Abstract
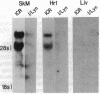
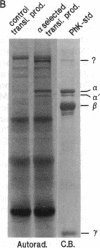
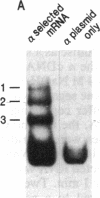
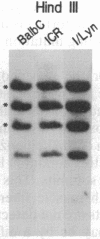
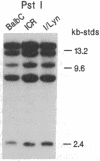
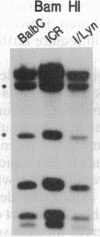
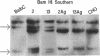
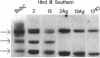
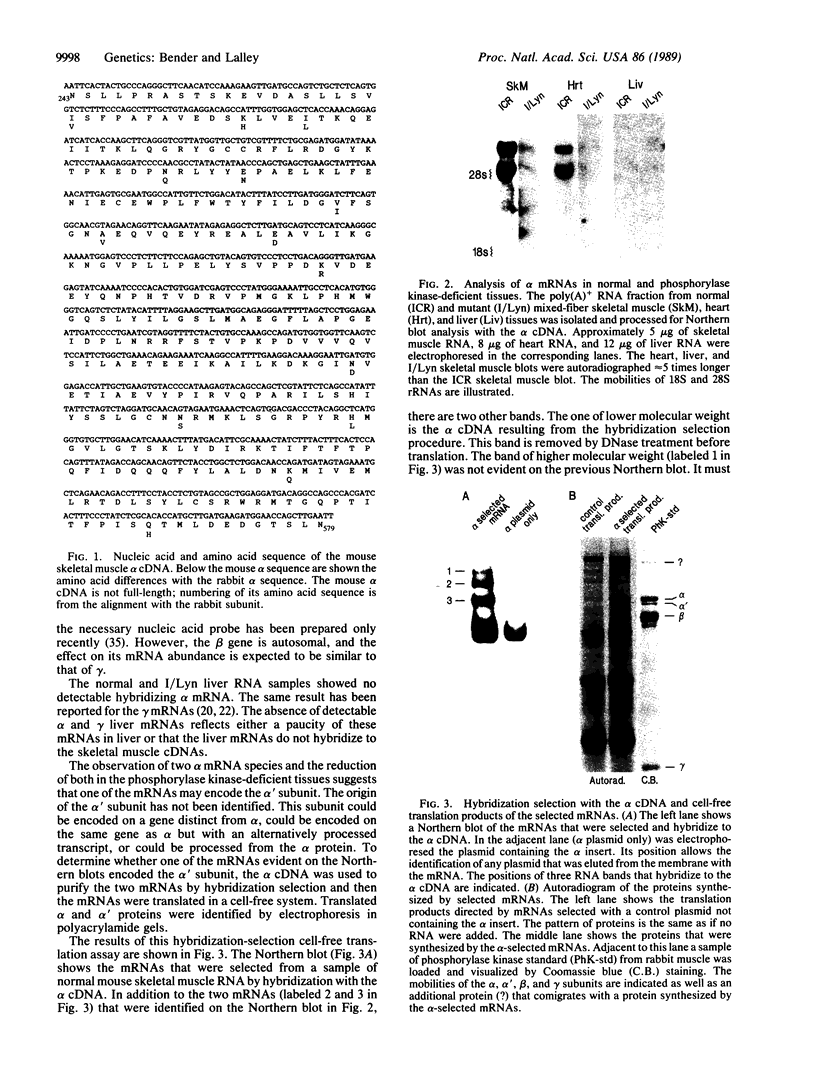
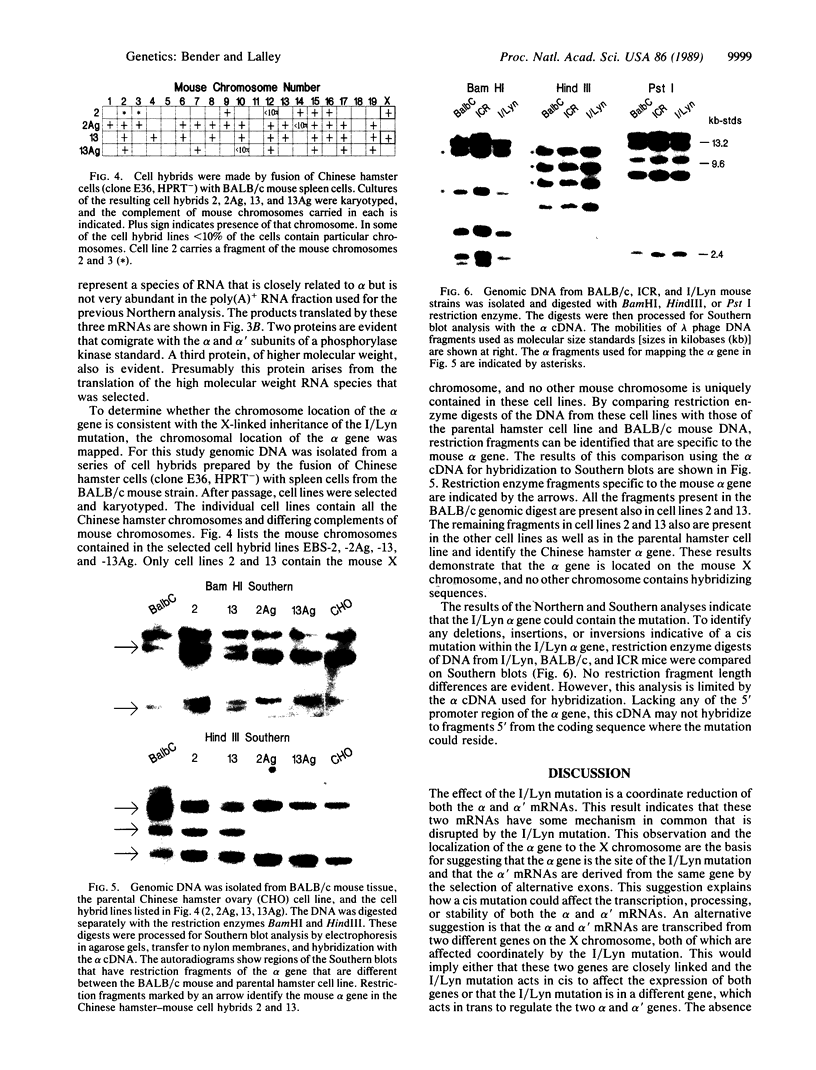
A cDNA encoding the alpha subunit of mouse skeletal muscle phosphorylase kinase was used to compare the expression of alpha mRNAs in normal and phosphorylase kinase-deficient tissues of the I/Lyn mouse. The results demonstrate that two different molecular weight species of poly(A)+ RNA in normal mouse heart and skeletal muscle hybridize to the alpha cDNA. These two mRNAs direct the synthesis of alpha protein and its isoform alpha' in a cell-free translation system. Thus, alpha and alpha' are encoded by two distinct mRNAs. The abundance of both of these mRNAs is reduced dramatically in the phosphorylase kinase-deficient skeletal muscle and heart tissues from the I/Lyn mouse strain. This result indicates that a mechanism common to both alpha and alpha' expression is disrupted by the I/Lyn mutation. The I/Lyn deficiency is inherited as an X chromosome trait. By Southern mapping of Chinese hamster-mouse cell hybrids the alpha gene was localized to the mouse X chromosome, supporting the possibility that the I/Lyn mutation is in the alpha gene. These results are discussed in terms of a cis or trans mutation influencing the expression of either a single alpha/alpha' gene or two genes encoding alpha and alpha'.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abarbanel J. M., Bashan N., Potashnik R., Osimani A., Moses S. W., Herishanu Y. Adult muscle phosphorylase "b" kinase deficiency. Neurology. 1986 Apr;36(4):560–562. doi: 10.1212/wnl.36.4.560. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bender P. K., Dedman J. R., Emerson C. P., Jr The abundance of calmodulin mRNAs is regulated in phosphorylase kinase-deficient skeletal muscle. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jul 15;263(20):9733–9737. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bender P. K., Emerson C. P., Jr Skeletal muscle phosphorylase kinase catalytic subunit mRNAs are expressed in heart tissue but not in liver. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jun 25;262(18):8799–8805. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brostrom C. O., Hunkeler F. L., Krebs E. G. The regulation of skeletal muscle phosphorylase kinase by Ca2+. J Biol Chem. 1971 Apr 10;246(7):1961–1967. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chamberlain J. S., VanTuinen P., Reeves A. A., Philip B. A., Caskey C. T. Isolation of cDNA clones for the catalytic gamma subunit of mouse muscle phosphorylase kinase: expression of mRNA in normal and mutant Phk mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(9):2886–2890. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.9.2886. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan K. F., Graves D. J. Rabbit skeletal muscle phosphorylase kinase. Catalytic and regulatory properties of the active alpha gamma delta and gamma delta complexes. J Biol Chem. 1982 May 25;257(10):5948–5955. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Qasba P. K. Alkaline transfer of DNA to plastic membrane. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Jul 18;122(1):340–344. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)90480-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Church G. M., Gilbert W. Genomic sequencing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):1991–1995. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen P. T., Burchell A., Cohen P. The molecular basis of skeletal muscle phosphorylase kinase deficiency. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Jul 1;66(2):347–356. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10524.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen P. The role of protein phosphorylation in neural and hormonal control of cellular activity. Nature. 1982 Apr 15;296(5858):613–620. doi: 10.1038/296613a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen P. The subunit structure of rabbit-skeletal-muscle phosphorylase kinase, and the molecular basis of its activation reactions. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Apr 2;34(1):1–14. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb02721.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper R. H., Sul H. S., McCullough T. E., Walsh D. A. Purification and properties of the cardiac isoenzyme of phosphorylase kinase. J Biol Chem. 1980 Dec 25;255(24):11794–11801. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francke U., Lalley P. A., Moss W., Ivy J., Minna J. D. Gene mapping in Mus musculus by interspecific cell hybridization: assignment of the genes for tripeptidase-1 to chromosome 10, dipeptidase-2 to chromosome 18, acid phosphatase-1 to chromosome 12, and adenylate kinase-1 to chromosome 2. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1977;19(2-3):57–84. doi: 10.1159/000130799. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jennissen H. P., Heilmeyer L. M., Jr Multiple forms of phosphorylase kinase in red and white skeletal muscle. FEBS Lett. 1974 May 15;42(1):77–80. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(74)80283-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KREBS E. G., LOVE D. S., BRATVOLD G. E., TRAYSER K. A., MEYER W. L., FISCHER E. H. PURIFICATION AND PROPERTIES OF RABBIT SKELETAL MUSCLE PHOSPHORYLASE B KINASE. Biochemistry. 1964 Aug;3:1022–1033. doi: 10.1021/bi00896a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kilimann M. W., Zander N. F., Kuhn C. C., Crabb J. W., Meyer H. E., Heilmeyer L. M., Jr The alpha and beta subunits of phosphorylase kinase are homologous: cDNA cloning and primary structure of the beta subunit. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(24):9381–9385. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.24.9381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lalley P. A., Francke U., Minna J. D. Homologous genes for enolase, phosphogluconate dehydrogenase, phosphoglucomutase, and adenylate kinase are syntenic on mouse chromosome 4 and human chromosome 1p. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 May;75(5):2382–2386. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.5.2382. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lalley P. A., Minna J. D., Francke U. Conservation of autosomal gene synteny groups in mouse and man. Nature. 1978 Jul 13;274(5667):160–163. doi: 10.1038/274160a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawrence J. C., Jr, Krsek J. A., Salsgiver W. J., Hiken J. F., Salmons S., Smith R. L. Phosphorylase kinase isozymes in normal and electrically stimulated skeletal muscles. Am J Physiol. 1986 Jan;250(1 Pt 1):C84–C89. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1986.250.1.C84. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lederer B., Van Hoof F., Van den Berghe G., Hers H. Glycogen phosphorylase and its converter enzymes in haemolysates of normal human subjects and of patients with type VI glycogen-storage disease. A study of phosphorylase kinase deficiency. Biochem J. 1975 Apr;147(1):23–35. doi: 10.1042/bj1470023. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lederer B., van de Werve G., de Barsy T., Hers H. G. The autosomal form of phosphorylase kinase deficiency in man: reduced activity of the muscle enzyme. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 Jan 15;92(1):169–174. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(80)91535-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linzer D. I., Nathans D. Growth-related changes in specific mRNAs of cultured mouse cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(14):4271–4275. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.14.4271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyon J. B., Jr The X-chromosome and the enzymes controlling muscle glycogen: phosphorylase kinase. Biochem Genet. 1970 Feb;4(1):169–185. doi: 10.1007/BF00484028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minna J. D., Marshall T. H., Shaffer-Berman P. V. Chinese hamster X mouse hybrid cells segregating mouse chromosomes and isozymes. Somatic Cell Genet. 1975 Oct;1(4):355–369. doi: 10.1007/BF01538667. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paudel H. K., Carlson G. M. Renaturation of phosphorylase kinase activity from sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gels. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1988 Aug 1;264(2):641–646. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(88)90330-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pickett-Gies C. A., Walsh D. A. Subunit phosphorylation and activation of skeletal muscle phosphorylase kinase by the cAMP-dependent protein kinase. Divalent metal ion, ATP, and protein concentration dependence. J Biol Chem. 1985 Feb 25;260(4):2046–2056. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Servidei S., Metlay L. A., Chodosh J., DiMauro S. Fatal infantile cardiopathy caused by phosphorylase b kinase deficiency. J Pediatr. 1988 Jul;113(1 Pt 1):82–85. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(88)80535-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shenolikar S., Cohen P. T., Cohen P., Nairn A. C., Perry S. V. The role of calmodulin in the structure and regulation of phosphorylase kinase from rabbit skeletal muscle. Eur J Biochem. 1979 Oct 15;100(2):329–337. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb04175.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabuchi H., Yamamura H. Studies on glycogen phosphorylase kinase: catalytic properties and isozymes. Kobe J Med Sci. 1982 Apr;28(2):75–90. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taira T., Kii R., Sakai K., Tabuchi H., Takimoto S., Nakamura S., Takahashi J., Hashimoto E., Yamamura H., Nishizuka Y. Comparison of glycogen phosphorylase kinases of various rat tissues. J Biochem. 1982 Mar;91(3):883–888. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a133776. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood W. I., Gitschier J., Lasky L. A., Lawn R. M. Base composition-independent hybridization in tetramethylammonium chloride: a method for oligonucleotide screening of highly complex gene libraries. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Mar;82(6):1585–1588. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.6.1585. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zander N. F., Meyer H. E., Hoffmann-Posorske E., Crabb J. W., Heilmeyer L. M., Jr, Kilimann M. W. cDNA cloning and complete primary structure of skeletal muscle phosphorylase kinase (alpha subunit). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 May;85(9):2929–2933. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.9.2929. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]