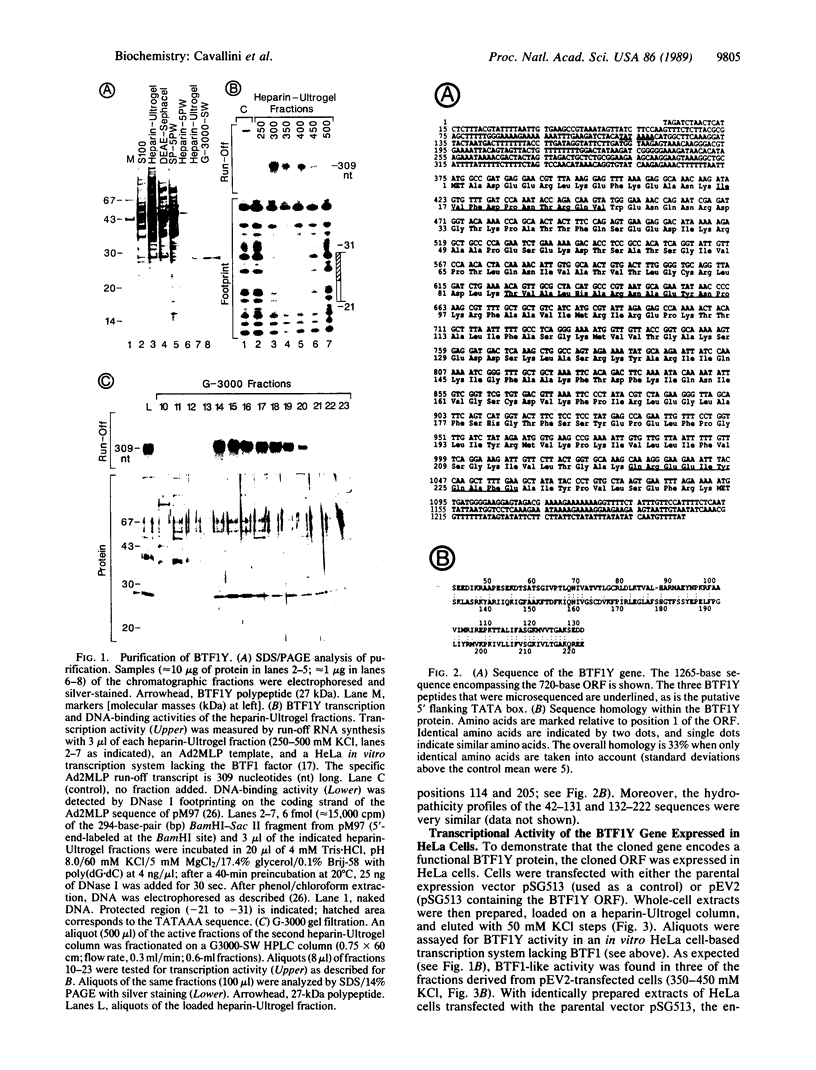
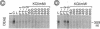Abstract
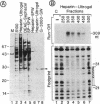
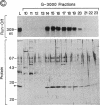
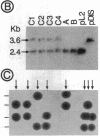
An activity (designated BTF1Y) in extracts of Saccharomyces cerevisiae can substitute for the human TATA box-binding factor BTF1 in a reconstituted transcription system containing the adenovirus 2 major late promoter, RNA polymerase B (II), and the basic transcription factors BTF2, BTF3, and STF. We have purified BTF1Y to homogeneity, using as assays reconstitution of in vitro transcription and DNase I footprinting on the TATA element. Both activities copurified with a 27-kDa polypeptide as determined by SDS/PAGE. Gel filtration indicated a molecular mass of 28 +/- 5 kDa under nondenaturing conditions, suggesting that the native BTF1Y protein is a monomer. BTF1Y was enzymatically cleaved, several peptides were sequenced, and appropriate oligonucleotide probes were synthesized to clone the BTF1Y gene from a yeast genomic library. The BTF1Y gene contains a 720-base-pair open reading frame encoding a protein of 27,003 Da. The recombinant protein expressed in HeLa cells exhibited the same chromatographic characteristics and in vitro transcriptional activity as BTF1Y prepared from yeast extracts, confirming the identity of the gene. Gene-disruption experiments indicated that the yeast BTF1Y gene is a single-copy essential gene.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aebersold R. H., Leavitt J., Saavedra R. A., Hood L. E., Kent S. B. Internal amino acid sequence analysis of proteins separated by one- or two-dimensional gel electrophoresis after in situ protease digestion on nitrocellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(20):6970–6974. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.20.6970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buratowski S., Hahn S., Guarente L., Sharp P. A. Five intermediate complexes in transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II. Cell. 1989 Feb 24;56(4):549–561. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90578-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buratowski S., Hahn S., Sharp P. A., Guarente L. Function of a yeast TATA element-binding protein in a mammalian transcription system. Nature. 1988 Jul 7;334(6177):37–42. doi: 10.1038/334037a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burton Z. F., Ortolan L. G., Greenblatt J. Proteins that bind to RNA polymerase II are required for accurate initiation of transcription at the adenovirus 2 major late promoter. EMBO J. 1986 Nov;5(11):2923–2930. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04588.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cavallini B., Huet J., Plassat J. L., Sentenac A., Egly J. M., Chambon P. A yeast activity can substitute for the HeLa cell TATA box factor. Nature. 1988 Jul 7;334(6177):77–80. doi: 10.1038/334077a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chevallier M. R. Cloning and transcriptional control of a eucaryotic permease gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Aug;2(8):977–984. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.8.977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davison B. L., Egly J. M., Mulvihill E. R., Chambon P. Formation of stable preinitiation complexes between eukaryotic class B transcription factors and promoter sequences. Nature. 1983 Feb 24;301(5902):680–686. doi: 10.1038/301680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dezélée S., Wyers F., Sentenac A., Fromageot P. Two forms of RNA polymerase B in yeast. Proteolytic conversion in vitro of enzyme BI into BII. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Jun 1;65(2):543–552. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10372.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fire A., Samuels M., Sharp P. A. Interactions between RNA polymerase II, factors, and template leading to accurate transcription. J Biol Chem. 1984 Feb 25;259(4):2509–2516. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flores O., Maldonado E., Burton Z., Greenblatt J., Reinberg D. Factors involved in specific transcription by mammalian RNA polymerase II. RNA polymerase II-associating protein 30 is an essential component of transcription factor IIF. J Biol Chem. 1988 Aug 5;263(22):10812–10816. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green S., Issemann I., Sheer E. A versatile in vivo and in vitro eukaryotic expression vector for protein engineering. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Jan 11;16(1):369–369. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.1.369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hahn S., Buratowski S., Sharp P. A., Guarente L. Yeast TATA-binding protein TFIID binds to TATA elements with both consensus and nonconsensus DNA sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Aug;86(15):5718–5722. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.15.5718. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hieter P., Mann C., Snyder M., Davis R. W. Mitotic stability of yeast chromosomes: a colony color assay that measures nondisjunction and chromosome loss. Cell. 1985 Feb;40(2):381–392. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90152-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horikoshi M., Wang C. K., Fujii H., Cromlish J. A., Weil P. A., Roeder R. G. Purification of a yeast TATA box-binding protein that exhibits human transcription factor IID activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(13):4843–4847. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.13.4843. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kakidani H., Ptashne M. GAL4 activates gene expression in mammalian cells. Cell. 1988 Jan 29;52(2):161–167. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90504-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. The scanning model for translation: an update. J Cell Biol. 1989 Feb;108(2):229–241. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.2.229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lech K., Anderson K., Brent R. DNA-bound Fos proteins activate transcription in yeast. Cell. 1988 Jan 29;52(2):179–184. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90506-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsudaira P. Sequence from picomole quantities of proteins electroblotted onto polyvinylidene difluoride membranes. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jul 25;262(21):10035–10038. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsui T., Segall J., Weil P. A., Roeder R. G. Multiple factors required for accurate initiation of transcription by purified RNA polymerase II. J Biol Chem. 1980 Dec 25;255(24):11992–11996. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metzger D., White J. H., Chambon P. The human oestrogen receptor functions in yeast. Nature. 1988 Jul 7;334(6177):31–36. doi: 10.1038/334031a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell P. J., Tjian R. Transcriptional regulation in mammalian cells by sequence-specific DNA binding proteins. Science. 1989 Jul 28;245(4916):371–378. doi: 10.1126/science.2667136. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyamoto N. G., Moncollin V., Wintzerith M., Hen R., Egly J. M., Chambon P. Stimulation of in vitro transcription by the upstream element of the adenovirus-2 major late promoter involves a specific factor. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Dec 11;12(23):8779–8799. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.23.8779. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moncollin V., Miyamoto N. G., Zheng X. M., Egly J. M. Purification of a factor specific for the upstream element of the adenovirus-2 major late promoter. EMBO J. 1986 Oct;5(10):2577–2584. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04537.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakajima N., Horikoshi M., Roeder R. G. Factors involved in specific transcription by mammalian RNA polymerase II: purification, genetic specificity, and TATA box-promoter interactions of TFIID. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Oct;8(10):4028–4040. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.10.4028. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinberg D., Roeder R. G. Factors involved in specific transcription by mammalian RNA polymerase II. Purification and functional analysis of initiation factors IIB and IIE. J Biol Chem. 1987 Mar 5;262(7):3310–3321. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samuels M., Fire A., Sharp P. A. Separation and characterization of factors mediating accurate transcription by RNA polymerase II. J Biol Chem. 1982 Dec 10;257(23):14419–14427. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schena M., Yamamoto K. R. Mammalian glucocorticoid receptor derivatives enhance transcription in yeast. Science. 1988 Aug 19;241(4868):965–967. doi: 10.1126/science.3043665. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt M. C., Kao C. C., Pei R., Berk A. J. Yeast TATA-box transcription factor gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Oct;86(20):7785–7789. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.20.7785. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webster N., Jin J. R., Green S., Hollis M., Chambon P. The yeast UASG is a transcriptional enhancer in human HeLa cells in the presence of the GAL4 trans-activator. Cell. 1988 Jan 29;52(2):169–178. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90505-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wingender E. Compilation of transcription regulating proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Mar 25;16(5):1879–1902. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.5.1879. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zheng X. M., Moncollin V., Egly J. M., Chambon P. A general transcription factor forms a stable complex with RNA polymerase B (II). Cell. 1987 Jul 31;50(3):361–368. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90490-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]