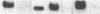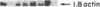Abstract
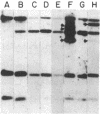
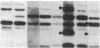
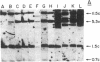
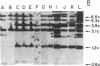
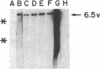
Analyses of the cellular and viral Kirsten ras genes (c-Ki-ras and v-Ki-ras, respectively) during malignant tumor progression were performed by using Kirsten murine sarcoma virus-transformed BALB/c 3T3 cells that harbor a replication-defective provirus. After injection into athymic nude mice by four different routes, primary tumors and secondary lung metastases were isolated, adapted to in vitro growth, and analyzed for DNA levels and mRNA expression of both genes for comparison with the originally injected transformed cells and untransformed 3T3 cells. For all tumors (primary or secondary), the v-Ki-ras gene was amplified and v-Ki-ras mRNA expression was highly elevated above that observed in the original transformed cell population. In two of five lung metastases from the i.v. and footpad injection routes, rearranged Ki-ras DNA sequences were observed. Micrometastases from the s.c. route of injection did not display these alterations. Injection of footpad lung tumor cells with rearrangements into a second group of animals led to multiple lung metastases with even further rearrangements correlating with more effective lung colonization/growth ability (overt lung tumors in five of eight animals less than 20 days after injection). However, reinjection of an i.v. lung tumor with rearranged Ki-ras led to no further rearrangements in the lung microfoci tumors isolated greater than 40 days after injection. These data suggest (i) the significance of amplification and elevated expression of v-Ki-ras in tumor formation, (ii) correlation of this amplification with more effective tumor progression, and (iii) the selective advantage that cells with Ki-ras DNA sequence additions have in the formation of overt lung tumors.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aaronson S. A., Rowe S. P. Nonproducer clones of murine sarcoma virus transformed BALB-3T3 cells. Virology. 1970 Sep;42(1):9–19. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(70)90233-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernstein S. C., Weinberg R. A. Expression of the metastatic phenotype in cells transfected with human metastatic tumor DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Mar;82(6):1726–1730. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.6.1726. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop J. M. Viral oncogenes. Cell. 1985 Aug;42(1):23–38. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80098-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Egan S. E., McClarty G. A., Jarolim L., Wright J. A., Spiro I., Hager G., Greenberg A. H. Expression of H-ras correlates with metastatic potential: evidence for direct regulation of the metastatic phenotype in 10T1/2 and NIH 3T3 cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Feb;7(2):830–837. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.2.830. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis R. W., DeFeo D., Furth M. E., Scolnick E. M. Mouse cells contain two distinct ras gene mRNA species that can be translated into a p21 onc protein. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Nov;2(11):1339–1345. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.11.1339. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis R. W., Defeo D., Shih T. Y., Gonda M. A., Young H. A., Tsuchida N., Lowy D. R., Scolnick E. M. The p21 src genes of Harvey and Kirsten sarcoma viruses originate from divergent members of a family of normal vertebrate genes. Nature. 1981 Aug 6;292(5823):506–511. doi: 10.1038/292506a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- George D. L., Scott A. F., Trusko S., Glick B., Ford E., Dorney D. J. Structure and expression of amplified cKi-ras gene sequences in Y1 mouse adrenal tumor cells. EMBO J. 1985 May;4(5):1199–1203. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03760.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goff S., Traktman P., Baltimore D. Isolation and properties of Moloney murine leukemia virus mutants: use of a rapid assay for release of virion reverse transcriptase. J Virol. 1981 Apr;38(1):239–248. doi: 10.1128/jvi.38.1.239-248.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greig R. G., Koestler T. P., Trainer D. L., Corwin S. P., Miles L., Kline T., Sweet R., Yokoyama S., Poste G. Tumorigenic and metastatic properties of "normal" and ras-transfected NIH/3T3 cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jun;82(11):3698–3701. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.11.3698. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HARVEY J. J. AN UNIDENTIFIED VIRUS WHICH CAUSES THE RAPID PRODUCTION OF TUMOURS IN MICE. Nature. 1964 Dec 12;204:1104–1105. doi: 10.1038/2041104b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein G. Specific chromosomal translocations and the genesis of B-cell-derived tumors in mice and men. Cell. 1983 Feb;32(2):311–315. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90449-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Land H., Chen A. C., Morgenstern J. P., Parada L. F., Weinberg R. A. Behavior of myc and ras oncogenes in transformation of rat embryo fibroblasts. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jun;6(6):1917–1925. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.6.1917. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyvisch C. Influence of implantation site on formation of metastases. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 1983;2(3):295–306. doi: 10.1007/BF00048482. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miketo L. J., Culp L. A. Proteoglycans from the substratum adhesion sites of MSV-transformed BALB/c 3T3 cells. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1983 Mar;221(2):447–457. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(83)90163-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muschel R. J., Williams J. E., Lowy D. R., Liotta L. A. Harvey ras induction of metastatic potential depends upon oncogene activation and the type of recipient cell. Am J Pathol. 1985 Oct;121(1):1–8. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicolson G. L., Brunson K. W., Fidler I. J. Specificity of arrest, survival, and growth of selected metastatic variant cell lines. Cancer Res. 1978 Nov;38(11 Pt 2):4105–4111. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicolson G. L. Tumor progression, oncogenes and the evolution of metastatic phenotypic diversity. Clin Exp Metastasis. 1984 Apr-Jun;2(2):85–105. doi: 10.1007/BF00052411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsen T. W., Maroney P. A., Goodwin R. G., Rottman F. M., Crittenden L. B., Raines M. A., Kung H. J. c-erbB activation in ALV-induced erythroblastosis: novel RNA processing and promoter insertion result in expression of an amino-truncated EGF receptor. Cell. 1985 Jul;41(3):719–726. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80052-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nowell P. C. Mechanisms of tumor progression. Cancer Res. 1986 May;46(5):2203–2207. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pozzatti R., Muschel R., Williams J., Padmanabhan R., Howard B., Liotta L., Khoury G. Primary rat embryo cells transformed by one or two oncogenes show different metastatic potentials. Science. 1986 Apr 11;232(4747):223–227. doi: 10.1126/science.3456644. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raines M. A., Lewis W. G., Crittenden L. B., Kung H. J. c-erbB activation in avian leukosis virus-induced erythroblastosis: clustered integration sites and the arrangement of provirus in the c-erbB alleles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Apr;82(8):2287–2291. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.8.2287. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakaguchi A. Y., Lalley P. A., Zabel B. U., Ellis R. W., Scolnick E. M., Naylor S. L. Chromosome assignments of four mouse cellular homologs of sarcoma and leukemia virus oncogenes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jan;81(2):525–529. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.2.525. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santos E., Reddy E. P., Pulciani S., Feldmann R. J., Barbacid M. Spontaneous activation of a human proto-oncogene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Aug;80(15):4679–4683. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.15.4679. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shen-Ong G. L., Keath E. J., Piccoli S. P., Cole M. D. Novel myc oncogene RNA from abortive immunoglobulin-gene recombination in mouse plasmacytomas. Cell. 1982 Dec;31(2 Pt 1):443–452. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90137-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorgeirsson U. P., Turpeenniemi-Hujanen T., Williams J. E., Westin E. H., Heilman C. A., Talmadge J. E., Liotta L. A. NIH/3T3 cells transfected with human tumor DNA containing activated ras oncogenes express the metastatic phenotype in nude mice. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Jan;5(1):259–262. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.1.259. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wells R. S., Campbell E. W., Swartzendruber D. E., Holland L. M., Kraemer P. M. Role of anchorage in the expression of tumorigenicity of untransformed mouse cell lines. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1982 Aug;69(2):415–423. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]