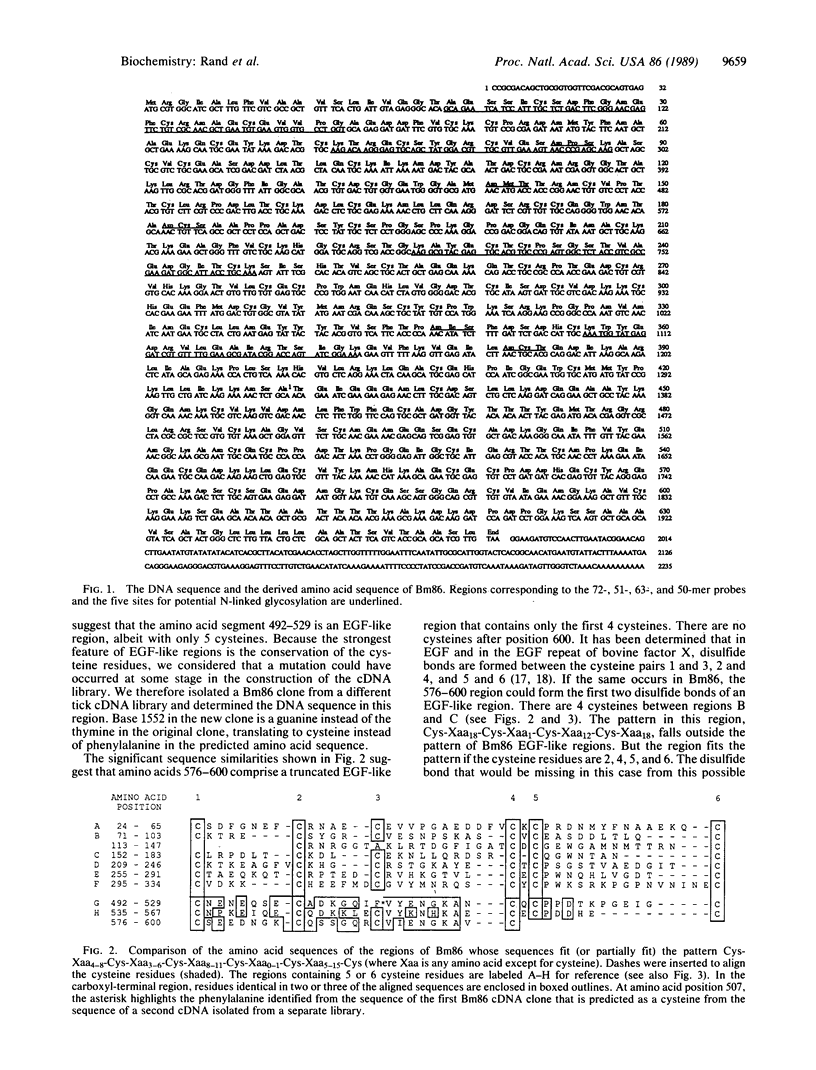
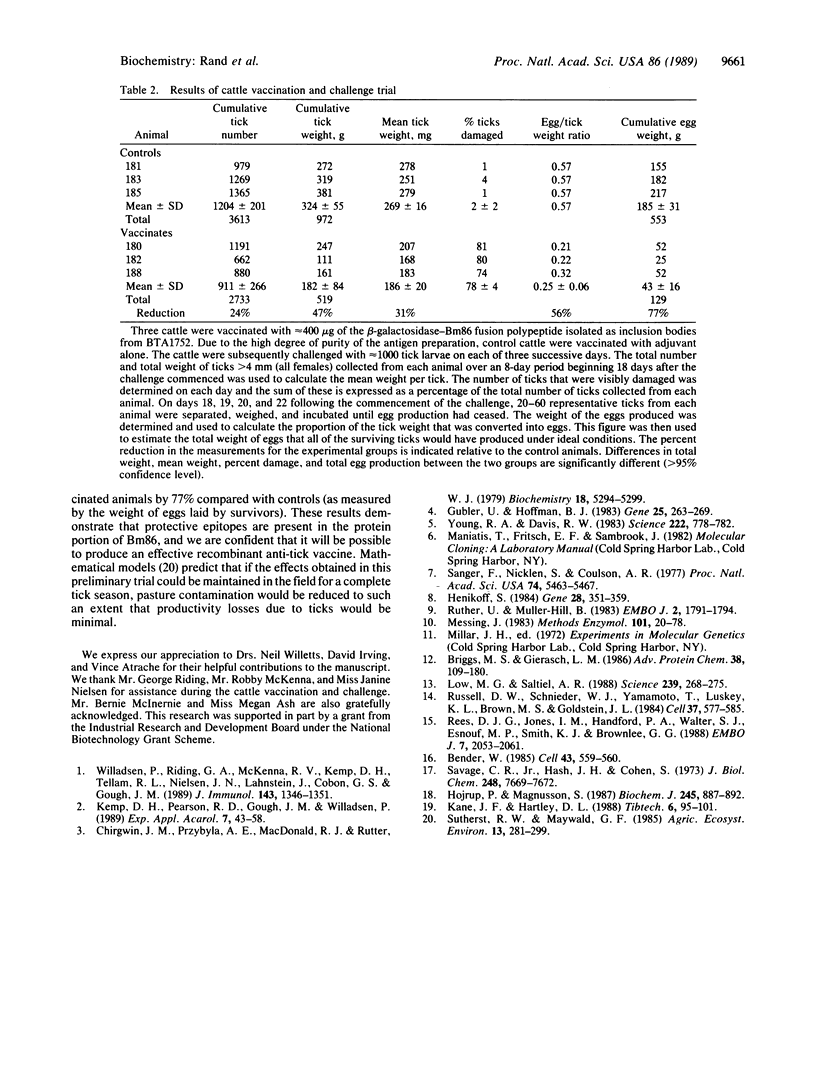
Abstract
Glycoproteins located on the luminal surface of the plasma membrane of tick gut epithelial cells, when used to vaccinate cattle, are capable of stimulating an immune response that protects cattle against subsequent tick infestation. One such tick gut glycoprotein, designated Bm86, has been purified to homogeneity and the amino acid sequences of peptide fragments generated by endoproteinase Lys-C digestion have been determined. We report here the isolation and characterization of a cDNA that encodes Bm86. The nucleotide sequence of the cDNA contains a 1982-base-pair open reading frame and predicts that Bm86 contains 650 amino acids including a 19-amino acid signal sequence and a 23-amino acid hydrophobic region adjacent to the carboxyl terminus. The main feature of the deduced protein sequence is the repeated pattern of 6 cysteine residues, suggesting the presence of several epidermal growth factor-like domains. A fusion protein consisting of 599 amino acids of Bm86 and 651 amino acids of beta-galactosidase was expressed in Escherichia coli as inclusion bodies. Ticks engorging on cattle vaccinated with these inclusion bodies were significantly damaged as a result of the immune response against the cloned antigen.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bender W. Homeotic gene products as growth factors. Cell. 1985 Dec;43(3 Pt 2):559–560. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90224-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Briggs M. S., Gierasch L. M. Molecular mechanisms of protein secretion: the role of the signal sequence. Adv Protein Chem. 1986;38:109–180. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3233(08)60527-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gubler U., Hoffman B. J. A simple and very efficient method for generating cDNA libraries. Gene. 1983 Nov;25(2-3):263–269. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90230-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henikoff S. Unidirectional digestion with exonuclease III creates targeted breakpoints for DNA sequencing. Gene. 1984 Jun;28(3):351–359. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90153-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Højrup P., Magnusson S. Disulphide bridges of bovine factor X. Biochem J. 1987 Aug 1;245(3):887–891. doi: 10.1042/bj2450887. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kemp D. H., Pearson R. D., Gough J. M., Willadsen P. Vaccination against Boophilus microplus: localization of antigens on tick gut cells and their interaction with the host immune system. Exp Appl Acarol. 1989 Jun;7(1):43–58. doi: 10.1007/BF01200452. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Low M. G., Saltiel A. R. Structural and functional roles of glycosyl-phosphatidylinositol in membranes. Science. 1988 Jan 15;239(4837):268–275. doi: 10.1126/science.3276003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J. New M13 vectors for cloning. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:20–78. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01005-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rees D. J., Jones I. M., Handford P. A., Walter S. J., Esnouf M. P., Smith K. J., Brownlee G. G. The role of beta-hydroxyaspartate and adjacent carboxylate residues in the first EGF domain of human factor IX. EMBO J. 1988 Jul;7(7):2053–2061. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03045.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell D. W., Schneider W. J., Yamamoto T., Luskey K. L., Brown M. S., Goldstein J. L. Domain map of the LDL receptor: sequence homology with the epidermal growth factor precursor. Cell. 1984 Jun;37(2):577–585. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90388-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rüther U., Müller-Hill B. Easy identification of cDNA clones. EMBO J. 1983;2(10):1791–1794. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01659.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savage C. R., Jr, Hash J. H., Cohen S. Epidermal growth factor. Location of disulfide bonds. J Biol Chem. 1973 Nov 25;248(22):7669–7672. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willadsen P., Riding G. A., McKenna R. V., Kemp D. H., Tellam R. L., Nielsen J. N., Lahnstein J., Cobon G. S., Gough J. M. Immunologic control of a parasitic arthropod. Identification of a protective antigen from Boophilus microplus. J Immunol. 1989 Aug 15;143(4):1346–1351. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young R. A., Davis R. W. Yeast RNA polymerase II genes: isolation with antibody probes. Science. 1983 Nov 18;222(4625):778–782. doi: 10.1126/science.6356359. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]