Abstract
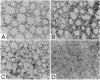
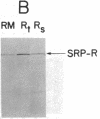
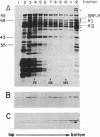
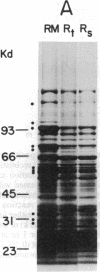
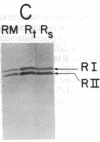
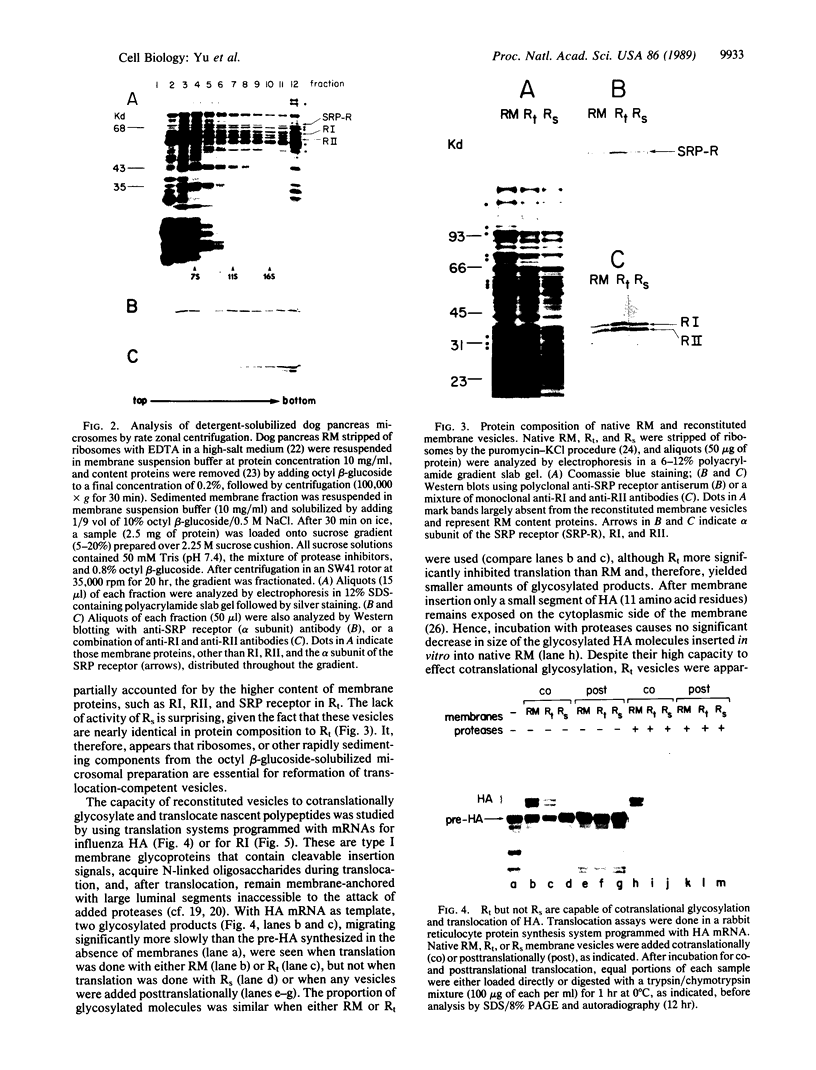
Dog pancreas rough microsomes were solubilized in 1% octyl beta-glucoside, and membrane vesicles were reconstituted by slow 30-fold dilution with a buffer of low ionic strength. Asymmetric assembly of the membranes occurred during reconstitution since the vesicles formed contained ribosomes bound only to the vesicular outer surfaces. The reconstituted vesicles were similar in protein composition to native rough microsomes, although these vesicles were largely devoid of luminal-content proteins. These reconstituted vesicles could translocate and process nascent secretory (human placental lactogen) and membrane proteins (influenza hemagglutinin and rat liver ribophorin I) synthesized in cell-free translation systems programmed with the corresponding mRNAs. Signal cleavage and N-glycosylation only occurred when the reconstituted membranes were present during translation, providing evidence that the translocation apparatus was asymmetrically assembled into the reconstituted membranes. When a supernatant lacking ribosomes and particles greater than 50S from centrifuging the detergent-solubilized microsomes at high speed was used for reconstitution, smooth-surfaced membrane vesicles were obtained that, except for the absence of ribosomal proteins, were similar in protein composition to that of the reconstituted vesicles from total solubilized rough microsomes. The reconstituted smooth-surfaced vesicles, however, were totally inactive in cotranslational processing and translocation of nascent polypeptides. These findings suggest that ribosomes and/or large macromolecular complexes, not dissociated under our solubilization conditions, are essential for in vitro assembly of a functional translocation apparatus.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adelman M. R., Sabatini D. D., Blobel G. Ribosome-membrane interaction. Nondestructive disassembly of rat liver rough microsomes into ribosomal and membranous components. J Cell Biol. 1973 Jan;56(1):206–229. doi: 10.1083/jcb.56.1.206. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amar-Costesec A., Todd J. A., Kreibich G. Segregation of the polypeptide translocation apparatus to regions of the endoplasmic reticulum containing ribophorins and ribosomes. I. Functional tests on rat liver microsomal subfractions. J Cell Biol. 1984 Dec;99(6):2247–2253. doi: 10.1083/jcb.99.6.2247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans E. A., Gilmore R., Blobel G. Purification of microsomal signal peptidase as a complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Feb;83(3):581–585. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.3.581. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finidori J., Rizzolo L., Gonzalez A., Kreibich G., Adesnik M., Sabatini D. D. The influenza hemagglutinin insertion signal is not cleaved and does not halt translocation when presented to the endoplasmic reticulum membrane as part of a translocating polypeptide. J Cell Biol. 1987 Jun;104(6):1705–1714. doi: 10.1083/jcb.104.6.1705. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freedman R. B. Protein disulfide isomerase: multiple roles in the modification of nascent secretory proteins. Cell. 1989 Jun 30;57(7):1069–1072. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90043-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geetha-Habib M., Noiva R., Kaplan H. A., Lennarz W. J. Glycosylation site binding protein, a component of oligosaccharyl transferase, is highly similar to three other 57 kd luminal proteins of the ER. Cell. 1988 Sep 23;54(7):1053–1060. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90120-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gekko K., Timasheff S. N. Thermodynamic and kinetic examination of protein stabilization by glycerol. Biochemistry. 1981 Aug 4;20(16):4677–4686. doi: 10.1021/bi00519a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gething M. J., Sambrook J. Construction of influenza haemagglutinin genes that code for intracellular and secreted forms of the protein. Nature. 1982 Dec 16;300(5893):598–603. doi: 10.1038/300598a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilmore R., Blobel G. Transient involvement of signal recognition particle and its receptor in the microsomal membrane prior to protein translocation. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(3 Pt 2):677–685. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90100-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harnik-Ort V., Prakash K., Marcantonio E., Colman D. R., Rosenfeld M. G., Adesnik M., Sabatini D. D., Kreibich G. Isolation and characterization of cDNA clones for rat ribophorin I: complete coding sequence and in vitro synthesis and insertion of the encoded product into endoplasmic reticulum membranes. J Cell Biol. 1987 Apr;104(4):855–863. doi: 10.1083/jcb.104.4.855. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartmann E., Wiedmann M., Rapoport T. A. A membrane component of the endoplasmic reticulum that may be essential for protein translocation. EMBO J. 1989 Aug;8(8):2225–2229. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08346.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan H. A., Welply J. K., Lennarz W. J. Oligosaccharyl transferase: the central enzyme in the pathway of glycoprotein assembly. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Jun 24;906(2):161–173. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(87)90010-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreibich G., Czakó-Graham M., Grebenau R. C., Sabatini D. D. Functional and structural characteristics of endoplasmic reticulum proteins associated with ribosome binding sites. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1980;343:17–33. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1980.tb47239.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreibich G., Debey P., Sabatini D. D. Selective release of content from microsomal vesicles without membrane disassembly. I. Permeability changes induced by low detergent concentrations. J Cell Biol. 1973 Aug;58(2):436–462. doi: 10.1083/jcb.58.2.436. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreibich G., Freienstein C. M., Pereyra B. N., Ulrich B. L., Sabatini D. D. Proteins of rough microsomal membranes related to ribosome binding. II. Cross-linking of bound ribosomes to specific membrane proteins exposed at the binding sites. J Cell Biol. 1978 May;77(2):488–506. doi: 10.1083/jcb.77.2.488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreibich G., Sabatini D. D. Procedure for the selective release of content from microsomal vesicles without membrane disassembly. Methods Enzymol. 1974;31:215–225. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(74)31023-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreibich G., Ulrich B. L., Sabatini D. D. Proteins of rough microsomal membranes related to ribosome binding. I. Identification of ribophorins I and II, membrane proteins characteristics of rough microsomes. J Cell Biol. 1978 May;77(2):464–487. doi: 10.1083/jcb.77.2.464. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcantonio E. E., Amar-Costesec A., Kreibich G. Segregation of the polypeptide translocation apparatus to regions of the endoplasmic reticulum containing ribophorins and ribosomes. II. Rat liver microsomal subfractions contain equimolar amounts of ribophorins and ribosomes. J Cell Biol. 1984 Dec;99(6):2254–2259. doi: 10.1083/jcb.99.6.2254. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer D. I., Krause E., Dobberstein B. Secretory protein translocation across membranes-the role of the "docking protein'. Nature. 1982 Jun 24;297(5868):647–650. doi: 10.1038/297647a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Redman C. M., Sabatini D. D. Vectorial discharge of peptides released by puromycin from attached ribosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Aug;56(2):608–615. doi: 10.1073/pnas.56.2.608. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenfeld M. G., Marcantonio E. E., Hakimi J., Ort V. M., Atkinson P. H., Sabatini D., Kreibich G. Biosynthesis and processing of ribophorins in the endoplasmic reticulum. J Cell Biol. 1984 Sep;99(3):1076–1082. doi: 10.1083/jcb.99.3.1076. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sabatini D. D., Kreibich G., Morimoto T., Adesnik M. Mechanisms for the incorporation of proteins in membranes and organelles. J Cell Biol. 1982 Jan;92(1):1–22. doi: 10.1083/jcb.92.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stubbs G. W., Smith H. G., Jr, Litman B. J. Alkyl glucosides as effective solubilizing agents for bovine rhodopsin. A comparison with several commonly used detergents. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Feb 19;426(1):46–56. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(76)90428-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tajima S., Lauffer L., Rath V. L., Walter P. The signal recognition particle receptor is a complex that contains two distinct polypeptide chains. J Cell Biol. 1986 Oct;103(4):1167–1178. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.4.1167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walter P., Blobel G. Preparation of microsomal membranes for cotranslational protein translocation. Methods Enzymol. 1983;96:84–93. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(83)96010-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walter P., Blobel G. Translocation of proteins across the endoplasmic reticulum III. Signal recognition protein (SRP) causes signal sequence-dependent and site-specific arrest of chain elongation that is released by microsomal membranes. J Cell Biol. 1981 Nov;91(2 Pt 1):557–561. doi: 10.1083/jcb.91.2.557. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walter P., Gilmore R., Blobel G. Protein translocation across the endoplasmic reticulum. Cell. 1984 Aug;38(1):5–8. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90520-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiedmann M., Kurzchalia T. V., Hartmann E., Rapoport T. A. A signal sequence receptor in the endoplasmic reticulum membrane. 1987 Aug 27-Sep 2Nature. 328(6133):830–833. doi: 10.1038/328830a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Womack M. D., Kendall D. A., MacDonald R. C. Detergent effects on enzyme activity and solubilization of lipid bilayer membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Sep 7;733(2):210–215. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(83)90524-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida H., Tondokoro N., Asano Y., Mizusawa K., Yamagishi R., Horigome T., Sugano H. Studies on membrane proteins involved in ribosome binding on the rough endoplasmic reticulum. Ribophorins have no ribosome-binding activity. Biochem J. 1987 Aug 1;245(3):811–819. doi: 10.1042/bj2450811. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]