Abstract
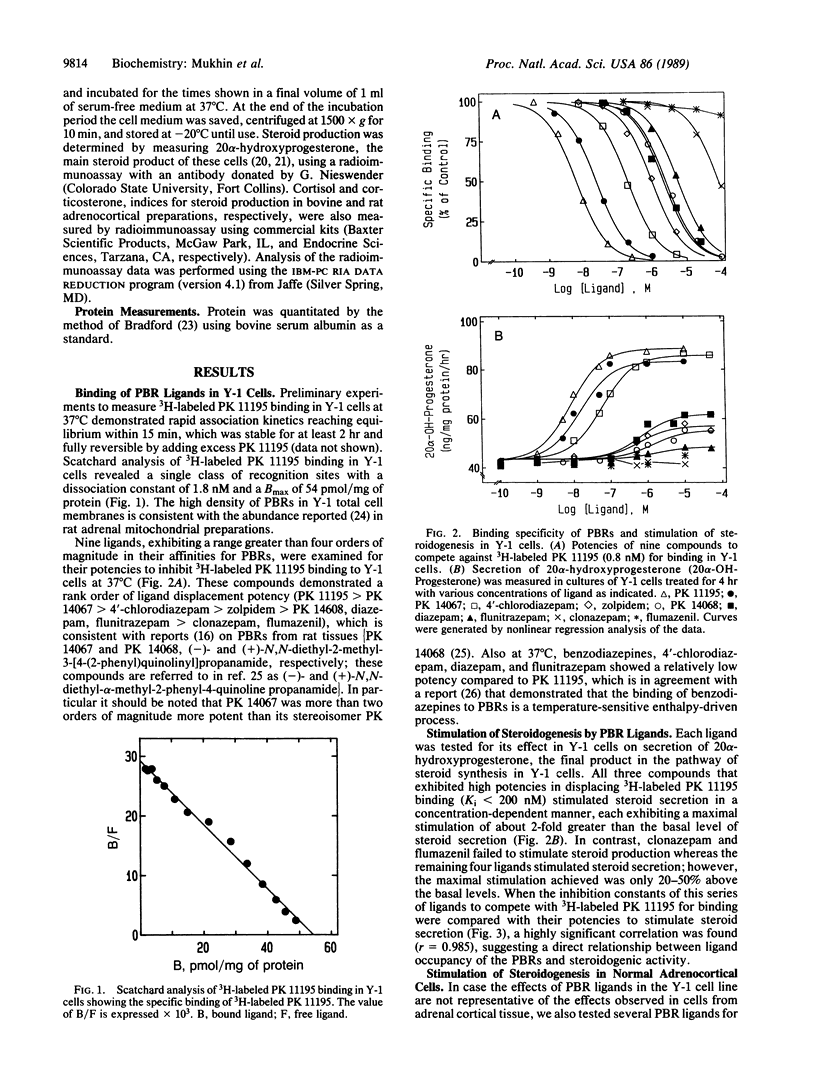
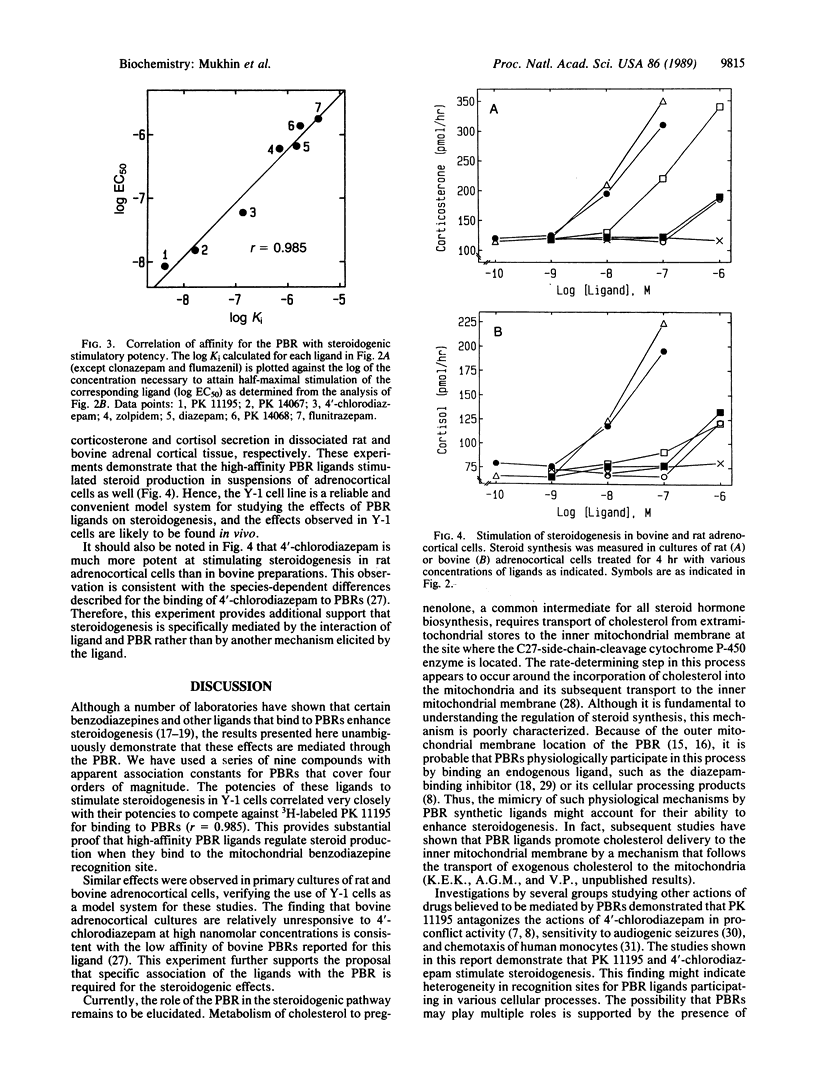
Recent observations on the steroid synthetic capability within the brain open the possibility that benzodiazepines may influence steroid synthesis in nervous tissue through interactions with peripheral-type benzodiazepine recognition sites, which are highly expressed in steroidogenic cells and associated with the outer mitochondrial membrane. To examine this possibility nine molecules that exhibit a greater than 10,000-fold difference in their affinities for peripheral-type benzodiazepine binding sites were tested for their effects on a well-established steroidogenic model system, the Y-1 mouse adrenal tumor cell line. 4'-Chlorodiazepam, PK 11195, and PK 14067 stimulated steroid production by 2-fold in Y-1 cells, whereas diazepam, flunitrazepam, zolpidem, and PK 14068 displayed a lower (1.2- to 1.5-fold) maximal stimulation. In contrast, clonazepam and flumazenil did not stimulate steroid synthesis. The potencies of these compounds to inhibit 3H-labeled PK 11195 binding to peripheral-type benzodiazepine recognition sites correlated (r = 0.985) with their potencies to stimulate steroid production. Similar findings were observed in bovine and rat adrenocortical cell preparations. These results suggest that ligands of the peripheral-type benzodiazepine recognition site acting on this mitochondrial receptor can enhance steroid production. This action may contribute specificity to the pharmacological profile of drugs preferentially acting on the benzodiazepine recognition site associated with the outer membrane of certain mitochondrial populations.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anholt R. R., De Souza E. B., Oster-Granite M. L., Snyder S. H. Peripheral-type benzodiazepine receptors: autoradiographic localization in whole-body sections of neonatal rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1985 May;233(2):517–526. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anholt R. R., Pedersen P. L., De Souza E. B., Snyder S. H. The peripheral-type benzodiazepine receptor. Localization to the mitochondrial outer membrane. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jan 15;261(2):576–583. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Antkiewicz-Michaluk L., Guidotti A., Krueger K. E. Molecular characterization and mitochondrial density of a recognition site for peripheral-type benzodiazepine ligands. Mol Pharmacol. 1988 Sep;34(3):272–278. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Awad M., Gavish M. Binding of [3H]Ro 5-4864 and [3H]PK 11195 to cerebral cortex and peripheral tissues of various species: species differences and heterogeneity in peripheral benzodiazepine binding sites. J Neurochem. 1987 Nov;49(5):1407–1414. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1987.tb01007.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnea E. R., Fares F., Gavish M. Modulatory action of benzodiazepines on human term placental steroidogenesis in vitro. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1989 Jul;64(2):155–159. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(89)90141-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Besman M. J., Yanagibashi K., Lee T. D., Kawamura M., Hall P. F., Shively J. E. Identification of des-(Gly-Ile)-endozepine as an effector of corticotropin-dependent adrenal steroidogenesis: stimulation of cholesterol delivery is mediated by the peripheral benzodiazepine receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(13):4897–4901. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.13.4897. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braestrup C., Squires R. F. Specific benzodiazepine receptors in rat brain characterized by high-affinity (3H)diazepam binding. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Sep;74(9):3805–3809. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.9.3805. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bénavidès J., Guilloux F., Allam D. E., Uzan A., Mizoule J., Renault C., Dubroeucq M. C., Guérémy C., Le Fur G. Opposite effects of an agonist, RO5-4864, and an antagonist, PK 11195, of the peripheral type benzodiazepine binding sites on audiogenic seizures in DBA/2J mice. Life Sci. 1984 Jun 25;34(26):2613–2620. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(84)90048-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costa E., Guidotti A. Molecular mechanisms in the receptor action of benzodiazepines. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1979;19:531–545. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.19.040179.002531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Souza E. B., Anholt R. R., Murphy K. M., Snyder S. H., Kuhar M. J. Peripheral-type benzodiazepine receptors in endocrine organs: autoradiographic localization in rat pituitary, adrenal, and testis. Endocrinology. 1985 Feb;116(2):567–573. doi: 10.1210/endo-116-2-567. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubroeucq M. C., Bénavidès J., Doble A., Guilloux F., Allam D., Vaucher N., Bertrand P., Guérémy C., Renault C., Uzan A. Stereoselective inhibition of the binding of [3H]PK 11195 to peripheral-type benzodiazepine binding sites by a quinolinepropanamide derivative. Eur J Pharmacol. 1986 Sep 9;128(3):269–272. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(86)90776-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallager D. W., Mallorga P., Oertel W., Henneberry R., Tallman J. [3H]Diazepam binding in mammalian central nervous system: a pharmacological characterization. J Neurosci. 1981 Feb;1(2):218–225. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.01-02-00218.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guidotti A., Forchetti C. M., Corda M. G., Konkel D., Bennett C. D., Costa E. Isolation, characterization, and purification to homogeneity of an endogenous polypeptide with agonistic action on benzodiazepine receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(11):3531–3535. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.11.3531. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall P. F. Cellular organization for steroidogenesis. Int Rev Cytol. 1984;86:53–95. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)60177-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirsch J. D., Beyer C. F., Malkowitz L., Loullis C. C., Blume A. J. Characterization of ligand binding to mitochondrial benzodiazepine receptors. Mol Pharmacol. 1989 Jan;35(1):164–172. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu Z. Y., Bourreau E., Jung-Testas I., Robel P., Baulieu E. E. Neurosteroids: oligodendrocyte mitochondria convert cholesterol to pregnenolone. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(23):8215–8219. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.23.8215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kowal J. ACTH and the metabolism of adrenal cell cultures. Recent Prog Horm Res. 1970;26:623–687. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-571126-5.50020-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Fur G., Vaucher N., Perrier M. L., Flamier A., Benavides J., Renault C., Dubroeucq M. C., Guérémy C., Uzan A. Differentiation between two ligands for peripheral benzodiazepine binding sites, [3H]RO5-4864 and [3H]PK 11195, by thermodynamic studies. Life Sci. 1983 Aug 1;33(5):449–457. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(83)90794-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Goascogne C., Robel P., Gouézou M., Sananès N., Baulieu E. E., Waterman M. Neurosteroids: cytochrome P-450scc in rat brain. Science. 1987 Sep 4;237(4819):1212–1215. doi: 10.1126/science.3306919. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Majewska M. D., Harrison N. L., Schwartz R. D., Barker J. L., Paul S. M. Steroid hormone metabolites are barbiturate-like modulators of the GABA receptor. Science. 1986 May 23;232(4753):1004–1007. doi: 10.1126/science.2422758. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mienville J. M., Vicini S. Pregnenolone sulfate antagonizes GABAA receptor-mediated currents via a reduction of channel opening frequency. Brain Res. 1989 Jun 5;489(1):190–194. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(89)90024-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizoule J., Gauthier A., Uzan A., Renault C., Dubroeucq M. C., Guérémy C., Le Fur G. Opposite effects of two ligands for peripheral type benzodiazepine binding sites, PK 11195 and RO5-4864, in a conflict situation in the rat. Life Sci. 1985 Mar 18;36(11):1059–1068. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(85)90491-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ritta M. N., Calandra R. S. Testicular interstitial cells as targets for peripheral benzodiazepines. Neuroendocrinology. 1989 Mar;49(3):262–266. doi: 10.1159/000125126. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruff M. R., Pert C. B., Weber R. J., Wahl L. M., Wahl S. M., Paul S. M. Benzodiazepine receptor-mediated chemotaxis of human monocytes. Science. 1985 Sep 20;229(4719):1281–1283. doi: 10.1126/science.2994216. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoemaker H., Boles R. G., Horst W. D., Yamamura H. I. Specific high-affinity binding sites for [3H]Ro 5-4864 in rat brain and kidney. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1983 Apr;225(1):61–69. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slobodyansky E., Guidotti A., Wambebe C., Berkovich A., Costa E. Isolation and characterization of a rat brain triakontatetraneuropeptide, a posttranslational product of diazepam binding inhibitor: specific action at the Ro 5-4864 recognition site. J Neurochem. 1989 Oct;53(4):1276–1284. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1989.tb07425.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Villiger J. W. Characterization of peripheral-type benzodiazepine recognition sites in the rat spinal cord. Neuropharmacology. 1985 Feb;24(2):95–98. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(85)90166-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weissman B. A., Cott J., Paul S. M., Skolnick P. Ro 5-4864: a potent benzodiazepine convulsant. Eur J Pharmacol. 1983 May 20;90(1):149–150. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(83)90229-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanagibashi K., Papadopoulos V., Masaki E., Iwaki T., Kawamura M., Hall P. F. Forskolin activates voltage-dependent Ca2+ channels in bovine but not in rat fasciculata cells. Endocrinology. 1989 May;124(5):2383–2391. doi: 10.1210/endo-124-5-2383. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



