Abstract
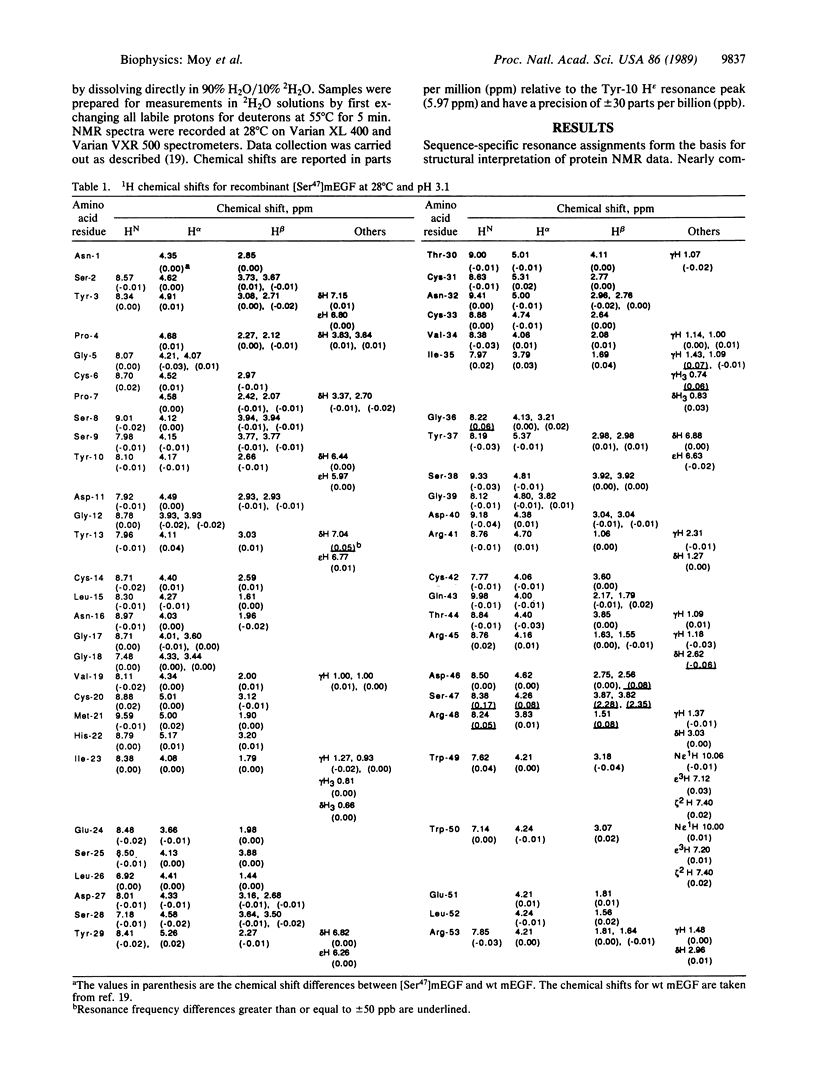
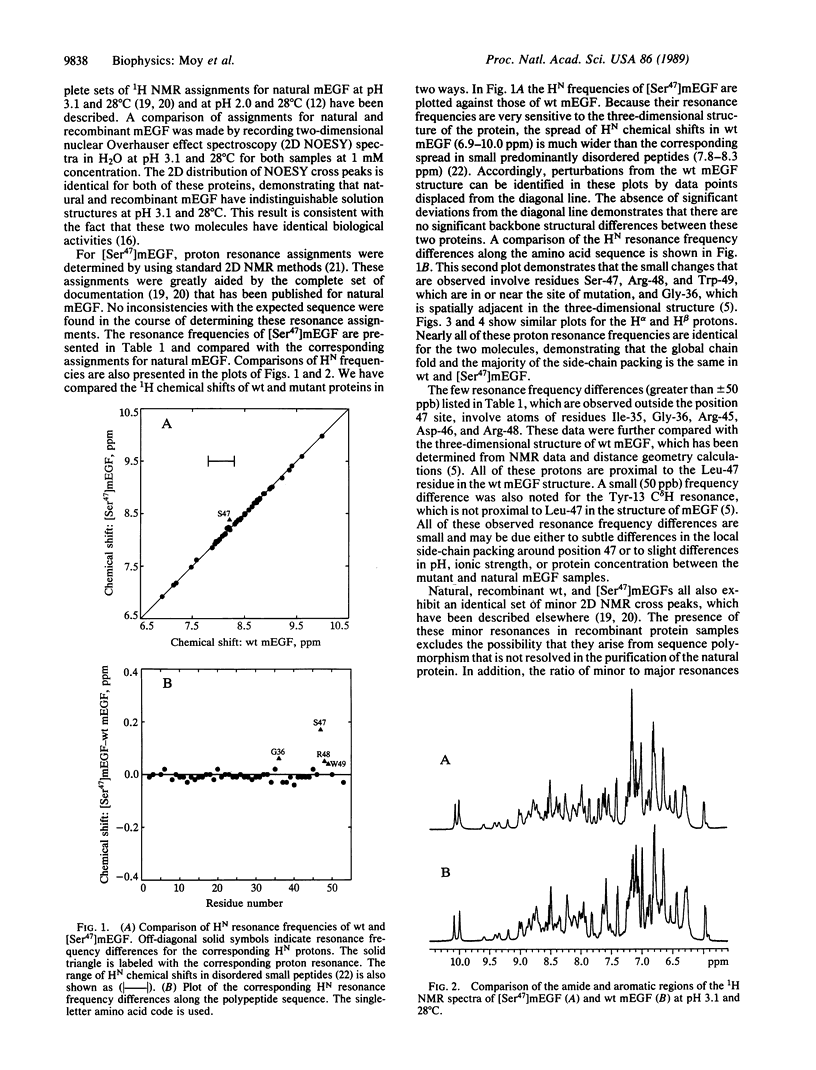
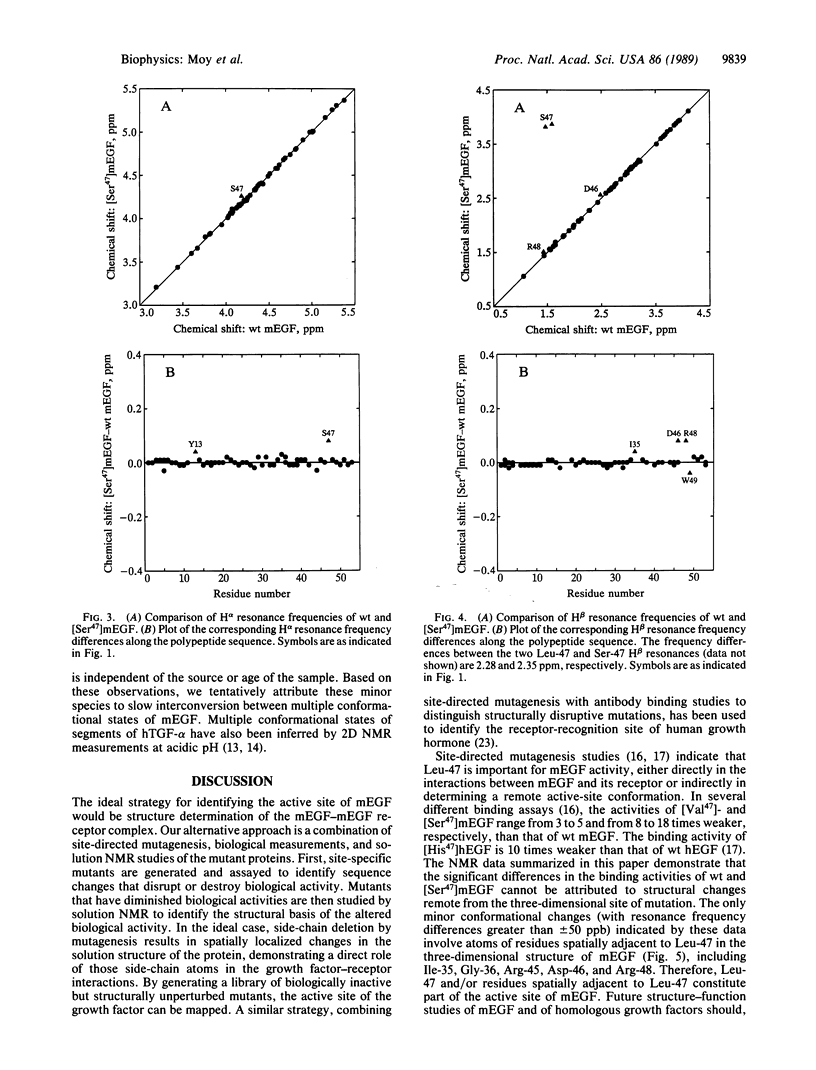
Epidermal growth factor (EGF) is a small protein containing 53 amino acids and three disulfide bonds. There is significant current interest in structure-function relationships in EGF and EGF-like proteins, including the homologous type-alpha transforming growth factors. The Leu-47 residue of murine EGF (mEGF) is one of several that are strongly conserved among the EGF-like growth factors, suggesting that it may contribute to the active site of mEGF. In several different binding assays, the activity of the mutant analog in which Leu-47 is replaced by Ser [( Ser47]mEGF) ranges from 8 to 18 times weaker than that of wild-type mEGF. The NMR data summarized in this paper demonstrate that the significant differences in the binding activities of wild-type and [Ser47]mEGF cannot be attributed to structural changes remote from the three-dimensional site of mutation. The only minor conformational changes that are indicated by these data involve side chains of residues proximal to Leu-47 in the three-dimensional structure. Therefore, Leu-47 and/or residues spatially adjacent to Leu-47 constitute part of the active site of mEGF.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brown S. C., Mueller L., Jeffs P. W. 1H NMR assignment and secondary structural elements of human transforming growth factor alpha. Biochemistry. 1989 Jan 24;28(2):593–599. doi: 10.1021/bi00428a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgess A. W. Epidermal growth factor and transforming growth factor alpha. Br Med Bull. 1989 Apr;45(2):401–424. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a072331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgess A. W., Lloyd C. J., Smith S., Stanley E., Walker F., Fabri L., Simpson R. J., Nice E. C. Murine epidermal growth factor: structure and function. Biochemistry. 1988 Jul 12;27(14):4977–4985. doi: 10.1021/bi00414a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carver J. A., Cooke R. M., Esposito G., Campbell I. D., Gregory H., Sheard B. A high resolution 1H NMR study of the solution structure of human epidermal growth factor. FEBS Lett. 1986 Sep 1;205(1):77–81. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)80869-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooke R. M., Wilkinson A. J., Baron M., Pastore A., Tappin M. J., Campbell I. D., Gregory H., Sheard B. The solution structure of human epidermal growth factor. 1987 May 28-Jun 3Nature. 327(6120):339–341. doi: 10.1038/327339a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cunningham B. C., Jhurani P., Ng P., Wells J. A. Receptor and antibody epitopes in human growth hormone identified by homolog-scanning mutagenesis. Science. 1989 Mar 10;243(4896):1330–1336. doi: 10.1126/science.2466339. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engler D. A., Matsunami R. K., Campion S. R., Stringer C. D., Stevens A., Niyogi S. K. Cloning of authentic human epidermal growth factor as a bacterial secretory protein and its initial structure-function analysis by site-directed mutagenesis. J Biol Chem. 1988 Sep 5;263(25):12384–12390. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohda D., Go N., Hayashi K., Inagaki F. Tertiary structure of mouse epidermal growth factor determined by two-dimensional 1H NMR. J Biochem. 1988 May;103(5):741–743. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a122338. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohda D., Shimada I., Miyake T., Fuwa T., Inagaki F. Polypeptide chain fold of human transforming growth factor alpha analogous to those of mouse and human epidermal growth factors as studied by two-dimensional 1H NMR. Biochemistry. 1989 Feb 7;28(3):953–958. doi: 10.1021/bi00429a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazar E., Watanabe S., Dalton S., Sporn M. B. Transforming growth factor alpha: mutation of aspartic acid 47 and leucine 48 results in different biological activities. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Mar;8(3):1247–1252. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.3.1247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Makino K., Morimoto M., Nishi M., Sakamoto S., Tamura A., Inooka H., Akasaka K. Proton nuclear magnetic resonance study on the solution conformation of human epidermal growth factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Nov;84(22):7841–7845. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.22.7841. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayo K. H., Cavalli R. C., Peters A. R., Boelens R., Kaptein R. Sequence-specific 1H-n.m.r. assignments and peptide backbone conformation in rat epidermal growth factor. Biochem J. 1989 Jan 1;257(1):197–205. doi: 10.1042/bj2570197. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montelione G. T., Winkler M. E., Burton L. E., Rinderknecht E., Sporn M. B., Wagner G. Sequence-specific 1H-NMR assignments and identification of two small antiparallel beta-sheets in the solution structure of recombinant human transforming growth factor alpha. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Mar;86(5):1519–1523. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.5.1519. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montelione G. T., Wüthrich K., Nice E. C., Burgess A. W., Scheraga H. A. Identification of two anti-parallel beta-sheet conformations in the solution structure of murine epidermal growth factor by proton magnetic resonance. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Nov;83(22):8594–8598. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.22.8594. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montelione G. T., Wüthrich K., Nice E. C., Burgess A. W., Scheraga H. A. Solution structure of murine epidermal growth factor: determination of the polypeptide backbone chain-fold by nuclear magnetic resonance and distance geometry. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(15):5226–5230. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.15.5226. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montelione G. T., Wüthrich K., Scheraga H. A. Sequence-specific 1H NMR assignments and identification of slowly exchanging amide protons in murine epidermal growth factor. Biochemistry. 1988 Mar 22;27(6):2235–2243. doi: 10.1021/bi00406a064. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ray P., Moy F. J., Montelione G. T., Liu J. F., Narang S. A., Scheraga H. A., Wu R. Structure-function studies of murine epidermal growth factor: expression and site-directed mutagenesis of epidermal growth factor gene. Biochemistry. 1988 Sep 20;27(19):7289–7295. doi: 10.1021/bi00419a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sporn M. B., Roberts A. B. Autocrine growth factors and cancer. 1985 Feb 28-Mar 6Nature. 313(6005):745–747. doi: 10.1038/313745a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sporn M. B., Todaro G. J. Autocrine secretion and malignant transformation of cells. N Engl J Med. 1980 Oct 9;303(15):878–880. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198010093031511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tappin M. J., Cooke R. M., Fitton J. E., Campbell I. D. A high-resolution 1H-NMR study of human transforming growth factor alpha. Structure and pH-dependent conformational interconversion. Eur J Biochem. 1989 Feb 15;179(3):629–637. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1989.tb14594.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]