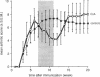
Abstract
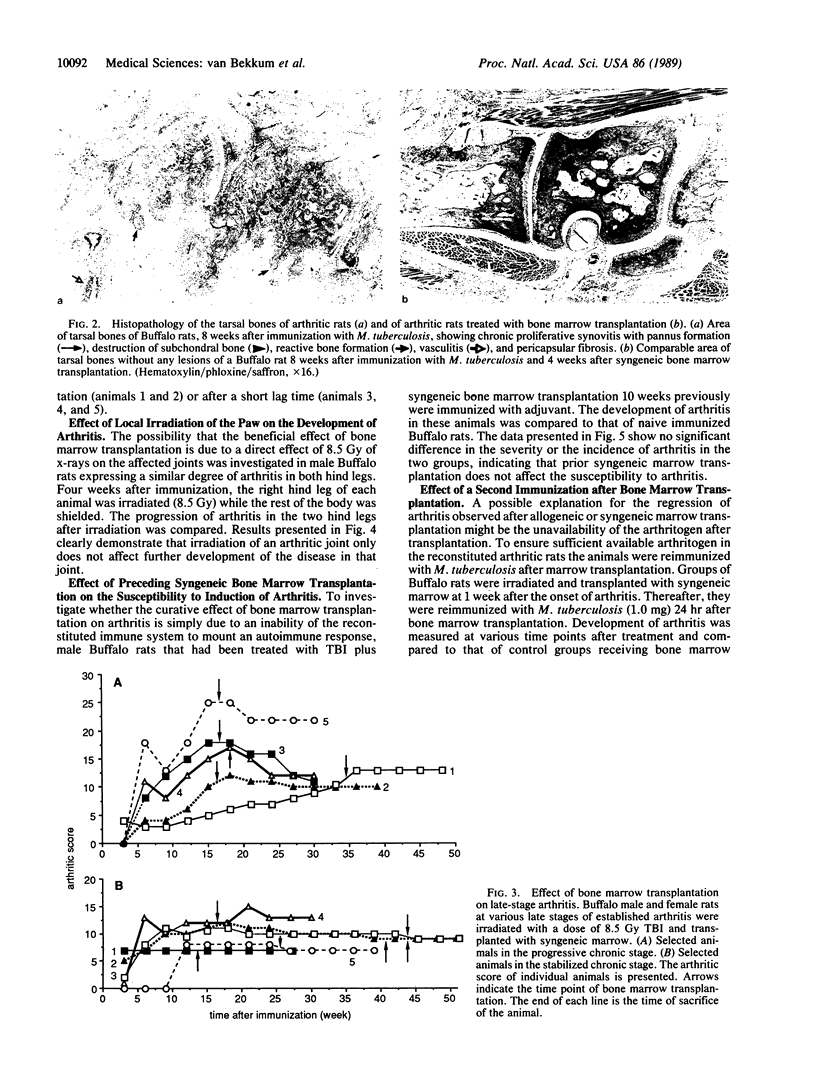
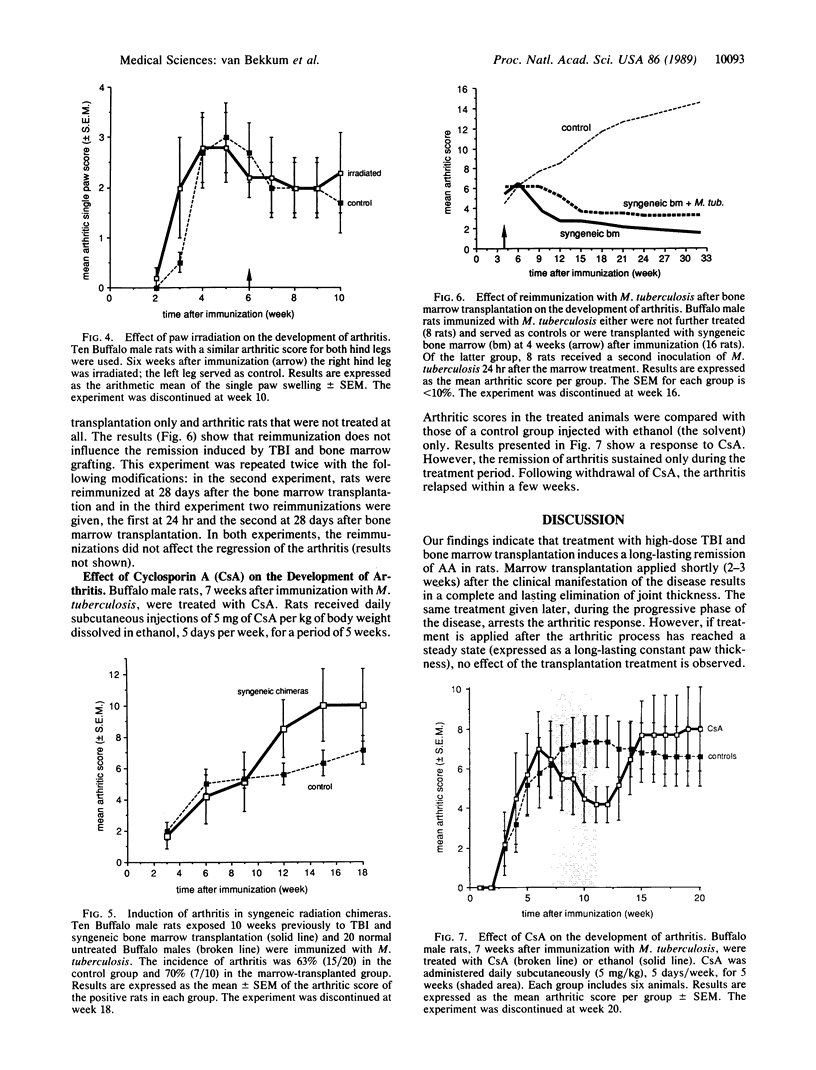
Total body irradiation followed by bone marrow transplantation was found to be an effective treatment for adjuvant arthritis induced in rats. This treatment is most effective when applied shortly after the clinical manifestation of arthritis--i.e., 4-7 weeks after administration of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Transplantation of bone marrow at a later stage results in a limited recovery, in that the inflammatory reaction regresses but the newly formed excessive bone is not eliminated. Local irradiation of the affected joints had no effect on the disease. It could also be excluded that the recovery of arthritis following marrow transplantation is due to lack of available antigen. Transplantation of syngeneic bone marrow is as effective as that of allogeneic bone marrow from a rat strain that is not susceptible to induction of adjuvant arthritis. The beneficial effect of this treatment cannot be ascribed to the immunosuppressive effect of total body irradiation, since treatment with the highly immunosuppressive drug Cyclosporin A resulted in a regression of the joint swelling but relapse occurred shortly after discontinuation of the treatment.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Argyris B. F. Suppressor activity in the spleen of neonatal mice. Cell Immunol. 1978 Mar 15;36(2):354–362. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(78)90279-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Auchincloss H., Jr, Sachs D. H. Mechanisms of tolerance in murine radiation bone marrow chimeras. I. Nonspecific suppression of alloreactivity by spleen cells from early, but not late, chimeras. Transplantation. 1983 Oct;36(4):436–441. doi: 10.1097/00007890-198310000-00016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ben-Nun A., Wekerle H., Cohen I. R. The rapid isolation of clonable antigen-specific T lymphocyte lines capable of mediating autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Eur J Immunol. 1981 Mar;11(3):195–199. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830110307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coccia P. F., Krivit W., Cervenka J., Clawson C., Kersey J. H., Kim T. H., Nesbit M. E., Ramsay N. K., Warkentin P. I., Teitelbaum S. L. Successful bone-marrow transplantation for infantile malignant osteopetrosis. N Engl J Med. 1980 Mar 27;302(13):701–708. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198003273021301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herbst M., Fritz H., Sauer R. Total lymphoid irradiation of intractable rheumatoid arthritis. Br J Radiol. 1986 Dec;59(708):1203–1207. doi: 10.1259/0007-1285-59-708-1203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holoshitz J., Naparstek Y., Ben-Nun A., Cohen I. R. Lines of T lymphocytes induce or vaccinate against autoimmune arthritis. Science. 1983 Jan 7;219(4580):56–58. doi: 10.1126/science.6336851. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs P., Vincent M. D., Martell R. W. Prolonged remission of severe refractory rheumatoid arthritis following allogeneic bone marrow transplantation for drug-induced aplastic anaemia. Bone Marrow Transplant. 1986 Dec;1(2):237–239. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janossy G., Panayi G., Duke O., Bofill M., Poulter L. W., Goldstein G. Rheumatoid arthritis: a disease of T-lymphocyte/macrophage immunoregulation. Lancet. 1981 Oct 17;2(8251):839–842. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(81)91107-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaraquemada D., Pachoula-Papasteriadis C., Festenstein H., Sachs J. A., Roitt I. M., Corbett M., Ansell B. HLA-D and DR determinants in rheumatoid arthritis. Transplant Proc. 1979 Jun;11(2):1306–1306. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kayashima K., Koga T., Onoue K. Role of T lymphocytes in adjuvant arthritis. I. Evidence for the regulatory function of thymus-derived cells in the induction of the disease. J Immunol. 1976 Nov;117(5 PT2):1878–1882. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kayashima K., Koga T., Onoue K. Role of T lymphocytes in adjuvant arthritis. II. Different subpopulations of T lymphocytes functioning in the development of the disease. J Immunol. 1978 Apr;120(4):1127–1131. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King D. P., Srober S., Kaplan H. S. Suppression of the mixed leukocyte response and of graft-vs-host disease by spleen cells following total lymphoid irradiation (TLI). J Immunol. 1981 Mar;126(3):1140–1145. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koevary S., Rossini A., Stoller W., Chick W., Williams R. M. Passive transfer of diabetes in the BB/W rat. Science. 1983 May 13;220(4598):727–728. doi: 10.1126/science.6836309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagler-Anderson C., van Vollenhoven R. F., Gurish M. F., Bober L. A., Siskind G. W., Thorbecke G. J. A cross-reactive idiotype on anti-collagen antibodies in collagen-induced arthritis: identification and relevance to disease. Cell Immunol. 1988 May;113(2):447–461. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(88)90041-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PEARSON C. M., WOOD F. D. Studies of arthritis and other lesions induced in rats by the injection of mycobacterial adjuvant. VII. Pathologic details of the arthritis and spondylitis. Am J Pathol. 1963 Jan;42:73–95. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roitt I. M., Corbett M., Festenstein H., Jaraquemada D., Papasteriadis C., Hay F. C., Nineham L. J. HLA-DRW4 and prognosis in rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet. 1978 May 6;1(8071):990–990. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(78)90280-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roubenoff R., Jones R. J., Karp J. E., Stevens M. B. Remission of rheumatoid arthritis with the successful treatment of acute myelogenous leukemia with cytosine arabinoside, daunorubicin, and m-AMSA. Arthritis Rheum. 1987 Oct;30(10):1187–1190. doi: 10.1002/art.1780301017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheven B. A., Visser J. W., Nijweide P. J. In vitro osteoclast generation from different bone marrow fractions, including a highly enriched haematopoietic stem cell population. Nature. 1986 May 1;321(6065):79–81. doi: 10.1038/321079a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwadron R. B., Gandour D. M., Strober S. Cloned natural suppressor cell lines derived from the spleens of neonatal mice. J Exp Med. 1985 Jul 1;162(1):297–310. doi: 10.1084/jem.162.1.297. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanescu R., Lider O., van Eden W., Holoshitz J., Cohen I. R. Histopathology of arthritis induced in rats by active immunization to mycobacterial antigens or by systemic transfer of T lymphocyte lines. A light and electron microscopic study of the articular surface using cationized ferritin. Arthritis Rheum. 1987 Jul;30(7):779–792. doi: 10.1002/art.1780300708. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strober S. Natural suppressor (NS) cells, neonatal tolerance, and total lymphoid irradiation: exploring obscure relationships. Annu Rev Immunol. 1984;2:219–237. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.02.040184.001251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strober S., Tanay A., Field E., Hoppe R. T., Calin A., Engleman E. G., Kotzin B., Brown B. W., Kaplan H. S. Efficacy of total lymphoid irradiation in intractable rheumatoid arthritis. A double-blind, randomized trial. Ann Intern Med. 1985 Apr;102(4):441–449. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-102-4-441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strominger J. L. Biology of the human histocompatibility leukocyte antigen (HLA) system and a hypothesis regarding the generation of autoimmune diseases. J Clin Invest. 1986 May;77(5):1411–1415. doi: 10.1172/JCI112451. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanay A., Field E. H., Hoppe R. T., Strober S. Long-term followup of rheumatoid arthritis patients treated with total lymphoid irradiation. Arthritis Rheum. 1987 Jan;30(1):1–10. doi: 10.1002/art.1780300101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taurog J. D., Sandberg G. P., Mahowald M. L. The cellular basis of adjuvant arthritis. I. Enhancement of cell-mediated passive transfer by concanavalin A and by immunosuppressive pretreatment of the recipient. Cell Immunol. 1983 Feb 1;75(2):271–282. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(83)90325-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taurog J. D., Sandberg G. P., Mahowald M. L. The cellular basis of adjuvant arthritis. II. Characterization of the cells mediating passive transfer. Cell Immunol. 1983 Aug;80(1):198–204. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(83)90106-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Bekkum D. W., Knaan-Shanzer S. Characterization of a subpopulation in neonatal thymus which suppress the graft-vs.-host reaction. Eur J Immunol. 1983 May;13(5):403–409. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830130510. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker D. G. Bone resorption restored in osteopetrotic mice by transplants of normal bone marrow and spleen cells. Science. 1975 Nov 21;190(4216):784–785. doi: 10.1126/science.1105786. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zinkernagel R. M. Major histocompatibility gene complex-disease associations may reflect T cell-mediated immunopathology. Eur J Clin Invest. 1986 Apr;16(2):101–105. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2362.1986.tb01315.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]