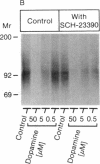
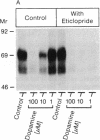
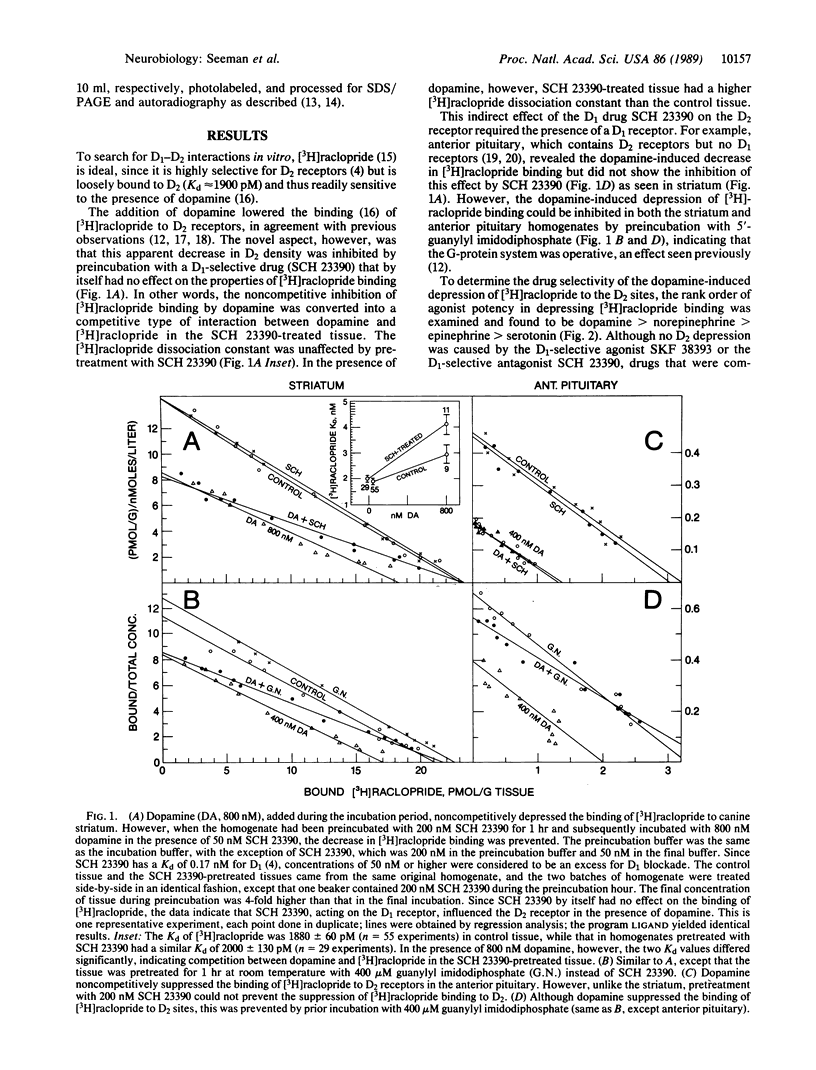
Abstract
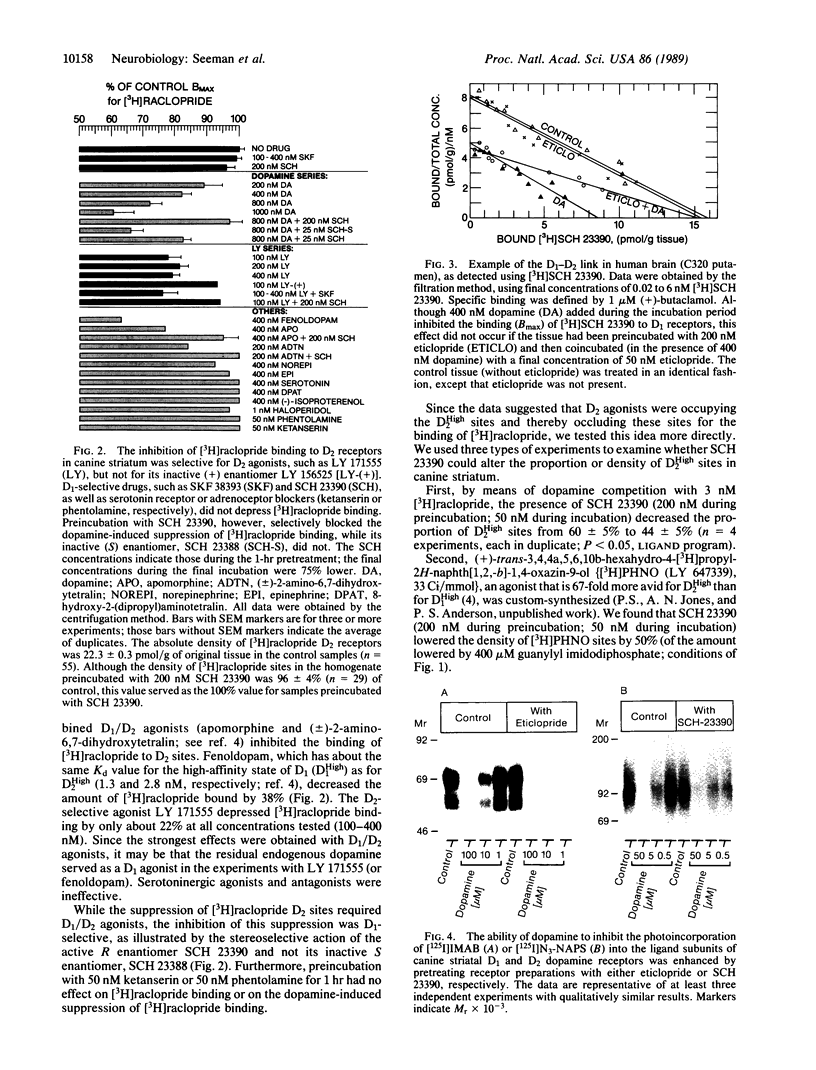
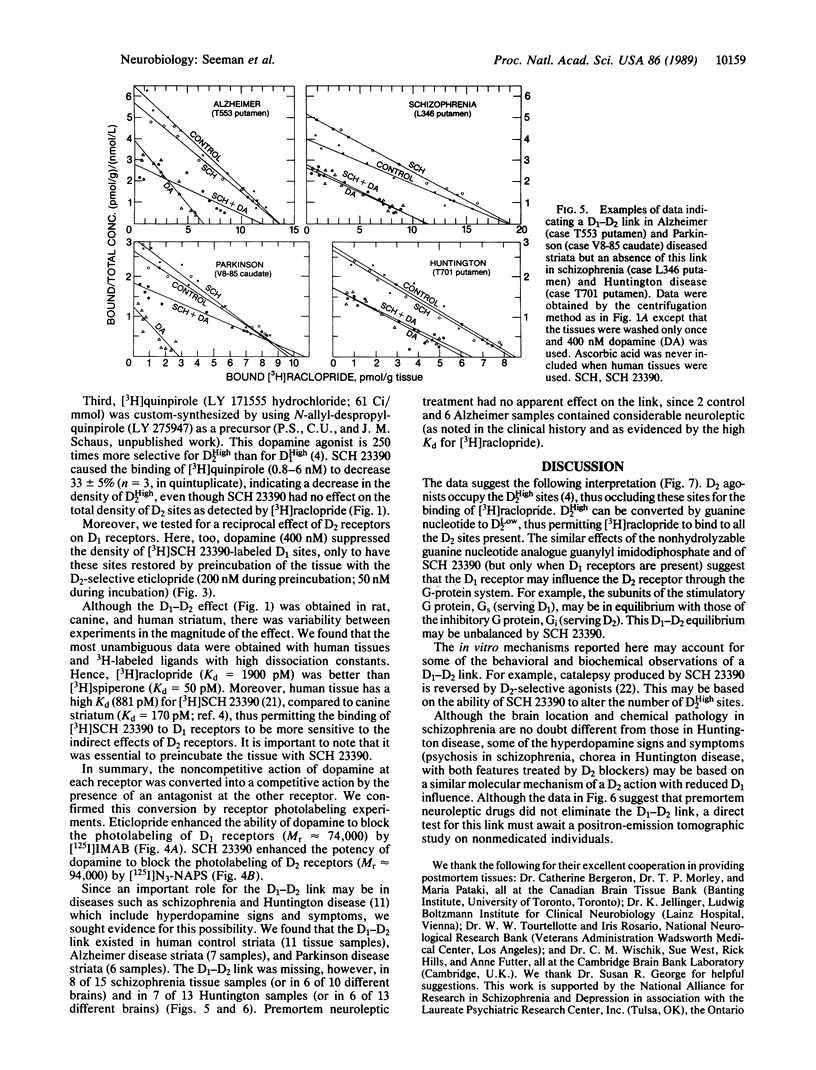
Dopamine receptor types D1 and D2 can oppose or enhance each other's actions for electrical, biochemical, and psychomotor effects. We report a D1-D2 interaction in homogenized tissue as revealed by ligand binding. D2 agonists lowered the binding of [3H]raclopride to D2 receptors in striatal and anterior pituitary tissues. Pretreating the tissue with the D1-selective antagonist SCH 23390 prevented the agonist-induced decrease in [3H]raclopride binding to D2 sites in the striatum but not in the anterior pituitary, which has no D1 receptors. Conversely, a dopamine-induced reduction in the binding of [3H]SCH 23390 to D1 receptors could be prevented by the D2-selective antagonist eticlopride. Receptor photolabeling experiments confirmed both these D1-D2 interactions. The blocking effect by SCH 23390 was similar to that produced by a nonhydrolyzable guanine nucleotide analogue, and SCH 23390 reduced the number of agonist-labeled D2 receptors in the high-affinity state. Thus, the D1-D2 link may be mediated by guanine nucleotide-binding protein components. The link may underlie D1-D2 interactions influencing behavior, since the link was missing in over half the postmortem striata from patients with schizophrenia and Huntington disease (both diseases that show some hyperdopamine signs) but was present in human control, Alzheimer, and Parkinson striata.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chatterjee T. K., Scott C. E., Vazquez D. M., Bhatnagar R. K. Interaction of [3H]spiperone with rat striatal dopamine D-2 receptors: kinetic evidence for antagonist-induced formation of ternary complex. Mol Pharmacol. 1988 Apr;33(4):402–413. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark D., White F. J. D1 dopamine receptor--the search for a function: a critical evaluation of the D1/D2 dopamine receptor classification and its functional implications. Synapse. 1987;1(4):347–388. doi: 10.1002/syn.890010408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- George S. R., Watanabe M., Seeman P. Dopamine D2 receptors in the anterior pituitary: a single population without reciprocal antagonist/agonist states. J Neurochem. 1985 Apr;44(4):1168–1177. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1985.tb08740.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gershanik O., Heikkila R. E., Duvoisin R. C. Behavioral correlations of dopamine receptor activation. Neurology. 1983 Nov;33(11):1489–1492. doi: 10.1212/wnl.33.11.1489. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilman A. G. G proteins: transducers of receptor-generated signals. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:615–649. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.003151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarvie K. R., Niznik H. B., Seeman P. Dopamine D2 receptor binding subunits of Mr congruent to 140,000 and 94,000 in brain: deglycosylation yields a common unit of Mr congruent to 44,000. Mol Pharmacol. 1988 Aug;34(2):91–97. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Köhler C., Hall H., Ogren S. O., Gawell L. Specific in vitro and in vivo binding of 3H-raclopride. A potent substituted benzamide drug with high affinity for dopamine D-2 receptors in the rat brain. Biochem Pharmacol. 1985 Jul 1;34(13):2251–2259. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(85)90778-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meller E., Kuga S., Friedhoff A. J., Goldstein M. Selective D2 dopamine receptor agonists prevent catalepsy induced by SCH 23390, a selective D1 antagonist. Life Sci. 1985 May 13;36(19):1857–1864. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(85)90159-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niznik H. B., Jarvie K. R., Bzowej N. H., Seeman P., Garlick R. K., Miller J. J., Jr, Baindur N., Neumeyer J. L. Photoaffinity labeling of dopamine D1 receptors. Biochemistry. 1988 Oct 4;27(20):7594–7599. doi: 10.1021/bi00420a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Onali P., Olianas M. C., Gessa G. L. Characterization of dopamine receptors mediating inhibition of adenylate cyclase activity in rat striatum. Mol Pharmacol. 1985 Aug;28(2):138–145. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosengarten H., Schweitzer J. W., Friedhoff A. J. Induction of oral dyskinesias in naive rats by D1 stimulation. Life Sci. 1983 Dec 19;33(25):2479–2482. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(83)90155-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rovescalli A. C., Brunello N., Monopoli A., Ongini E., Racagni G. Absence of [3H]SCH 23390 specific binding sites in anterior pituitary: dissociation from effects on prolactin secretion. Eur J Pharmacol. 1987 Mar 17;135(2):129–136. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(87)90604-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seeman P., Bzowej N. H., Guan H. C., Bergeron C., Becker L. E., Reynolds G. P., Bird E. D., Riederer P., Jellinger K., Watanabe S. Human brain dopamine receptors in children and aging adults. Synapse. 1987;1(5):399–404. doi: 10.1002/syn.890010503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seeman P., Bzowej N. H., Guan H. C., Bergeron C., Reynolds G. P., Bird E. D., Riederer P., Jellinger K., Tourtellotte W. W. Human brain D1 and D2 dopamine receptors in schizophrenia, Alzheimer's, Parkinson's, and Huntington's diseases. Neuropsychopharmacology. 1987 Dec;1(1):5–15. doi: 10.1016/0893-133x(87)90004-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sibley D. R., Creese I. Pseudo non-competitive agonist interactions with dopamine receptors. Eur J Pharmacol. 1980 Jul 11;65(1):131–133. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(80)90224-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spano P. F., Govoni S., Trabucchi M. Studies on the pharmacological properties of dopamine receptors in various areas of the central nervous system. Adv Biochem Psychopharmacol. 1978;19:155–165. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoof J. C., Kebabian J. W. Opposing roles for D-1 and D-2 dopamine receptors in efflux of cyclic AMP from rat neostriatum. Nature. 1981 Nov 26;294(5839):366–368. doi: 10.1038/294366a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Titeler M., Van Loon G. R., Seeman P., Brown G. M. D2- but not D3-dopamine receptors detected in the anterior pituitary. Eur J Pharmacol. 1981 Apr 24;71(1):143–146. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(81)90398-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walters J. R., Bergstrom D. A., Carlson J. H., Chase T. N., Braun A. R. D1 dopamine receptor activation required for postsynaptic expression of D2 agonist effects. Science. 1987 May 8;236(4802):719–722. doi: 10.1126/science.2953072. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]