Abstract
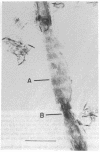
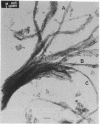
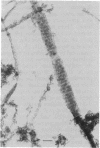
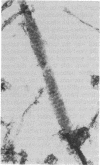
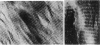
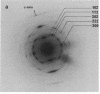
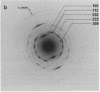
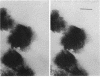
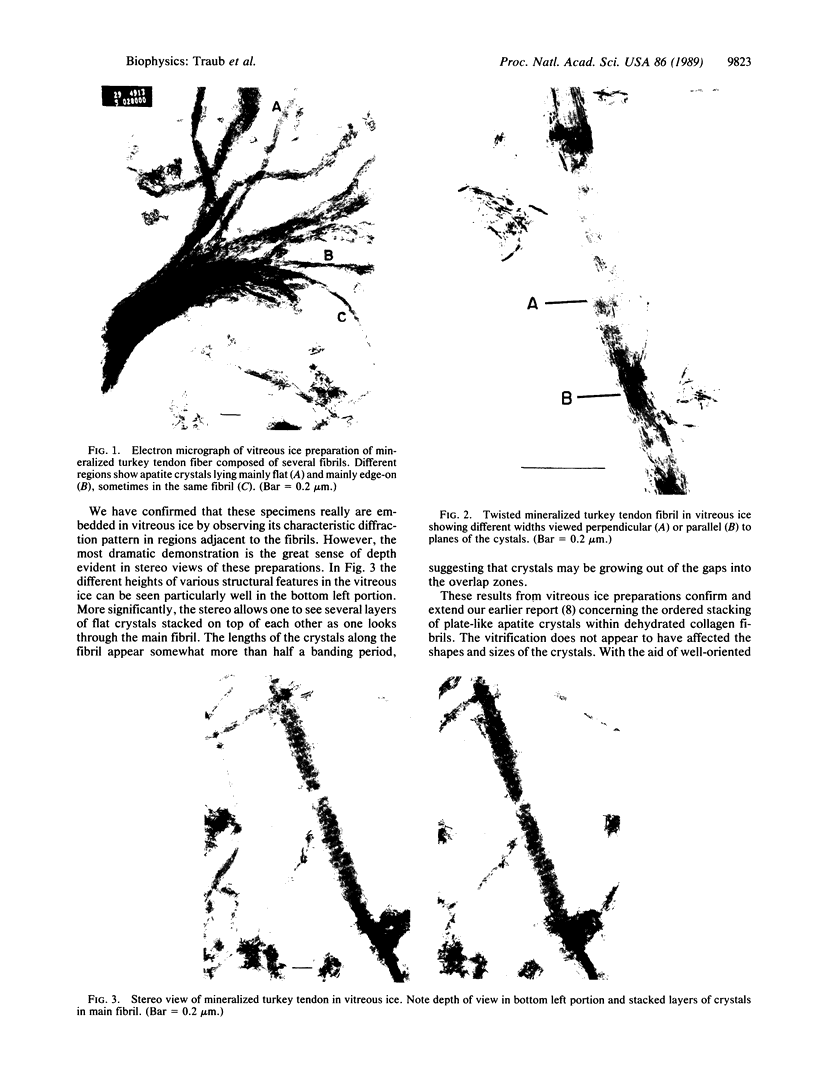
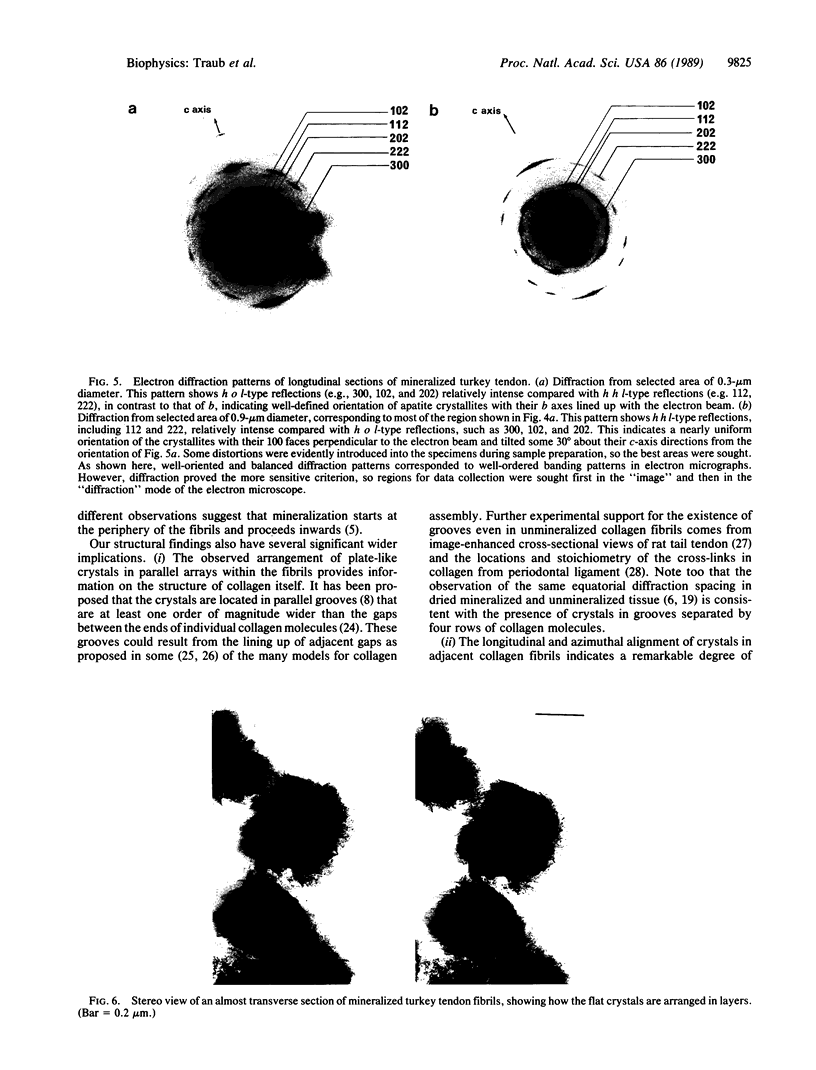
The organization of apatite crystals and collagen fibrils in mineralized turkey tendon has been studied by electron microscopy and electron diffraction. To minimize artifactual distortions the tissue was examined, for the first time, as isolated fibrils in an aqueous environment of vitreous ice, as well as in conventionally prepared sections. The electron micrographs show that the plate-shaped apatite crystals are arranged in parallel arrays across the collagen fibrils. This provides direct evidence for highly asymmetric assembly in collagen fibrils, and, indeed, the fibrils were observed to be elongated rather than round in cross-section. There is, furthermore, a pronounced tendency for the layers of crystals to be coherently aligned in adjacent fibrils. These observations may also be important for understanding the mechanical behavior of bone at the molecular level, as such extended, aligned aggregates of flat crystals could develop into natural fracture planes in mature bone.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adrian M., Dubochet J., Lepault J., McDowall A. W. Cryo-electron microscopy of viruses. Nature. 1984 Mar 1;308(5954):32–36. doi: 10.1038/308032a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arsenault A. L. Crystal-collagen relationships in calcified turkey leg tendons visualized by selected-area dark field electron microscopy. Calcif Tissue Int. 1988 Oct;43(4):202–212. doi: 10.1007/BF02555136. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bellare J. R., Davis H. T., Scriven L. E., Talmon Y. Controlled environment vitrification system: an improved sample preparation technique. J Electron Microsc Tech. 1988 Sep;10(1):87–111. doi: 10.1002/jemt.1060100111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berthet-Colominas C., Miller A., White S. W. Structural study of the calcifying collagen in turkey leg tendons. J Mol Biol. 1979 Nov 5;134(3):431–445. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90362-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birk D. E., Trelstad R. L. Extracellular compartments in tendon morphogenesis: collagen fibril, bundle, and macroaggregate formation. J Cell Biol. 1986 Jul;103(1):231–240. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.1.231. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eanes E. D., Lundy D. R., Martin G. N. X-ray diffraction study of the mineralization of turkey leg tendon. Calcif Tissue Res. 1970;6(3):239–248. doi: 10.1007/BF02196204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraser R. D., MacRae T. P., Miller A., Suzuki E. Molecular conformation and packing in collagen fibrils. J Mol Biol. 1983 Jun 25;167(2):497–521. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80347-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hulmes D. J., Holmes D. F., Cummings C. Crystalline regions in collagen fibrils. J Mol Biol. 1985 Aug 5;184(3):473–477. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90295-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JACKSON S. F. The fine structure of developing bone in the embryonic fowl. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1956 Mar 26;146(923):270–280. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1957.0010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JOHANSEN E., PARKS H. F. Electron microscopic observations on the three-dimensional morphology of apatite crystallites of human dentine and bone. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1960 Jul;7:743–746. doi: 10.1083/jcb.7.4.743. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson S. A., Cartwright A. G., Lewis D. The morphology of bone mineral crystals. Calcif Tissue Res. 1978 Aug 18;25(3):217–222. doi: 10.1007/BF02010772. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KAY M. I., YOUNG R. A., POSNER A. S. CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF HYDROXYAPATITE. Nature. 1964 Dec 12;204:1050–1052. doi: 10.1038/2041050a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz E. P., Li S. T. The intermolecular space of reconstituted collagen fibrils. J Mol Biol. 1973 Feb 19;73(3):351–369. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90347-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landis W. J. A study of calcification in the leg tendons from the domestic turkey. J Ultrastruct Mol Struct Res. 1986 Mar;94(3):217–238. doi: 10.1016/0889-1605(86)90069-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lees S., Prostak K. The locus of mineral crystallites in bone. Connect Tissue Res. 1988;18(1):41–54. doi: 10.3109/03008208809019071. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROBINSON R. A. An electron-microscopic study of the crystalline inorganic component of bone and its relationship to the organic matrix. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1952 Apr;34-A(2):389–passim. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROBINSON R. A., WATSON M. L. Collagen-crystal relationships in bone as seen in the electron microscope. Anat Rec. 1952 Nov;114(3):383–409. doi: 10.1002/ar.1091140302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Termine J. D., Eanes E. D., Greenfield D. J., Nylen M. U., Harper R. A. Hydrazine-deproteinated bone mineral. Physical and chemical properties. Calcif Tissue Res. 1973;12(1):73–90. doi: 10.1007/BF02013723. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiner S., Price P. A. Disaggregation of bone into crystals. Calcif Tissue Int. 1986 Dec;39(6):365–375. doi: 10.1007/BF02555173. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiner S., Traub W. Organization of hydroxyapatite crystals within collagen fibrils. FEBS Lett. 1986 Oct 6;206(2):262–266. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)80993-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamauchi M., Katz E. P., Mechanic G. L. Intermolecular cross-linking and stereospecific molecular packing in type I collagen fibrils of the periodontal ligament. Biochemistry. 1986 Aug 26;25(17):4907–4913. doi: 10.1021/bi00365a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]