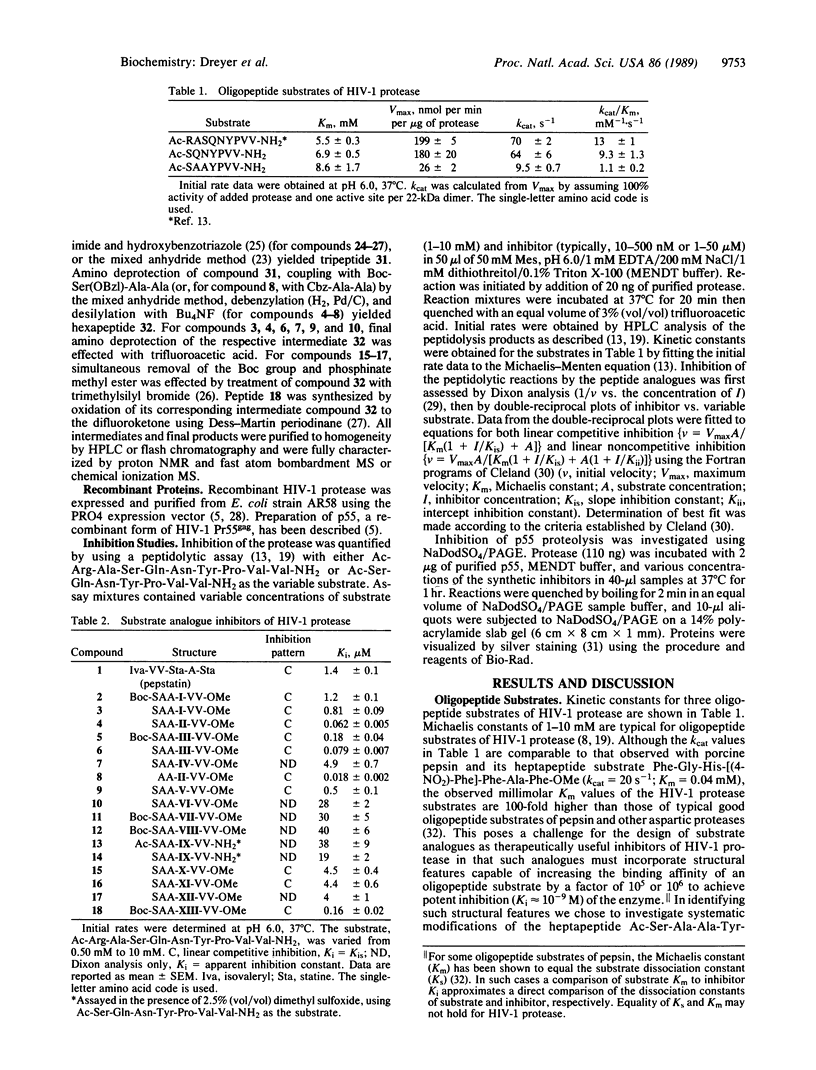
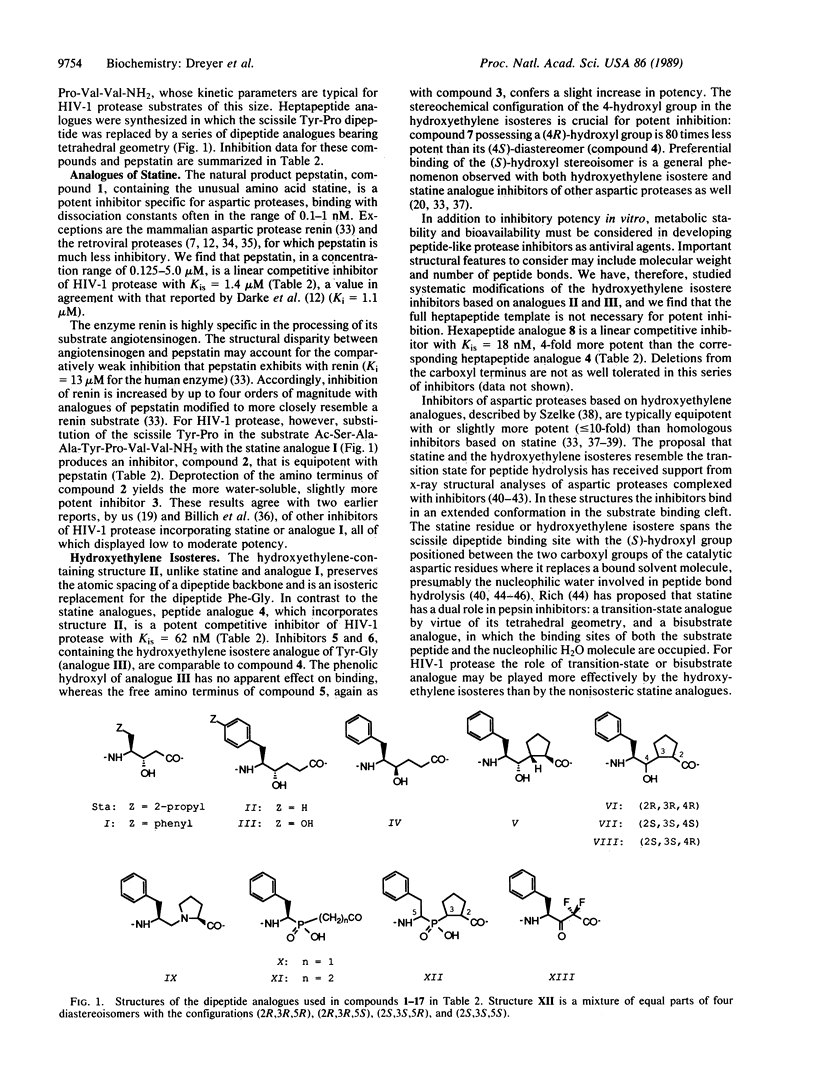
Abstract
Inhibitors of the protease from human immunodeficiency virus 1 (HIV-1) were designed, synthesized, and kinetically characterized. Analogues of a heptapeptide substrate of HIV-1 protease with sequence similar to the p17-p24 cleavage site in the natural substrate, Pr55gag, were synthesized in which the scissile dipeptide bond was replaced with bonds from six categories of stable mimics of an aspartic proteolysis transition state or intermediate. These mimics included an analogue of statine, hydroxyethylene isosteres, two categories of phosphinic acids, a reduced amide isostere, and an alpha,alpha-difluoroketone. The resulting peptide analogues were linear competitive inhibitors of purified recombinant HIV-1 protease with inhibition constants ranging from 18 nM to 40 microM depending on the type of inhibitor. A truncated inhibitor, an analogue of a hexapeptide, retained full inhibitory potency. The most potent inhibitors, containing the hydroxyethylene isostere, effectively blocked the proteolytic processing of a recombinant form of Pr55gag by HIV-1 protease in a cell-free assay.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Agarwal N. S., Rich D. H. Inhibition of cathepsin D by substrate analogues containing statine and by analogues of pepstatin. J Med Chem. 1986 Dec;29(12):2519–2524. doi: 10.1021/jm00162a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartlett P. A., Marlowe C. K., Giannousis P. P., Hanson J. E. Phosphorus-containing peptide analogs as peptidase inhibitors. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1987;52:83–90. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1987.052.01.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Billich S., Knoop M. T., Hansen J., Strop P., Sedlacek J., Mertz R., Moelling K. Synthetic peptides as substrates and inhibitors of human immune deficiency virus-1 protease. J Biol Chem. 1988 Dec 5;263(34):17905–17908. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blundell T. L., Cooper J., Foundling S. I., Jones D. M., Atrash B., Szelke M. On the rational design of renin inhibitors: X-ray studies of aspartic proteinases complexed with transition-state analogues. Biochemistry. 1987 Sep 8;26(18):5585–5590. doi: 10.1021/bi00392a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boger J., Lohr N. S., Ulm E. H., Poe M., Blaine E. H., Fanelli G. M., Lin T. Y., Payne L. S., Schorn T. W., LaMont B. I. Novel renin inhibitors containing the amino acid statine. Nature. 1983 May 5;303(5912):81–84. doi: 10.1038/303081a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bott R., Subramanian E., Davies D. R. Three-dimensional structure of the complex of the Rhizopus chinensis carboxyl proteinase and pepstatin at 2.5-A resolution. Biochemistry. 1982 Dec 21;21(26):6956–6962. doi: 10.1021/bi00269a052. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleland W. W. Statistical analysis of enzyme kinetic data. Methods Enzymol. 1979;63:103–138. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)63008-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crawford S., Goff S. P. A deletion mutation in the 5' part of the pol gene of Moloney murine leukemia virus blocks proteolytic processing of the gag and pol polyproteins. J Virol. 1985 Mar;53(3):899–907. doi: 10.1128/jvi.53.3.899-907.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DIXON M. The determination of enzyme inhibitor constants. Biochem J. 1953 Aug;55(1):170–171. doi: 10.1042/bj0550170. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darke P. L., Leu C. T., Davis L. J., Heimbach J. C., Diehl R. E., Hill W. S., Dixon R. A., Sigal I. S. Human immunodeficiency virus protease. Bacterial expression and characterization of the purified aspartic protease. J Biol Chem. 1989 Feb 5;264(4):2307–2312. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darke P. L., Nutt R. F., Brady S. F., Garsky V. M., Ciccarone T. M., Leu C. T., Lumma P. K., Freidinger R. M., Veber D. F., Sigal I. S. HIV-1 protease specificity of peptide cleavage is sufficient for processing of gag and pol polyproteins. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Oct 14;156(1):297–303. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)80839-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Debouck C., Gorniak J. G., Strickler J. E., Meek T. D., Metcalf B. W., Rosenberg M. Human immunodeficiency virus protease expressed in Escherichia coli exhibits autoprocessing and specific maturation of the gag precursor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(24):8903–8906. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.24.8903. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farmerie W. G., Loeb D. D., Casavant N. C., Hutchison C. A., 3rd, Edgell M. H., Swanstrom R. Expression and processing of the AIDS virus reverse transcriptase in Escherichia coli. Science. 1987 Apr 17;236(4799):305–308. doi: 10.1126/science.2436298. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer G. Trends in protease inhibition. Nat Prod Rep. 1988 Oct;5(5):465–495. doi: 10.1039/np9880500465. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foundling S. I., Cooper J., Watson F. E., Cleasby A., Pearl L. H., Sibanda B. L., Hemmings A., Wood S. P., Blundell T. L., Valler M. J. High resolution X-ray analyses of renin inhibitor-aspartic proteinase complexes. 1987 May 28-Jun 3Nature. 327(6120):349–352. doi: 10.1038/327349a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fruton J. S. The mechanism of the catalytic action of pepsin and related acid proteinases. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1976;44:1–36. doi: 10.1002/9780470122891.ch1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gelb M. H., Svaren J. P., Abeles R. H. Fluoro ketone inhibitors of hydrolytic enzymes. Biochemistry. 1985 Apr 9;24(8):1813–1817. doi: 10.1021/bi00329a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giam C. Z., Boros I. In vivo and in vitro autoprocessing of human immunodeficiency virus protease expressed in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1988 Oct 15;263(29):14617–14620. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graves M. C., Lim J. J., Heimer E. P., Kramer R. A. An 11-kDa form of human immunodeficiency virus protease expressed in Escherichia coli is sufficient for enzymatic activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(8):2449–2453. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.8.2449. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holladay M. W., Salituro F. G., Rich D. H. Synthetic and enzyme inhibition studies of pepstatin analogues containing hydroxyethylene and ketomethylene dipeptide isosteres. J Med Chem. 1987 Feb;30(2):374–383. doi: 10.1021/jm00385a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James M. N., Sielecki A. R. Stereochemical analysis of peptide bond hydrolysis catalyzed by the aspartic proteinase penicillopepsin. Biochemistry. 1985 Jul 2;24(14):3701–3713. doi: 10.1021/bi00335a045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James M. N., Sielecki A., Salituro F., Rich D. H., Hofmann T. Conformational flexibility in the active sites of aspartyl proteinases revealed by a pepstatin fragment binding to penicillopepsin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Oct;79(20):6137–6141. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.20.6137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katoh I., Yasunaga T., Ikawa Y., Yoshinaka Y. Inhibition of retroviral protease activity by an aspartyl proteinase inhibitor. Nature. 1987 Oct 15;329(6140):654–656. doi: 10.1038/329654a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katoh I., Yoshinaka Y., Rein A., Shibuya M., Odaka T., Oroszlan S. Murine leukemia virus maturation: protease region required for conversion from "immature" to "mature" core form and for virus infectivity. Virology. 1985 Sep;145(2):280–292. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90161-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohl N. E., Emini E. A., Schleif W. A., Davis L. J., Heimbach J. C., Dixon R. A., Scolnick E. M., Sigal I. S. Active human immunodeficiency virus protease is required for viral infectivity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jul;85(13):4686–4690. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.13.4686. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meek T. D., Dayton B. D., Metcalf B. W., Dreyer G. B., Strickler J. E., Gorniak J. G., Rosenberg M., Moore M. L., Magaard V. W., Debouck C. Human immunodeficiency virus 1 protease expressed in Escherichia coli behaves as a dimeric aspartic protease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Mar;86(6):1841–1845. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.6.1841. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merril C. R., Goldman D., Sedman S. A., Ebert M. H. Ultrasensitive stain for proteins in polyacrylamide gels shows regional variation in cerebrospinal fluid proteins. Science. 1981 Mar 27;211(4489):1437–1438. doi: 10.1126/science.6162199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mervis R. J., Ahmad N., Lillehoj E. P., Raum M. G., Salazar F. H., Chan H. W., Venkatesan S. The gag gene products of human immunodeficiency virus type 1: alignment within the gag open reading frame, identification of posttranslational modifications, and evidence for alternative gag precursors. J Virol. 1988 Nov;62(11):3993–4002. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.11.3993-4002.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore M. L., Bryan W. M., Fakhoury S. A., Magaard V. W., Huffman W. F., Dayton B. D., Meek T. D., Hyland L., Dreyer G. B., Metcalf B. W. Peptide substrates and inhibitors of the HIV-1 protease. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Mar 15;159(2):420–425. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)90008-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Navia M. A., Fitzgerald P. M., McKeever B. M., Leu C. T., Heimbach J. C., Herber W. K., Sigal I. S., Darke P. L., Springer J. P. Three-dimensional structure of aspartyl protease from human immunodeficiency virus HIV-1. Nature. 1989 Feb 16;337(6208):615–620. doi: 10.1038/337615a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearl L. H., Taylor W. R. A structural model for the retroviral proteases. Nature. 1987 Sep 24;329(6137):351–354. doi: 10.1038/329351a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ratner L., Haseltine W., Patarca R., Livak K. J., Starcich B., Josephs S. F., Doran E. R., Rafalski J. A., Whitehorn E. A., Baumeister K. Complete nucleotide sequence of the AIDS virus, HTLV-III. Nature. 1985 Jan 24;313(6000):277–284. doi: 10.1038/313277a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rich D. H. Pepstatin-derived inhibitors of aspartic proteinases. A close look at an apparent transition-state analogue inhibitor. J Med Chem. 1985 Mar;28(3):263–273. doi: 10.1021/jm00381a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rich D. H., Sun E. T., Ulm E. Synthesis of analogues of the carboxyl protease inhibitor pepstatin. Effects of structure on inhibition of pepsin and renin. J Med Chem. 1980 Jan;23(1):27–33. doi: 10.1021/jm00175a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanchez-Pescador R., Power M. D., Barr P. J., Steimer K. S., Stempien M. M., Brown-Shimer S. L., Gee W. W., Renard A., Randolph A., Levy J. A. Nucleotide sequence and expression of an AIDS-associated retrovirus (ARV-2). Science. 1985 Feb 1;227(4686):484–492. doi: 10.1126/science.2578227. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seelmeier S., Schmidt H., Turk V., von der Helm K. Human immunodeficiency virus has an aspartic-type protease that can be inhibited by pepstatin A. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Sep;85(18):6612–6616. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.18.6612. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suguna K., Padlan E. A., Smith C. W., Carlson W. D., Davies D. R. Binding of a reduced peptide inhibitor to the aspartic proteinase from Rhizopus chinensis: implications for a mechanism of action. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(20):7009–7013. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.20.7009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szelke M., Leckie B., Hallett A., Jones D. M., Sueiras J., Atrash B., Lever A. F. Potent new inhibitors of human renin. Nature. 1982 Oct 7;299(5883):555–557. doi: 10.1038/299555a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thaisrivongs S., Pals D. T., Kati W. M., Turner S. R., Thomasco L. M., Watt W. Design and synthesis of potent and specific renin inhibitors containing difluorostatine, difluorostatone, and related analogues. J Med Chem. 1986 Oct;29(10):2080–2087. doi: 10.1021/jm00160a048. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wlodawer A., Miller M., Jaskólski M., Sathyanarayana B. K., Baldwin E., Weber I. T., Selk L. M., Clawson L., Schneider J., Kent S. B. Conserved folding in retroviral proteases: crystal structure of a synthetic HIV-1 protease. Science. 1989 Aug 11;245(4918):616–621. doi: 10.1126/science.2548279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolfenden R. Transition state analog inhibitors and enzyme catalysis. Annu Rev Biophys Bioeng. 1976;5:271–306. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.05.060176.001415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



