Abstract
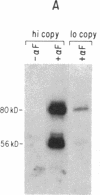
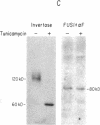
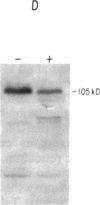
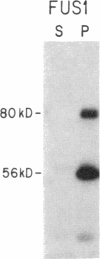
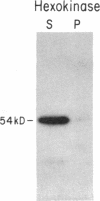
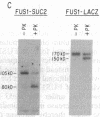
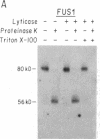
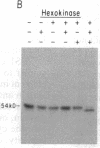
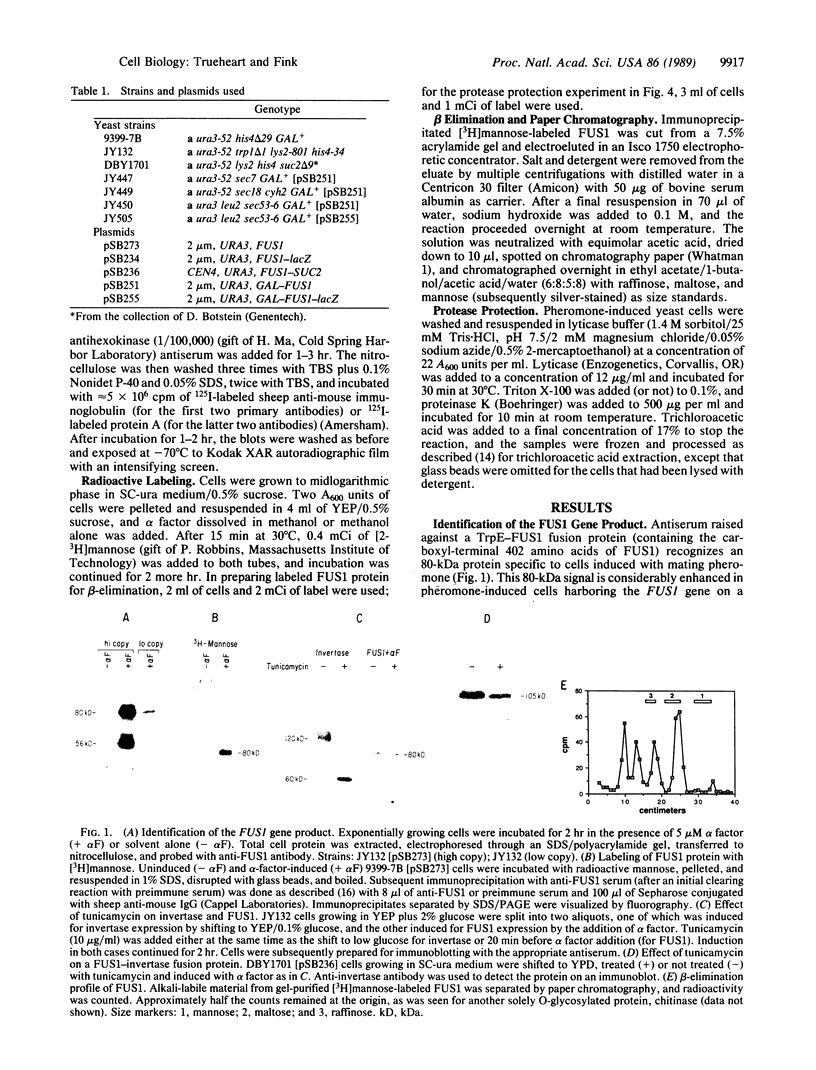
Previous work has shown that efficient cell fusion during conjugation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae requires a pheromone-induced surface protein encoded by FUS1. We show that the FUS1 protein migrates on SDS/polyacrylamide gels with an apparent molecular mass of 80 kDa, although the mass is predicted to be 58 kDa from the gene coding capacity. This discrepancy results from the presence of O-linked mannose oligosaccharides attached to the clustered serines and threonines at the amino terminus of the protein. The addition of mannose is completely abolished in the early secretory mutant sec53, attenuated in the late-endoplasmic reticulum-blocked sec18, and unaffected in sec7, which is blocked late in the Golgi phase of secretion. Membrane fractionation and protease protection experiments indicate that FUS1 spans the plasma membrane, with its glycosylated amino terminus projecting into the periplasmic space.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Davis C. G., Elhammer A., Russell D. W., Schneider W. J., Kornfeld S., Brown M. S., Goldstein J. L. Deletion of clustered O-linked carbohydrates does not impair function of low density lipoprotein receptor in transfected fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1986 Feb 25;261(6):2828–2838. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duntze W., MacKay V., Manney T. R. Saccharomyces cerevisiae: a diffusible sex factor. Science. 1970 Jun 19;168(3938):1472–1473. doi: 10.1126/science.168.3938.1472. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emr S. D., Schauer I., Hansen W., Esmon P., Schekman R. Invertase beta-galactosidase hybrid proteins fail to be transported from the endoplasmic reticulum in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Nov;4(11):2347–2355. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.11.2347. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esmon B., Novick P., Schekman R. Compartmentalized assembly of oligosaccharides on exported glycoproteins in yeast. Cell. 1981 Aug;25(2):451–460. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90063-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldman R. I., Bernstein M., Schekman R. Product of SEC53 is required for folding and glycosylation of secretory proteins in the lumen of the yeast endoplasmic reticulum. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jul 5;262(19):9332–9339. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuller R. S., Brake A. J., Thorner J. Intracellular targeting and structural conservation of a prohormone-processing endoprotease. Science. 1989 Oct 27;246(4929):482–486. doi: 10.1126/science.2683070. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haarer B. K., Pringle J. R. Immunofluorescence localization of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae CDC12 gene product to the vicinity of the 10-nm filaments in the mother-bud neck. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Oct;7(10):3678–3687. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.10.3678. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haselbeck A., Tanner W. O-glycosylation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae is initiated at the endoplasmic reticulum. FEBS Lett. 1983 Jul 25;158(2):335–338. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(83)80608-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito H., Fukuda Y., Murata K., Kimura A. Transformation of intact yeast cells treated with alkali cations. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jan;153(1):163–168. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.1.163-168.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaiser C. A., Preuss D., Grisafi P., Botstein D. Many random sequences functionally replace the secretion signal sequence of yeast invertase. Science. 1987 Jan 16;235(4786):312–317. doi: 10.1126/science.3541205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kepes F., Schekman R. The yeast SEC53 gene encodes phosphomannomutase. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jul 5;263(19):9155–9161. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleid D. G., Yansura D., Small B., Dowbenko D., Moore D. M., Grubman M. J., McKercher P. D., Morgan D. O., Robertson B. H., Bachrach H. L. Cloned viral protein vaccine for foot-and-mouth disease: responses in cattle and swine. Science. 1981 Dec 4;214(4525):1125–1129. doi: 10.1126/science.6272395. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kukuruzinska M. A., Bergh M. L., Jackson B. J. Protein glycosylation in yeast. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:915–944. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.004411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuo S. C., Lampen J. O. Tunicamycin--an inhibitor of yeast glycoprotein synthesis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 May 7;58(1):287–295. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(74)90925-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyte J., Doolittle R. F. A simple method for displaying the hydropathic character of a protein. J Mol Biol. 1982 May 5;157(1):105–132. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90515-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehle L., Bauer F., Tanner W. The formation of glycosidic bonds in yeast glycoproteins. Intracellular localisation of the reactions. Arch Microbiol. 1977 Jul 26;114(1):77–81. doi: 10.1007/BF00429634. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehle L., Tanner W. The specific site of tunicamycin inhibition in the formation of dolichol-bound N-acetylglucosamine derivatives. FEBS Lett. 1976 Nov 15;72(1):167–170. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(76)80922-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCaffrey G., Clay F. J., Kelsay K., Sprague G. F., Jr Identification and regulation of a gene required for cell fusion during mating of the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Aug;7(8):2680–2690. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.8.2680. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohashi A., Gibson J., Gregor I., Schatz G. Import of proteins into mitochondria. The precursor of cytochrome c1 is processed in two steps, one of them heme-dependent. J Biol Chem. 1982 Nov 10;257(21):13042–13047. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakai K., Yanagishima N. Mating reaction in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. II. Hormonal regulation of agglutinability of a type cells. Arch Mikrobiol. 1972;84(3):191–198. doi: 10.1007/BF00425197. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schekman R. Protein localization and membrane traffic in yeast. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1985;1:115–143. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.01.110185.000555. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt J. J., Colowick S. P. Identification of a peptide sequence involved in association of subunits of yeast hexokinases. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1973 Oct;158(2):471–477. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(73)90538-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Serrano R. In vivo glucose activation of the yeast plasma membrane ATPase. FEBS Lett. 1983 May 30;156(1):11–14. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(83)80237-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terrance K., Lipke P. N. Sexual agglutination in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Bacteriol. 1981 Dec;148(3):889–896. doi: 10.1128/jb.148.3.889-896.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trueheart J., Boeke J. D., Fink G. R. Two genes required for cell fusion during yeast conjugation: evidence for a pheromone-induced surface protein. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jul;7(7):2316–2328. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.7.2316. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson L. E., Pringle J. R. Transient G1 arrest of S. cerevisiae cells of mating type alpha by a factor produced by cells of mating type a. Exp Cell Res. 1974 Nov;89(1):175–187. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(74)90200-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]