Abstract
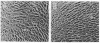
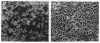
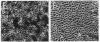
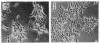
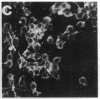
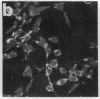
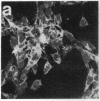
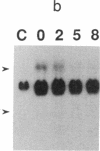
Okadaic acid is a non-phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate (PMA)-type tumor promoter on mouse skin and known to be a potent inhibitor of serine/threonine protein phosphatases. Contrary to expectation from its tumor-promoting activity, okadaic acid was shown to have a potential to revert the phenotypes of cells transformed by raf and ret-II to that of normal cells. Two to 3 days after addition of 8 ng of okadaic acid per ml to the culture medium, raf and ret-II transformants changed to flat cells and gained contact inhibition. The amount of fibronectin, which was decreased in malignant transformed cells, was increased in the flat revertants. Moreover, okadaic acid caused a dose-dependent loss of ability to grow in soft agar. The morphology of the cells reverted to malignant phenotype within 1 week after removal of okadaic acid. The levels of mRNA and protein of activated c-raf in flat revertants were similar to those in parental transformed cells. The level of mRNA of ret-II was also not changed by flat reversion. No induction of flat reversion was observed with okadaic acid tetramethyl ether, an inactive compound, or a phorbol ester, PMA. As okadaic acid is a potent inhibitor of protein phosphatases 1 and 2A, the possibility that these phosphatases are involved in signal transduction from the raf and ret-II oncogenes is suggested.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arndt K. T., Styles C. A., Fink G. R. A suppressor of a HIS4 transcriptional defect encodes a protein with homology to the catalytic subunit of protein phosphatases. Cell. 1989 Feb 24;56(4):527–537. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90576-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballou L. M., Jenö P., Thomas G. Protein phosphatase 2A inactivates the mitogen-stimulated S6 kinase from Swiss mouse 3T3 cells. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jan 25;263(3):1188–1194. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bialojan C., Takai A. Inhibitory effect of a marine-sponge toxin, okadaic acid, on protein phosphatases. Specificity and kinetics. Biochem J. 1988 Nov 15;256(1):283–290. doi: 10.1042/bj2560283. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borer R. A., Lehner C. F., Eppenberger H. M., Nigg E. A. Major nucleolar proteins shuttle between nucleus and cytoplasm. Cell. 1989 Feb 10;56(3):379–390. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90241-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiquet-Ehrismann R., Mackie E. J., Pearson C. A., Sakakura T. Tenascin: an extracellular matrix protein involved in tissue interactions during fetal development and oncogenesis. Cell. 1986 Oct 10;47(1):131–139. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90374-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dotto G. P., Parada L. F., Weinberg R. A. Specific growth response of ras-transformed embryo fibroblasts to tumour promoters. Nature. 1985 Dec 5;318(6045):472–475. doi: 10.1038/318472a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujiki H., Sugimura T. New classes of tumor promoters: teleocidin, aplysiatoxin, and palytoxin. Adv Cancer Res. 1987;49:223–264. doi: 10.1016/s0065-230x(08)60799-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg D. A. Isolation and partial characterization of the Drosophila alcohol dehydrogenase gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Oct;77(10):5794–5798. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.10.5794. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haystead T. A., Sim A. T., Carling D., Honnor R. C., Tsukitani Y., Cohen P., Hardie D. G. Effects of the tumour promoter okadaic acid on intracellular protein phosphorylation and metabolism. Nature. 1989 Jan 5;337(6202):78–81. doi: 10.1038/337078a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishihara H., Martin B. L., Brautigan D. L., Karaki H., Ozaki H., Kato Y., Fusetani N., Watabe S., Hashimoto K., Uemura D. Calyculin A and okadaic acid: inhibitors of protein phosphatase activity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Mar 31;159(3):871–877. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)92189-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishikawa F., Sakai R., Ochiai M., Takaku F., Sugimura T., Nagao M. Identification of a transforming activity suppressing sequence in the c-raf oncogene. Oncogene. 1988 Dec;3(6):653–658. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishikawa F., Takaku F., Hayashi K., Nagao M., Sugimura T. Activation of rat c-raf during transfection of hepatocellular carcinoma DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 May;83(10):3209–3212. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.10.3209. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
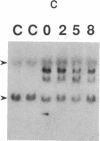
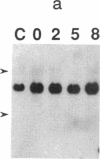
- Ishizaka Y., Tahira T., Ochiai M., Ikeda I., Sugimura T., Nagao M. Molecular cloning and characterization of human ret-II oncogene. Oncogene Res. 1988 Sep;3(2):193–197. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Issinger O. G., Martin T., Richter W. W., Olson M., Fujiki H. Hyperphosphorylation of N-60, a protein structurally and immunologically related to nucleolin after tumour-promoter treatment. EMBO J. 1988 Jun;7(6):1621–1626. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02988.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison D. K., Kaplan D. R., Rapp U., Roberts T. M. Signal transduction from membrane to cytoplasm: growth factors and membrane-bound oncogene products increase Raf-1 phosphorylation and associated protein kinase activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(23):8855–8859. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.23.8855. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nitta N., Ochiai M., Nagao M., Sugimura T. Amino-acid substitution at codon 13 of the N-ras oncogene in rectal cancer in a Japanese patient. Jpn J Cancer Res. 1987 Jan;78(1):21–26. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohkura H., Kinoshita N., Miyatani S., Toda T., Yanagida M. The fission yeast dis2+ gene required for chromosome disjoining encodes one of two putative type 1 protein phosphatases. Cell. 1989 Jun 16;57(6):997–1007. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90338-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelling J. C., Neades R., Strawhecker J. Epidermal papillomas and carcinomas induced in uninitiated mouse skin by tumor promoters alone contain a point mutation in the 61st codon of the Ha-ras oncogene. Carcinogenesis. 1988 Apr;9(4):665–667. doi: 10.1093/carcin/9.4.665. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quintanilla M., Brown K., Ramsden M., Balmain A. Carcinogen-specific mutation and amplification of Ha-ras during mouse skin carcinogenesis. Nature. 1986 Jul 3;322(6074):78–80. doi: 10.1038/322078a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasaki K., Mizusawa H., Ishidate M. Isolation and characterization of ras-transfected BALB/3T3 clone showing morphological transformation by 12-O-tetradecanoyl-phorbol-13-acetate. Jpn J Cancer Res. 1988 Aug;79(8):921–930. doi: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.1988.tb00056.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schultz A. M., Copeland T. D., Mark G. E., Rapp U. R., Oroszlan S. Detection of the myristylated gag-raf transforming protein with raf-specific antipeptide sera. Virology. 1985 Oct 15;146(1):78–89. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90054-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suganuma M., Fujiki H., Suguri H., Yoshizawa S., Hirota M., Nakayasu M., Ojika M., Wakamatsu K., Yamada K., Sugimura T. Okadaic acid: an additional non-phorbol-12-tetradecanoate-13-acetate-type tumor promoter. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Mar;85(6):1768–1771. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.6.1768. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tahira T., Hayashi K., Ochiai M., Tsuchida N., Nagao M., Sugimura T. Structure of the c-Ki-ras gene in a rat fibrosarcoma induced by 1,8-dinitropyrene. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Apr;6(4):1349–1351. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.4.1349. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tahira T., Ishizaka Y., Sugimura T., Nagao M. Expression of proto-ret mRNA in embryonic and adult rat tissues. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Jun 30;153(3):1290–1295. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)81368-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tahira T., Ochiai M., Hayashi K., Nagao M., Sugimura T. Activation of human c-raf-1 by replacing the N-terminal region with different sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jun 25;15(12):4809–4820. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.12.4809. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada K. M., Olden K. Fibronectins--adhesive glycoproteins of cell surface and blood. Nature. 1978 Sep 21;275(5677):179–184. doi: 10.1038/275179a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]