Abstract
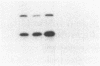
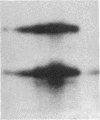
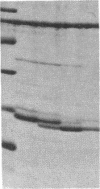
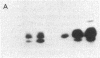
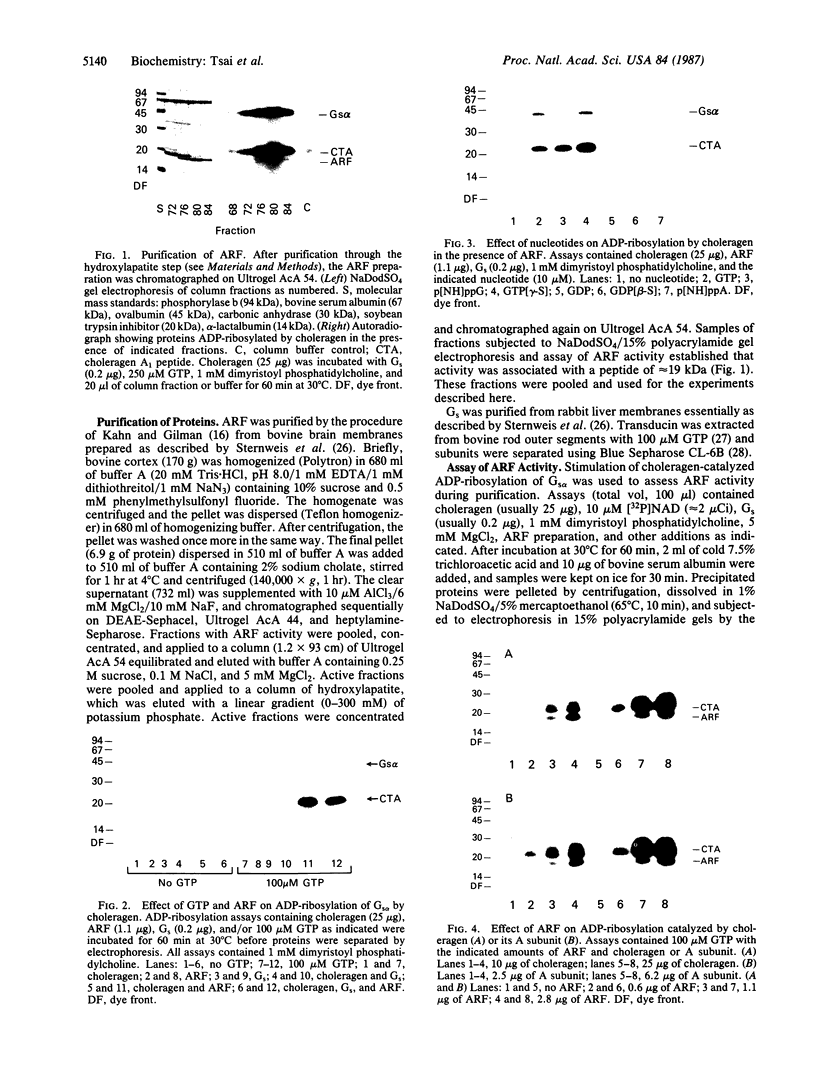
Choleragen activates adenylate cyclase by catalyzing, in the presence of NAD, the ADP-ribosylation of Gs alpha, the stimulatory guanyl nucleotide-binding protein of the cyclase system. Kahn and Gilman [Kahn, R. A. & Gilman, A. G. (1986) J. Biol. Chem. 261, 7906-7911] identified another guanyl nucleotide-binding protein termed ADP-ribosylation factor (ARF) that stimulated this reaction. It was proposed that the toxin substrate is an ARF-Gs alpha complex and that ARF may have a physiological role in regulation of Gs alpha activity. We have found that purified ARF from bovine brain enhances not only the ADP-ribosylation of Gs alpha but also Gs alpha-independent choleragen-catalyzed reactions. These are (i) ADP-ribosylation of agmatine, a low molecular weight guanidino compound; (ii) ADP-ribosylation of several proteins unrelated to Gs alpha; and (iii) auto-ADP-ribosylation of the toxin A1 peptide. These reactions, as well as the ADP-ribosylation of ARF itself, were stimulated by GTP or stable GTP analogues such as guanyl-5'-yl imido-beta gamma-diphosphate and guanosine 5'-O-[gamma-thio]triphosphate; GDP and guanosine 5'-O-[beta-thio]diphosphate were inactive. These observations are consistent with the conclusion that ARF interacts directly with the A subunit of choleragen in a GTP-dependent fashion thereby enhancing catalytic activity manifest as transfer of ADP-ribose to Gs alpha and other proteins, to the toxin A1 peptide, or to agmatine. It is tempting to speculate that ARF may be involved in regulating one or another of the ADP-ribosyltransferases found in animal cells.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cassel D., Selinger Z. Mechanism of adenylate cyclase activation by cholera toxin: inhibition of GTP hydrolysis at the regulatory site. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Aug;74(8):3307–3311. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.8.3307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enomoto K., Gill D. M. Cholera toxin activation of adenylate cyclase. Roles of nucleoside triphosphates and a macromolecular factor in the ADP ribosylation of the GTP-dependent regulatory component. J Biol Chem. 1980 Feb 25;255(4):1252–1258. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enomoto K., Gill D. M. Requirement for guanosine triphosphate in the activation of adenylate cyclase by cholera toxin. J Supramol Struct. 1979;10(1):51–60. doi: 10.1002/jss.400100106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill D. M., Meren R. A second guanyl nucleotide-binding site associated with adenylate cyclase. Distinct nucleotides activate adenylate cyclase and permit ADP-ribosylation by cholera toxin. J Biol Chem. 1983 Oct 10;258(19):11908–11914. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilman A. G. Guanine nucleotide-binding regulatory proteins and dual control of adenylate cyclase. J Clin Invest. 1984 Jan;73(1):1–4. doi: 10.1172/JCI111179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayaishi O., Ueda K. Poly(ADP-ribose) and ADP-ribosylation of proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1977;46:95–116. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.46.070177.000523. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hildebrandt J. D., Codina J., Risinger R., Birnbaumer L. Identification of a gamma subunit associated with the adenylyl cyclase regulatory proteins Ns and Ni. J Biol Chem. 1984 Feb 25;259(4):2039–2042. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn R. A., Gilman A. G. ADP-ribosylation of Gs promotes the dissociation of its alpha and beta subunits. J Biol Chem. 1984 May 25;259(10):6235–6240. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn R. A., Gilman A. G. Purification of a protein cofactor required for ADP-ribosylation of the stimulatory regulatory component of adenylate cyclase by cholera toxin. J Biol Chem. 1984 May 25;259(10):6228–6234. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn R. A., Gilman A. G. The protein cofactor necessary for ADP-ribosylation of Gs by cholera toxin is itself a GTP binding protein. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jun 15;261(17):7906–7911. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kühn H. Light- and GTP-regulated interaction of GTPase and other proteins with bovine photoreceptor membranes. Nature. 1980 Feb 7;283(5747):587–589. doi: 10.1038/283587a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Vine H., 3rd, Cuatrecasas P. Activation of pigeon erythrocyte adenylate cyclase by cholera toxin. Partial purification of an essential macromolecular factor from horse erythrocyte cytosol. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Feb 5;672(3):248–261. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(81)90291-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lefkowitz R. J., Caron M. G., Stiles G. L. Mechanisms of membrane-receptor regulation. Biochemical, physiological, and clinical insights derived from studies of the adrenergic receptors. N Engl J Med. 1984 Jun 14;310(24):1570–1579. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198406143102406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin M. C., Welton A. F., Berman M. F. Essential role of GTP in the expression of adenylate cyclase activity after cholera toxin treatment. J Cyclic Nucleotide Res. 1978 Jun;4(3):159–168. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss J., Manganiello V. C., Vaughan M. Hydrolysis of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide by choleragen and its A protomer: possible role in the activation of adenylate cyclase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Dec;73(12):4424–4427. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.12.4424. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss J., Stanley S. J., Watkins P. A., Vaughan M. ADP-ribosyltransferase activity of mono- and multi-(ADP-ribosylated) choleragen. J Biol Chem. 1980 Aug 25;255(16):7835–7837. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss J., Vaughan M. Isolation of an avian erythrocyte protein possessing ADP-ribosyltransferase activity and capable of activating adenylate cyclase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Aug;75(8):3621–3624. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.8.3621. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss J., Vaughan M. Mechanism of action of choleragen. Evidence for ADP-ribosyltransferase activity with arginine as an acceptor. J Biol Chem. 1977 Apr 10;252(7):2455–2457. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakaya S., Moss J., Vaughan M. Effects of nucleoside triphosphates on choleragen-activated brain adenylate cyclase. Biochemistry. 1980 Oct 14;19(21):4871–4874. doi: 10.1021/bi00562a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Northup J. K., Sternweis P. C., Gilman A. G. The subunits of the stimulatory regulatory component of adenylate cyclase. Resolution, activity, and properties of the 35,000-dalton (beta) subunit. J Biol Chem. 1983 Sep 25;258(18):11361–11368. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinkett M. O., Anderson W. B. Plasma membrane-associated component(s) that confer(s) cholera toxin sensitivity to adenylate cyclase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Feb 2;714(2):337–343. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(82)90342-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schleifer L. S., Kahn R. A., Hanski E., Northup J. K., Sternweis P. C., Gilman A. G. Requirements for cholera toxin-dependent ADP-ribosylation of the purified regulatory component of adenylate cyclase. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jan 10;257(1):20–23. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinozawa T., Uchida S., Martin E., Cafiso D., Hubbell W., Bitensky M. Additional component required for activity and reconstitution of light-activated vertebrate photoreceptor GTPase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Mar;77(3):1408–1411. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.3.1408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sternweis P. C., Northup J. K., Smigel M. D., Gilman A. G. The regulatory component of adenylate cyclase. Purification and properties. J Biol Chem. 1981 Nov 25;256(22):11517–11526. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watkins P. A., Moss J., Vaughan M. Effects of GTP on choleragen-catalyzed ADP ribosylation of membrane and soluble proteins. J Biol Chem. 1980 May 10;255(9):3959–3963. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ZATMAN L. J., KAPLAN N. O., COLOWICK S. P. Inhibition of spleen diphosphopyridine nucleotidase by nicotinamide, an exchange reaction. J Biol Chem. 1953 Jan;200(1):197–212. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]