Abstract
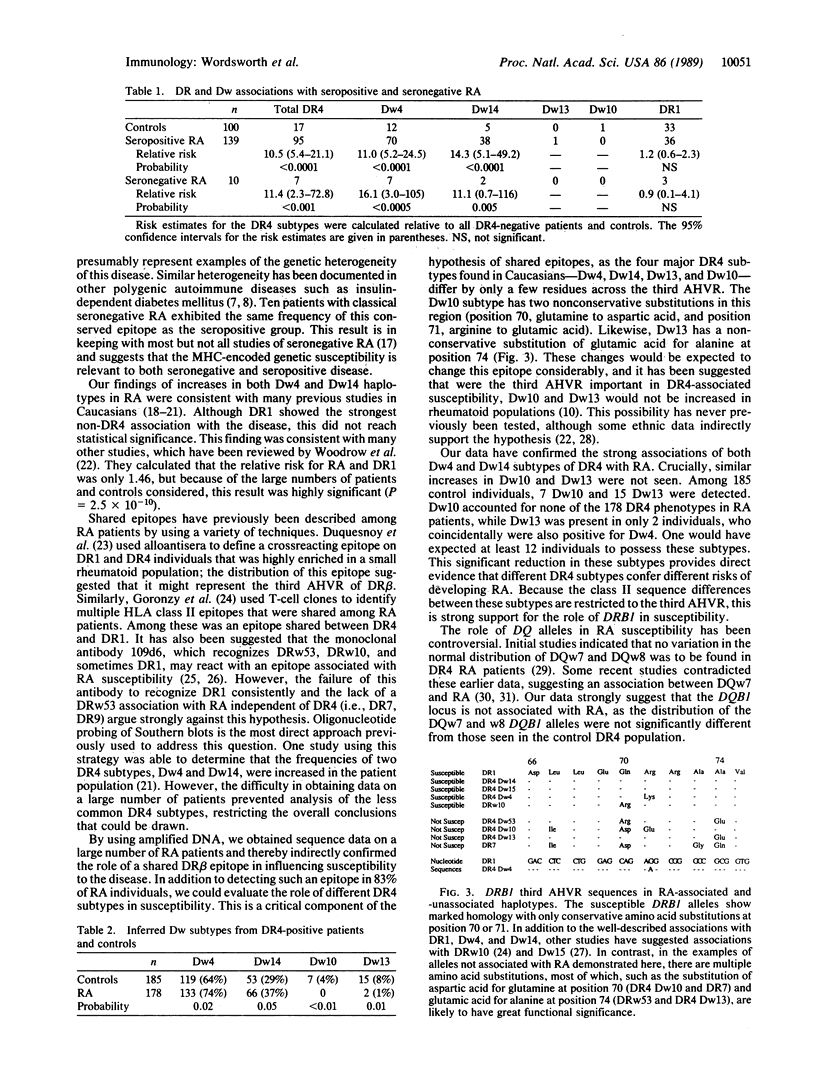
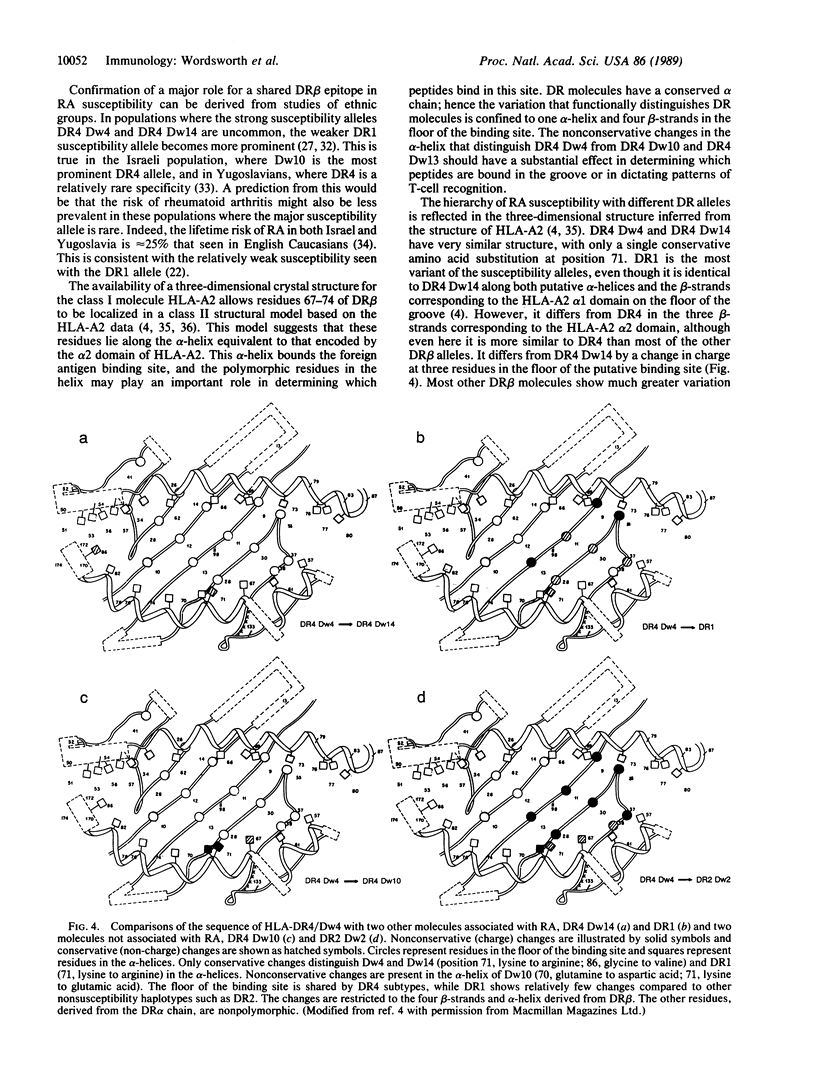
Susceptibility to rheumatoid arthritis (RA) may be due to the presence of shared functional epitopes common to the HLA-DR beta chains of several RA-associated haplotypes. We have obtained direct evidence for this hypothesis by using the polymerase chain reaction and sequencing the DRB1 and DQB1 genes from RA patients. A highly conserved epitope present on DR beta chains of DR4 and DR1 haplotypes was found in 83% of 149 patients with classical or definite RA but was found in only 46% of 100 control individuals (P less than 0.0001). Two Dw subtypes of DR4 (Dw4 and Dw14) were associated with disease susceptibility but two other subtypes (Dw10 and Dw13) were not. Sequence differences between these subtypes implicate those residues around the putative antigen binding site of the DR beta molecule in the pathogenesis of RA. These data provide a basis for understanding host susceptibility to RA at a molecular level.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bell J. I., Denney D., Jr, Foster L., Belt T., Todd J. A., McDevitt H. O. Allelic variation in the DR subregion of the human major histocompatibility complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Sep;84(17):6234–6238. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.17.6234. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell J. I., Todd J. A., McDevitt H. O. The molecular basis of HLA-disease association. Adv Hum Genet. 1989;18:1–41. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benoist C. O., Mathis D. J., Kanter M. R., Williams V. E., 2nd, McDevitt H. O. Regions of allelic hypervariability in the murine A alpha immune response gene. Cell. 1983 Aug;34(1):169–177. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90147-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bjorkman P. J., Saper M. A., Samraoui B., Bennett W. S., Strominger J. L., Wiley D. C. Structure of the human class I histocompatibility antigen, HLA-A2. Nature. 1987 Oct 8;329(6139):506–512. doi: 10.1038/329506a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bjorkman P. J., Saper M. A., Samraoui B., Bennett W. S., Strominger J. L., Wiley D. C. The foreign antigen binding site and T cell recognition regions of class I histocompatibility antigens. Nature. 1987 Oct 8;329(6139):512–518. doi: 10.1038/329512a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown J. H., Jardetzky T., Saper M. A., Samraoui B., Bjorkman P. J., Wiley D. C. A hypothetical model of the foreign antigen binding site of class II histocompatibility molecules. Nature. 1988 Apr 28;332(6167):845–850. doi: 10.1038/332845a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dobloug J. H., Førre O., Kåss E., Thorsby E. HLA antigens and rheumatoid arthritis. Association between HLA-DRw4 positivity and IgM rheumatoid factor production. Arthritis Rheum. 1980 Mar;23(3):309–313. doi: 10.1002/art.1780230307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duquesnoy R. J., Marrari M., Hackbarth S., Zeevi A. Serological and cellular definition of a new HLA-DR associated determinant, MC1, and its association with rheumatoid arthritis. Hum Immunol. 1984 Jul;10(3):165–176. doi: 10.1016/0198-8859(84)90037-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goronzy J., Weyand C. M., Fathman C. G. Shared T cell recognition sites on human histocompatibility leukocyte antigen class II molecules of patients with seropositive rheumatoid arthritis. J Clin Invest. 1986 Mar;77(3):1042–1049. doi: 10.1172/JCI112358. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorski J., Mach B. Polymorphism of human Ia antigens: gene conversion between two DR beta loci results in a new HLA-D/DR specificity. Nature. 1986 Jul 3;322(6074):67–70. doi: 10.1038/322067a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gregersen P. K., Shen M., Song Q. L., Merryman P., Degar S., Seki T., Maccari J., Goldberg D., Murphy H., Schwenzer J. Molecular diversity of HLA-DR4 haplotypes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Apr;83(8):2642–2646. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.8.2642. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gregersen P. K., Silver J., Winchester R. J. The shared epitope hypothesis. An approach to understanding the molecular genetics of susceptibility to rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1987 Nov;30(11):1205–1213. doi: 10.1002/art.1780301102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grennan D. M., Sanders P. A. Rheumatoid arthritis. Baillieres Clin Rheumatol. 1988 Dec;2(3):585–601. doi: 10.1016/s0950-3579(88)80030-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horn G. T., Bugawan T. L., Long C. M., Erlich H. A. Allelic sequence variation of the HLA-DQ loci: relationship to serology and to insulin-dependent diabetes susceptibility. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(16):6012–6016. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.16.6012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jajić Z., Jajić I. Antigens of HLA-DR locus in rheumatoid arthritis. Br J Rheumatol. 1988;27 (Suppl 2):139–140. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaraquemada D., Ollier W., Awad J., Young A., Silman A., Roitt I. M., Corbett M., Hay F., Cosh J. A., Maini R. N. HLA and rheumatoid arthritis: a combined analysis of 440 British patients. Ann Rheum Dis. 1986 Aug;45(8):627–636. doi: 10.1136/ard.45.8.627. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirwan J. R., Silman A. J. Epidemiological, sociological and environmental aspects of rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthrosis. Baillieres Clin Rheumatol. 1987 Dec;1(3):467–489. doi: 10.1016/s0950-3579(87)80041-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee S. H., Gregersen P. K., Shen H. H., Nunez-Roldan A., Silver J., Winchester R. J. Strong association of rheumatoid arthritis with the presence of a polymorphic Ia epitope defined by a monoclonal antibody: comparison with the allodeterminant DR4. Rheumatol Int. 1984;4 (Suppl):17–23. doi: 10.1007/BF00541274. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee S. H., Matsuyama T., Logalbo P., Silver J., Winchester R. J. Ia antigens and susceptibility to rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Rheum Dis. 1985 Dec;11(3):645–664. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MANTEL N., HAENSZEL W. Statistical aspects of the analysis of data from retrospective studies of disease. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1959 Apr;22(4):719–748. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMichael A. J., Sasazuki T., McDevitt H. O., Payne R. O. Increased frequency of HLA-Cw3 and HLA-Dw4 in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1977 Jun;20(5):1037–1042. doi: 10.1002/art.1780200501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nepom B. S., Palmer J., Kim S. J., Hansen J. A., Holbeck S. L., Nepom G. T. Specific genomic markers for the HLA-DQ subregion discriminate between DR4+ insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus and DR4+ seropositive juvenile rheumatoid arthritis. J Exp Med. 1986 Jul 1;164(1):345–350. doi: 10.1084/jem.164.1.345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nepom G. T., Byers P., Seyfried C., Healey L. A., Wilske K. R., Stage D., Nepom B. S. HLA genes associated with rheumatoid arthritis. Identification of susceptibility alleles using specific oligonucleotide probes. Arthritis Rheum. 1989 Jan;32(1):15–21. doi: 10.1002/anr.1780320104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nepom G. T., Seyfried C. E., Holbeck S. L., Wilske K. R., Nepom B. S. Identification of HLA-Dw14 genes in DR4+ rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet. 1986 Nov 1;2(8514):1002–1005. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(86)92614-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohta N., Nishimura Y. K., Tanimoto K., Horiuchi Y., Abe C., Shiokawa Y., Abe T., Katagiri M., Yoshiki T., Sasazuki T. Association between HLA and Japanese patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Hum Immunol. 1982 Oct;5(2):123–132. doi: 10.1016/0198-8859(82)90057-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROPES M. W., BENNETT G. A., COBB S., JACOX R., JESSAR R. A. 1958 Revision of diagnostic criteria for rheumatoid arthritis. Bull Rheum Dis. 1958 Dec;9(4):175–176. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Gelfand D. H., Stoffel S., Scharf S. J., Higuchi R., Horn G. T., Mullis K. B., Erlich H. A. Primer-directed enzymatic amplification of DNA with a thermostable DNA polymerase. Science. 1988 Jan 29;239(4839):487–491. doi: 10.1126/science.2448875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sansom D. M., Bidwell J. L., Maddison P. J., Campion G., Klouda P. T., Bradley B. A. HLA DQ alpha and DQ beta restriction fragment length polymorphisms associated with Felty's syndrome and DR4-positive rheumatoid arthritis. Hum Immunol. 1987 Aug;19(4):269–278. doi: 10.1016/0198-8859(87)90044-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schenning L., Larhammar D., Bill P., Wiman K., Jonsson A. K., Rask L., Peterson P. A. Both alpha and beta chains of HLA-DC class II histocompatibility antigens display extensive polymorphism in their amino-terminal domains. EMBO J. 1984 Feb;3(2):447–452. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01826.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiff B., Mizrachi Y., Orgad S., Yaron M., Gazit E. Association of HLA-Aw31 and HLA-DR1 with adult rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1982 Aug;41(4):403–404. doi: 10.1136/ard.41.4.403. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singal D. P., D'Souza M., Reid B., Bensen W. G., Kassam Y. B., Adachi J. D. HLA-DQ beta-chain polymorphism in HLA-DR4 haplotypes associated with rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet. 1987 Nov 14;2(8568):1118–1120. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(87)91548-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Todd J. A., Acha-Orbea H., Bell J. I., Chao N., Fronek Z., Jacob C. O., McDermott M., Sinha A. A., Timmerman L., Steinman L. A molecular basis for MHC class II--associated autoimmunity. Science. 1988 May 20;240(4855):1003–1009. doi: 10.1126/science.3368786. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Todd J. A., Bell J. I., McDevitt H. O. HLA-DQ beta gene contributes to susceptibility and resistance to insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Nature. 1987 Oct 15;329(6140):599–604. doi: 10.1038/329599a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waye M. M., Verhoeyen M. E., Jones P. T., Winter G. EcoK selection vectors for shotgun cloning into M13 and deletion mutagenesis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Dec 9;13(23):8561–8571. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.23.8561. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodrow J. C., Nichol F. E., Zaphiropoulos G. DR antigens and rheumatoid arthritis: a study of two populations. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1981 Nov 14;283(6302):1287–1288. doi: 10.1136/bmj.283.6302.1287. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]