Abstract
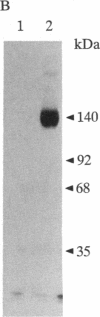
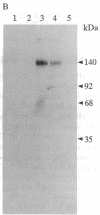
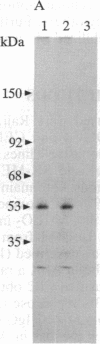
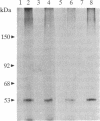
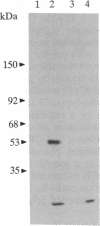
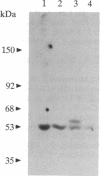
Epstein-Barr virus and the C3d fragment of the third component of complement are specific extracellular ligands for complement receptor type 2 (CR2). However, intracellular proteins that react specifically with CR2 and are involved in post-membrane signals remain unknown. We recently prepared polyclonal anti-idiotypic anti-CR2 antibodies (Ab2) by using the highly purified CR2 molecule as original immunogen. We showed that Ab2 contained anti-idiotypic specificities that mimicked extracellular domains of CR2 and detected two distinct binding sites on CR2 for its specific extracellular ligands, Epstein-Barr virus and C3d. We postulated that Ab2 might also contain specificities that could mimic intracellular domains of CR2. Here we report that Ab2, which did not react with Raji B-lymphoma cell surface components, detected specifically, among all components solubilized from Raji cell membranes, a single intracellular membrane protein of apparent molecular mass of 53 kDa. This protein was identified as the p53 cellular antioncogene-encoded membrane phosphoprotein by analyzing its antigenic properties with Pab1801, a monoclonal anti-p53 antibody, and by comparing its biochemical properties with those of p53. Additionally, solubilized and purified CR2 bound to solubilized p53 immobilized on Pab1801-Sepharose. p53, like CR2, was localized only in purified plasma membranes and nuclei of Raji cells. These data suggest strongly that p53, a cellular antioncogene-encoded phosphoprotein, reacted specifically with CR2 in Raji membranes. This interaction may represent one of the important steps through which CR2 could be involved in human B-lymphocyte proliferation and transformation.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Banks L., Matlashewski G., Crawford L. Isolation of human-p53-specific monoclonal antibodies and their use in the studies of human p53 expression. Eur J Biochem. 1986 Sep 15;159(3):529–534. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb09919.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barel M., Charriaut C., Frade R. Isolation and characterization of a C3b receptor-like molecule from membranes of a human B lymphoblastoid cell line (Raji). FEBS Lett. 1981 Dec 21;136(1):111–114. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(81)81225-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barel M., Fiandino A., Delcayre A. X., Lyamani F., Frade R. Monoclonal and anti-idiotypic anti-EBV/C3d receptor antibodies detect two binding sites, one for EBV and one for C3d on glycoprotein 140, the EBV/C3dR, expressed on human B lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1988 Sep 1;141(5):1590–1595. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barel M., Vazquez A., Charriaut C., Aufredou M. T., Galanaud P., Frade R. gp 140, the C3d/EBV receptor (CR2), is phosphorylated upon in vitro activation of human peripheral B lymphocytes. FEBS Lett. 1986 Mar 3;197(1-2):353–356. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)80356-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bijsterbosch M. K., Meade C. J., Turner G. A., Klaus G. G. B lymphocyte receptors and polyphosphoinositide degradation. Cell. 1985 Jul;41(3):999–1006. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80080-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter R. H., Spycher M. O., Ng Y. C., Hoffman R., Fearon D. T. Synergistic interaction between complement receptor type 2 and membrane IgM on B lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1988 Jul 15;141(2):457–463. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Changelian P. S., Fearon D. T. Tissue-specific phosphorylation of complement receptors CR1 and CR2. J Exp Med. 1986 Jan 1;163(1):101–115. doi: 10.1084/jem.163.1.101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coggeshall K. M., Cambier J. C. B cell activation. VIII. Membrane immunoglobulins transduce signals via activation of phosphatidylinositol hydrolysis. J Immunol. 1984 Dec;133(6):3382–3386. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crawford L. V., Pim D. C., Gurney E. G., Goodfellow P., Taylor-Papadimitriou J. Detection of a common feature in several human tumor cell lines--a 53,000-dalton protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jan;78(1):41–45. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.1.41. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delcayre A. X., Fiandino A., Barel M., Frade R. gp140, the EBV/C3d receptor (CR2) of human B lymphocytes, is involved in cell-free phosphorylation of p120, a nuclear ribonucleoprotein. Eur J Immunol. 1987 Dec;17(12):1827–1833. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830171223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delcayre A. X., Fiandino A., Lyamani F., Barel M., Frade R. Enhancement of Epstein-Barr virus/C3d receptor (EBV/C3dR or CR2) and nuclear p120 ribonucleoprotein phosphorylation by specific EBV/C3dR ligands in subcellular fractions of the human B lymphoma cell line, Raji. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Mar 31;159(3):1213–1220. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)92239-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deppert W., Haug M. Evidence for free and metabolically stable p53 protein in nuclear subfractions of simian virus 40-transformed cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jun;6(6):2233–2240. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.6.2233. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frade R., Barel M., Ehlin-Henriksson B., Klein G. gp140, the C3d receptor of human B lymphocytes, is also the Epstein-Barr virus receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Mar;82(5):1490–1493. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.5.1490. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frade R., Barel M., Krikorian L., Charriaut C. Analysis of gp 140, a C3b-binding membrane component present on Raji cells: a comparison with factor H. Eur J Immunol. 1984 Jun;14(6):542–548. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830140611. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frade R., Crevon M. C., Barel M., Vazquez A., Krikorian L., Charriaut C., Galanaud P. Enhancement of human B cell proliferation by an antibody to the C3d receptor, the gp 140 molecule. Eur J Immunol. 1985 Jan;15(1):73–76. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830150114. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frade R., Myones B. L., Barel M., Krikorian L., Charriaut C., Ross G. D. gp140, a C3b-binding membrane component of lymphocytes, is the B cell C3dg/C3d receptor (CR2) and is distinct from the neutrophil C3dg receptor (CR4). Eur J Immunol. 1985 Dec;15(12):1192–1197. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830151210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frade R. Structure and functions of gp 140, the C3d/EBV receptor (CR2) of human B lymphocytes. Mol Immunol. 1986 Nov;23(11):1249–1253. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(86)90159-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujisaku A., Harley J. B., Frank M. B., Gruner B. A., Frazier B., Holers V. M. Genomic organization and polymorphisms of the human C3d/Epstein-Barr virus receptor. J Biol Chem. 1989 Feb 5;264(4):2118–2125. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green M. R. When the products of oncogenes and anti-oncogenes meet. Cell. 1989 Jan 13;56(1):1–3. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90975-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatzfeld J., Charriaut-Marlangue C., Levesque J. P., Barel M., Stancou R., Krikorian L., Hatzfeld A., Frade R. Le C3 stimule la prolifération des cellules humaines pré-B de la lignée Raji. Ann Inst Pasteur Immunol. 1987 May-Jun;138(3):451–455. doi: 10.1016/s0769-2625(87)80055-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinds P., Finlay C., Levine A. J. Mutation is required to activate the p53 gene for cooperation with the ras oncogene and transformation. J Virol. 1989 Feb;63(2):739–746. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.2.739-746.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jay G., Khoury G., DeLeo A. B., Dippold W. G., Old L. J. p53 transformation-related protein: detection of an associated phosphotransferase activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 May;78(5):2932–2936. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.5.2932. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jörnvall H., Luka J., Klein G., Appella E. A 53-kilodalton protein common to chemically and virally transformed cells shows extensive sequence similarities between species. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jan;79(2):287–291. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.2.287. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambris J. D., Ganu V. S., Hirani S., Müller-Eberhard H. J. Mapping of the C3d receptor (CR2)-binding site and a neoantigenic site in the C3d domain of the third component of complement. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jun;82(12):4235–4239. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.12.4235. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lane D. P., Crawford L. V. T antigen is bound to a host protein in SV40-transformed cells. Nature. 1979 Mar 15;278(5701):261–263. doi: 10.1038/278261a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luka J., Jörnvall H., Klein G. Purification and biochemical characterization of the Epstein-Barr virus-determined nuclear antigen and an associated protein with a 53,000-dalton subunit. J Virol. 1980 Sep;35(3):592–602. doi: 10.1128/jvi.35.3.592-602.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masucci M. G., Szigeti R., Ernberg I., Hu C. P., Torsteinsdottir S., Frade R., Klein E. Activation of B lymphocytes by Epstein-Barr virus/CR2 receptor interaction. Eur J Immunol. 1987 Jun;17(6):815–820. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830170613. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKeel D. W., Jarett L. Preparation and characterization of a plasma membrane fraction from isolated fat cells. J Cell Biol. 1970 Feb;44(2):417–432. doi: 10.1083/jcb.44.2.417. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melchers F., Erdei A., Schulz T., Dierich M. P. Growth control of activated, synchronized murine B cells by the C3d fragment of human complement. Nature. 1985 Sep 19;317(6034):264–267. doi: 10.1038/317264a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore M. D., Cooper N. R., Tack B. F., Nemerow G. R. Molecular cloning of the cDNA encoding the Epstein-Barr virus/C3d receptor (complement receptor type 2) of human B lymphocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(24):9194–9198. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.24.9194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nadler L. M., Stashenko P., Hardy R., van Agthoven A., Terhorst C., Schlossman S. F. Characterization of a human B cell-specific antigen (B2) distinct from B1. J Immunol. 1981 May;126(5):1941–1947. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nemerow G. R., McNaughton M. E., Cooper N. R. Binding of monoclonal antibody to the Epstein Barr virus (EBV)/CR2 receptor induces activation and differentiation of human B lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1985 Nov;135(5):3068–3073. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishizuka Y. The role of protein kinase C in cell surface signal transduction and tumour promotion. Nature. 1984 Apr 19;308(5961):693–698. doi: 10.1038/308693a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinhasi-Kimhi O., Michalovitz D., Ben-Zeev A., Oren M. Specific interaction between the p53 cellular tumour antigen and major heat shock proteins. Nature. 1986 Mar 13;320(6058):182–184. doi: 10.1038/320182a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez de Córdoba S., Rubinstein P., Ferreira A. High resolution isoelectric focusing of immunoprecipitated proteins under denaturing conditions. A simple analytical method applied to the study of complement component polymorphisms. J Immunol Methods. 1984 Apr 27;69(2):165–172. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(84)90314-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rotter V., Abutbul H., Ben-Ze'ev A. P53 transformation-related protein accumulates in the nucleus of transformed fibroblasts in association with the chromatin and is found in the cytoplasm of non-transformed fibroblasts. EMBO J. 1983;2(7):1041–1047. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01543.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rotter V., Wolf D. Biological and molecular analysis of p53 cellular-encoded tumor antigen. Adv Cancer Res. 1985;43:113–141. doi: 10.1016/s0065-230x(08)60944-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarnow P., Ho Y. S., Williams J., Levine A. J. Adenovirus E1b-58kd tumor antigen and SV40 large tumor antigen are physically associated with the same 54 kd cellular protein in transformed cells. Cell. 1982 Feb;28(2):387–394. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90356-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanner J., Whang Y., Sample J., Sears A., Kieff E. Soluble gp350/220 and deletion mutant glycoproteins block Epstein-Barr virus adsorption to lymphocytes. J Virol. 1988 Dec;62(12):4452–4464. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.12.4452-4464.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weis J. J., Toothaker L. E., Smith J. A., Weis J. H., Fearon D. T. Structure of the human B lymphocyte receptor for C3d and the Epstein-Barr virus and relatedness to other members of the family of C3/C4 binding proteins. J Exp Med. 1988 Mar 1;167(3):1047–1066. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.3.1047. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]