by the voltage-regulated sodium channel isolated from the electroplax of Electrophorus electricus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Feb;81(4):1239–1243. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.4.1239. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg R. L., Tomiko S. A., Agnew W. S. Single-channel properties of the reconstituted voltage-regulated Na channel isolated from the electroplax of Electrophorus electricus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Sep;81(17):5594–5598. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.17.5594. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stämpfli R. Intraaxonal iodate inhibits sodium inactivation. Experientia. 1974 May 15;30(5):505–508. doi: 10.1007/BF01926319. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomiko S. A., Rosenberg R. L., Emerick M. C., Agnew W. S. Fluorescence assay for neurotoxin-modulated ion transport by the reconstituted voltage-activated sodium channel isolated from eel electric organ. Biochemistry. 1986 Apr 22;25(8):2162–2174. doi: 10.1021/bi00356a047. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodbury D. J., Hall J. E. Role of channels in the fusion of vesicles with a planar bilayer. Biophys J. 1988 Dec;54(6):1053–1063. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(88)83042-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



