Abstract
By transfecting mouse fibroblast L-M cells with human genomic DNA, we have established and identified several clonal cell lines that stably express a high-affinity serotonin (5-HT)-uptake mechanism absent in untransfected host cells. One such cell line, L-S1, possesses features of 5-[3H]HT uptake similar to those previously characterized in the central nervous system and blood platelets: (i) specificity for 5-HT; (ii) antagonism by imipramine, a known inhibitor of high-affinity 5-HT uptake; (iii) both Na+ and temperature dependences; (iv) kinetic saturability; and (v) high affinity for 5-HT (Km = 0.39 +/- 0.10 microM; Vmax = 2.14 +/- 0.55 pmol/min per mg of protein). This cell line can be used to compare the relative efficacies of known blockers of 5-HT uptake and thereby offers a rapid and reliable assay system for testing novel inhibitors of this system. Since L-S1 contains stably integrated human DNA in its genome, we postulate that the observed 5-HT-uptake system resulted from the expression of human gene(s) coding for the 5-HT transporter. Thus, cell lines such as L-S1 may represent novel means for screening and developing therapeutic agents specific for neurotransmitter-uptake systems as well as substrates for the cloning and elucidation of the genes encoding the various neurotransmitter transporters.
Full text
PDF
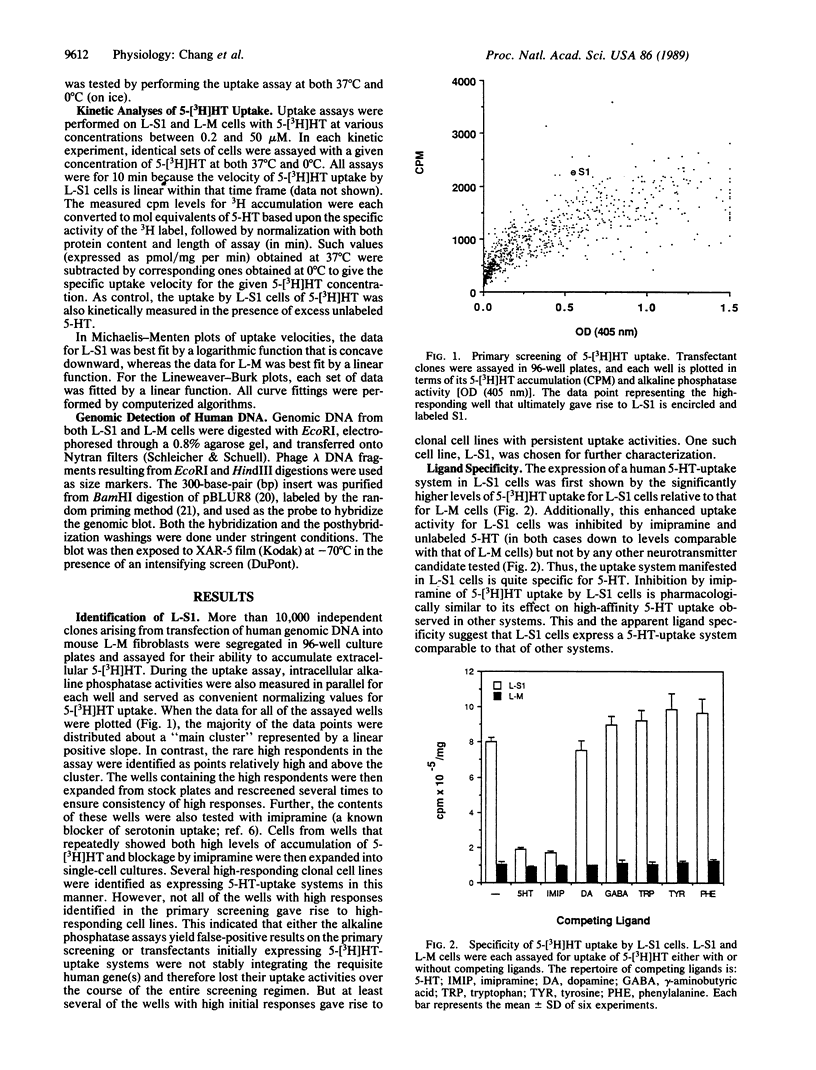
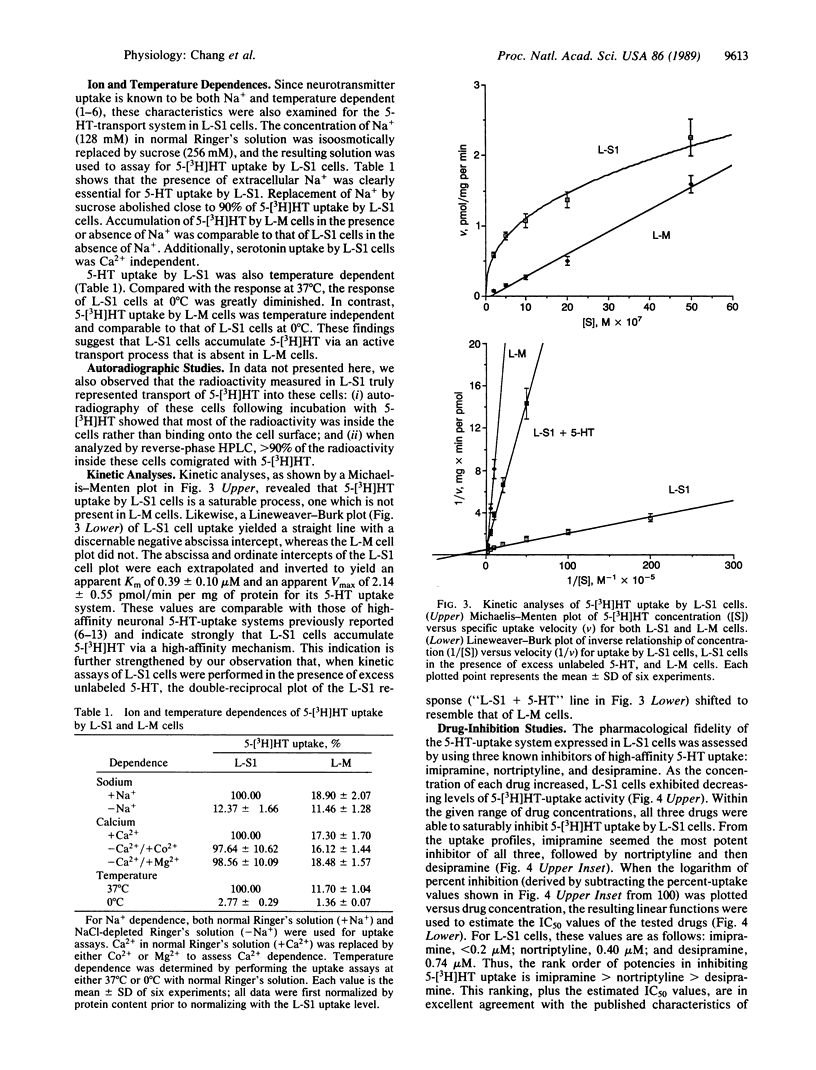
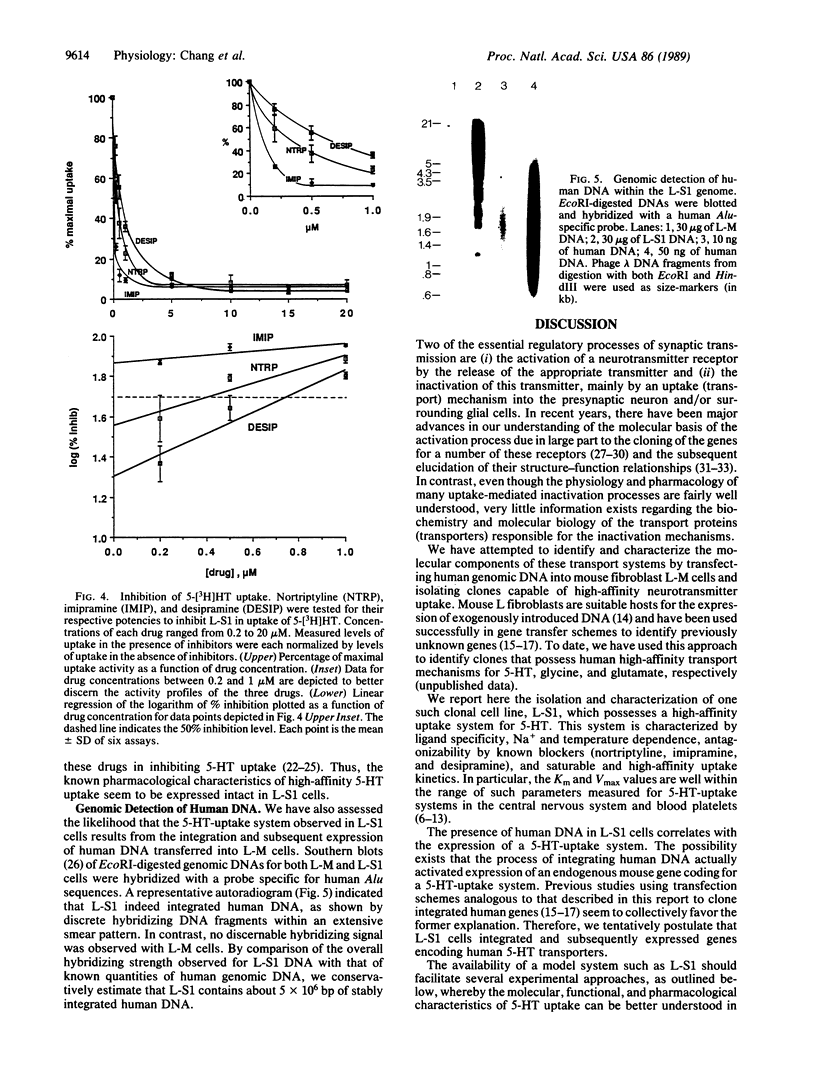

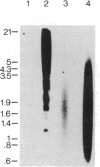
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chin C. A., Lam D. M. The uptake and release of [3H]glycine in the goldfish retina. J Physiol. 1980 Nov;308:185–195. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013467. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fargin A., Raymond J. R., Lohse M. J., Kobilka B. K., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J. The genomic clone G-21 which resembles a beta-adrenergic receptor sequence encodes the 5-HT1A receptor. Nature. 1988 Sep 22;335(6188):358–360. doi: 10.1038/335358a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., van der Eb A. J. A new technique for the assay of infectivity of human adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1973 Apr;52(2):456–467. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greco A., Ittmann M., Basilico C. Molecular cloning of a gene that is necessary for G1 progression in mammalian cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Mar;84(6):1565–1569. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.6.1565. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grenningloh G., Rienitz A., Schmitt B., Methfessel C., Zensen M., Beyreuther K., Gundelfinger E. D., Betz H. The strychnine-binding subunit of the glycine receptor shows homology with nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. Nature. 1987 Jul 16;328(6127):215–220. doi: 10.1038/328215a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hwu H. R., Roberts J. W., Davidson E. H., Britten R. J. Insertion and/or deletion of many repeated DNA sequences in human and higher ape evolution. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(11):3875–3879. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.11.3875. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imoto K., Methfessel C., Sakmann B., Mishina M., Mori Y., Konno T., Fukuda K., Kurasaki M., Bujo H., Fujita Y. Location of a delta-subunit region determining ion transport through the acetylcholine receptor channel. Nature. 1986 Dec 18;324(6098):670–674. doi: 10.1038/324670a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jelinek W. R., Toomey T. P., Leinwand L., Duncan C. H., Biro P. A., Choudary P. V., Weissman S. M., Rubin C. M., Houck C. M., Deininger P. L. Ubiquitous, interspersed repeated sequences in mammalian genomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Mar;77(3):1398–1402. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.3.1398. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johns M. A., Azmitia E. C., Krieger D. T. Specific in vitro uptake of serotonin by cells in the anterior pituitary of the rat. Endocrinology. 1982 Mar;110(3):754–760. doi: 10.1210/endo-110-3-754. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Julius D., MacDermott A. B., Axel R., Jessell T. M. Molecular characterization of a functional cDNA encoding the serotonin 1c receptor. Science. 1988 Jul 29;241(4865):558–564. doi: 10.1126/science.3399891. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz D. M., Kimelberg H. K. Kinetics and autoradiography of high affinity uptake of serotonin by primary astrocyte cultures. J Neurosci. 1985 Jul;5(7):1901–1908. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.05-07-01901.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobilka B. K., Kobilka T. S., Daniel K., Regan J. W., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J. Chimeric alpha 2-,beta 2-adrenergic receptors: delineation of domains involved in effector coupling and ligand binding specificity. Science. 1988 Jun 3;240(4857):1310–1316. doi: 10.1126/science.2836950. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kühn L. C., Barbosa J. A., Kamarck M. E., Ruddle F. H. An approach to the cloning of cell surface protein genes. Selection by cell sorting of mouse L-cells that express HLA or 4F2 antigens after transformation with total human DNA. Mol Biol Med. 1983 Oct;1(3):335–352. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lam D. M., Steinman L. The uptake of ( - 3 H) aminobutyric acid in the goldfish retina. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Nov;68(11):2777–2781. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.11.2777. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langer S. Z., Moret C., Raisman R., Dubocovich M. L., Briley M. High-affinity [3H]imipramine binding in rat hypothalamus: association with uptake of serotonin but not of norepinephrine. Science. 1980 Dec 5;210(4474):1133–1135. doi: 10.1126/science.7444441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell C. K., Redburn D. A. Analysis of pre- and postsynaptic factors of the serotonin system in rabbit retina. J Cell Biol. 1985 Jan;100(1):64–73. doi: 10.1083/jcb.100.1.64. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakaki T., Roth B. L., Chuang D. M., Costa E. 5-Hydroxytryptamine uptake and imipramine binding sites in neurotumor NCB-20 cells. J Neurochem. 1985 Sep;45(3):920–925. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1985.tb04081.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noda M., Takahashi H., Tanabe T., Toyosato M., Kikyotani S., Hirose T., Asai M., Takashima H., Inayama S., Miyata T. Primary structures of beta- and delta-subunit precursors of Torpedo californica acetylcholine receptor deduced from cDNA sequences. Nature. 1983 Jan 20;301(5897):251–255. doi: 10.1038/301251a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborne N. N. Uptake, localization and release of serotonin in the chick retina. J Physiol. 1982 Oct;331:469–479. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014384. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paul S. M., Rehavi M., Skolnick P., Goodwin F. K. Demonstration of specific "high affinity" binding sites for [3H] imipramine on human platelets. Life Sci. 1980 Mar 24;26(12):953–959. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(80)90116-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rehavi M., Ittah Y., Rice K. C., Skolnick P., Goodwin F. K., Paul S. M. 2-nitroimipramine: a selective irreversible inhibitor of [3H] serotonin uptake and [3H] imipramine binding in platelets. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1981 Apr 15;99(3):954–959. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(81)91255-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarthy P. V., Lam D. M. The uptake and release of [3H]dopamine in the goldfish retina. J Neurochem. 1979 Apr;32(4):1269–1277. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1979.tb11054.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schofield P. R., Darlison M. G., Fujita N., Burt D. R., Stephenson F. A., Rodriguez H., Rhee L. M., Ramachandran J., Reale V., Glencorse T. A. Sequence and functional expression of the GABA A receptor shows a ligand-gated receptor super-family. Nature. 1987 Jul 16;328(6127):221–227. doi: 10.1038/328221a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shank R. P., Schneider C. R., Tighe J. J. Ion dependence of neurotransmitter uptake: inhibitory effects of ion substitutes. J Neurochem. 1987 Aug;49(2):381–388. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1987.tb02876.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern P. J., Berg P. Transformation of mammalian cells to antibiotic resistance with a bacterial gene under control of the SV40 early region promoter. J Mol Appl Genet. 1982;1(4):327–341. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitaker P. M., Vint C. K., Morin R. [3H]imipramine labels sites on brain astroglial cells not related to serotonin uptake. J Neurochem. 1983 Nov;41(5):1319–1323. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1983.tb00827.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wigler M., Sweet R., Sim G. K., Wold B., Pellicer A., Lacy E., Maniatis T., Silverstein S., Axel R. Transformation of mammalian cells with genes from procaryotes and eucaryotes. Cell. 1979 Apr;16(4):777–785. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90093-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood M. D., Broadhurst A. M., Wyllie M. G. Examination of the relationship between the uptake system for 5-hydroxytryptamine and the high-affinity [3H]imipramine binding site--I. Inhibition by drugs. Neuropharmacology. 1986 May;25(5):519–525. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(86)90178-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]