Abstract
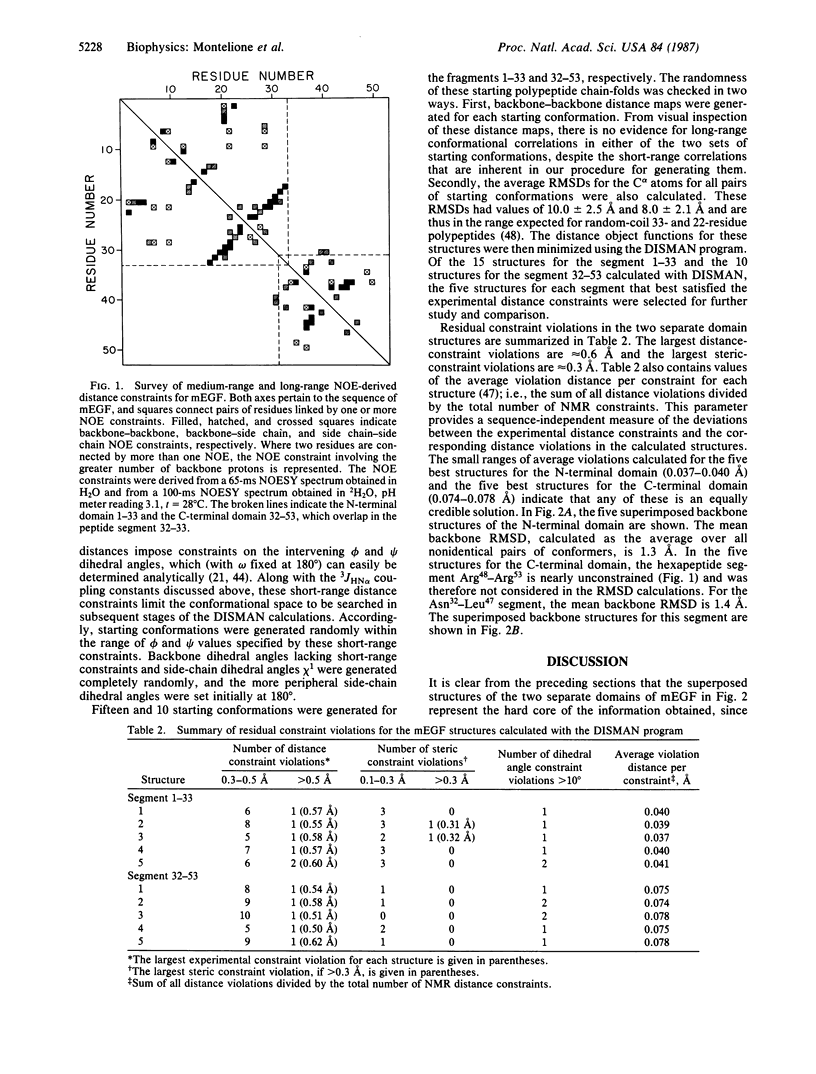
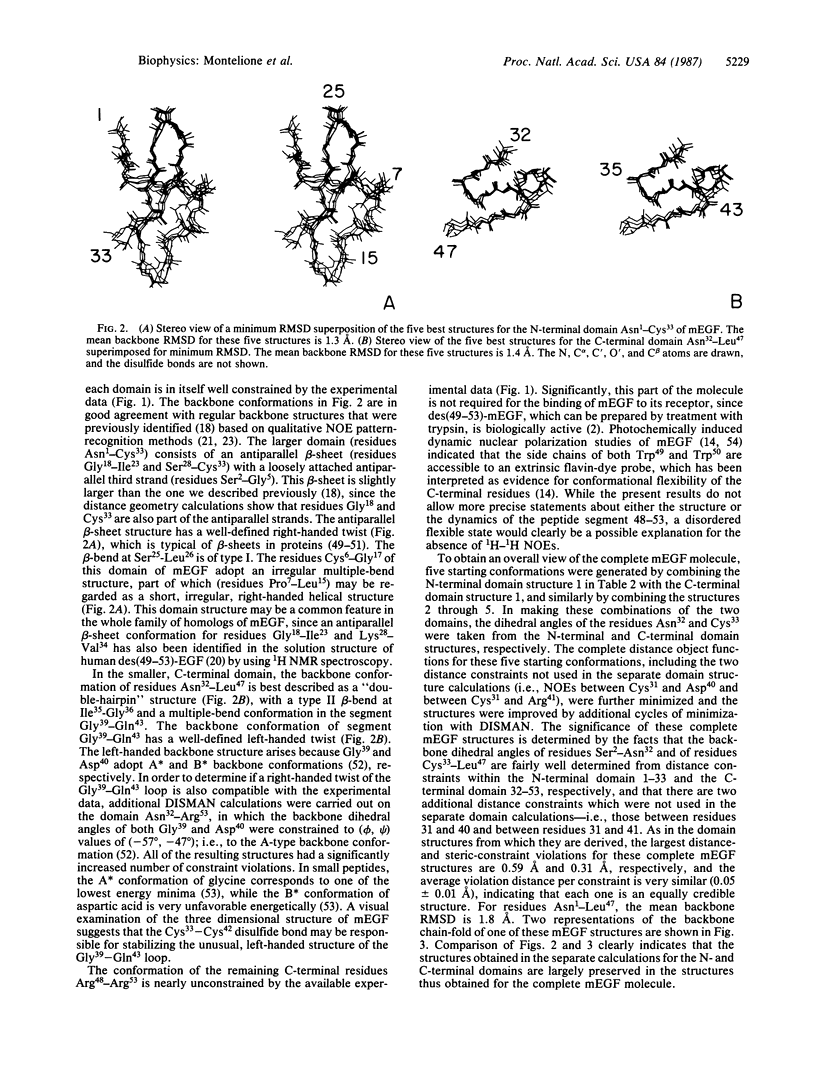
The polypeptide backbone fold in the solution structure of murine epidermal growth factor has been determined by nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy and distance geometry calculations. The results are based on nearly complete sequence-specific resonance assignments and on 333 distance and dihedral-angle constraints; these were determined from nuclear Overhauser effect measurements, identification of hydrogen-bonded amide protons, the known locations of disulfide bonds, and backbone vicinal spin-spin coupling constants. The polypeptide chain of the protein is arranged into two distinct domains. The structures of these domains were determined independently in separate calculations and then combined to obtain an overall view of the protein. The backbone fold thus determined includes the regular backbone structure elements that were previously identified using different techniques for the analysis of the nuclear magnetic resonance data. The distance geometry calculations also provided additional details about the conformations of bends and loops and about the twists of the beta-sheets.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Billeter M., Braun W., Wüthrich K. Sequential resonance assignments in protein 1H nuclear magnetic resonance spectra. Computation of sterically allowed proton-proton distances and statistical analysis of proton-proton distances in single crystal protein conformations. J Mol Biol. 1982 Mar 5;155(3):321–346. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90008-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun W., Go N. Calculation of protein conformations by proton-proton distance constraints. A new efficient algorithm. J Mol Biol. 1985 Dec 5;186(3):611–626. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90134-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buckley A., Davidson J. M., Kamerath C. D., Wolt T. B., Woodward S. C. Sustained release of epidermal growth factor accelerates wound repair. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Nov;82(21):7340–7344. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.21.7340. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgess A. W., Knesel J., Sparrow L. G., Nicola N. A., Nice E. C. Two forms of murine epidermal growth factor: rapid separation by using reverse-phase HPLC. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Oct;79(19):5753–5757. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.19.5753. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgess A. W., Lloyd C. J., Nice E. C. Murine epidermal growth factor: heterogeneity on high resolution ion-exchange chromatography. EMBO J. 1983;2(11):2065–2069. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01701.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COHEN S. Isolation of a mouse submaxillary gland protein accelerating incisor eruption and eyelid opening in the new-born animal. J Biol Chem. 1962 May;237:1555–1562. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carver J. A., Cooke R. M., Esposito G., Campbell I. D., Gregory H., Sheard B. A high resolution 1H NMR study of the solution structure of human epidermal growth factor. FEBS Lett. 1986 Sep 1;205(1):77–81. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)80869-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chothia C. Conformation of twisted beta-pleated sheets in proteins. J Mol Biol. 1973 Apr 5;75(2):295–302. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90022-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou K. C., Pottle M., Némethy G., Ueda Y., Scheraga H. A. Structure of beta-sheets. Origin of the right-handed twist and of the increased stability of antiparallel over parallel sheets. J Mol Biol. 1982 Nov 25;162(1):89–112. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90163-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Marco A., Mayo K. H., Bartolotti F., Scalia S., Menegatti E., Kaptein R. Proton NMR and photochemically induced dynamic nuclear polarization studies of peptide fragments obtained by controlled proteolysis of mouse epidermal growth factor. J Biol Chem. 1986 Oct 15;261(29):13510–13516. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eppstein D. A., Marsh Y. V., Schreiber A. B., Newman S. R., Todaro G. J., Nestor J. J., Jr Epidermal growth factor receptor occupancy inhibits vaccinia virus infection. Nature. 1985 Dec 19;318(6047):663–665. doi: 10.1038/318663a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heath W. F., Merrifield R. B. A synthetic approach to structure-function relationships in the murine epidermal growth factor molecule. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(17):6367–6371. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.17.6367. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kline A. D., Braun W., Wüthrich K. Studies by 1H nuclear magnetic resonance and distance geometry of the solution conformation of the alpha-amylase inhibitor tendamistat. J Mol Biol. 1986 May 20;189(2):377–382. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90519-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch J. H., Fifis T., Bender V. J., Moss B. A. Molecular species of epidermal growth factor carrying immunosuppressive activity. J Cell Biochem. 1984;25(1):45–59. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240250105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Komoriya A., Hortsch M., Meyers C., Smith M., Kanety H., Schlessinger J. Biologically active synthetic fragments of epidermal growth factor: localization of a major receptor-binding region. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Mar;81(5):1351–1355. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.5.1351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumar A., Ernst R. R., Wüthrich K. A two-dimensional nuclear Overhauser enhancement (2D NOE) experiment for the elucidation of complete proton-proton cross-relaxation networks in biological macromolecules. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 Jul 16;95(1):1–6. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(80)90695-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marion D., Wüthrich K. Application of phase sensitive two-dimensional correlated spectroscopy (COSY) for measurements of 1H-1H spin-spin coupling constants in proteins. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Jun 29;113(3):967–974. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)91093-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayo K. H., De Marco A., Kaptein R. Photo-CIDNP nuclear magnetic resonance as a probe for conformational changes in epidermal growth factor. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Nov 21;874(2):181–186. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(86)90116-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayo K. H. Epidermal growth factor from the mouse. Physical evidence for a tiered beta-sheet domain: two-dimensional NMR correlated spectroscopy and nuclear Overhauser experiments on backbone amide protons. Biochemistry. 1985 Jul 2;24(14):3783–3794. doi: 10.1021/bi00335a055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayo K. H. Epidermal growth factor from the mouse. Structural characterization by proton nuclear magnetic resonance and nuclear overhauser experiments at 500 MHz. Biochemistry. 1984 Aug 14;23(17):3960–3973. doi: 10.1021/bi00312a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayo K. H., Schaudies P., Savage C. R., De Marco A., Kaptein R. Structural characterization and exposure of aromatic residues in epidermal growth factor from the rat. Biochem J. 1986 Oct 1;239(1):13–18. doi: 10.1042/bj2390013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLachlan A. D. How alike are the shapes of two random chains? Biopolymers. 1984 Jul;23(7):1325–1331. doi: 10.1002/bip.360230716. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meinwald Y. C., Stimson E. R., Scheraga H. A. Deamidation of the asparaginyl-glycyl sequence. Int J Pept Protein Res. 1986 Jul;28(1):79–84. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-3011.1986.tb03231.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montelione G. T., Wüthrich K., Nice E. C., Burgess A. W., Scheraga H. A. Identification of two anti-parallel beta-sheet conformations in the solution structure of murine epidermal growth factor by proton magnetic resonance. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Nov;83(22):8594–8598. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.22.8594. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nestor J. J., Jr, Newman S. R., DeLustro B., Todaro G. J., Schreiber A. B. A synthetic fragment of rat transforming growth factor alpha with receptor binding and antigenic properties. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 May 31;129(1):226–232. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)91426-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neuhaus D., Wagner G., Vasák M., Kägi J. H., Wüthrich K. Systematic application of high-resolution, phase-sensitive two-dimensional 1H-NMR techniques for the identification of the amino-acid-proton spin systems in proteins. Rabbit metallothionein-2. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Sep 2;151(2):257–273. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb09096.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oka T., Sakamoto S., Miyoshi K., Fuwa T., Yoda K., Yamasaki M., Tamura G., Miyake T. Synthesis and secretion of human epidermal growth factor by Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Nov;82(21):7212–7216. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.21.7212. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pardi A., Billeter M., Wüthrich K. Calibration of the angular dependence of the amide proton-C alpha proton coupling constants, 3JHN alpha, in a globular protein. Use of 3JHN alpha for identification of helical secondary structure. J Mol Biol. 1984 Dec 15;180(3):741–751. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90035-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson J. S. The anatomy and taxonomy of protein structure. Adv Protein Chem. 1981;34:167–339. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3233(08)60520-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savage C. R., Jr, Hash J. H., Cohen S. Epidermal growth factor. Location of disulfide bonds. J Biol Chem. 1973 Nov 25;248(22):7669–7672. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savage C. R., Jr, Inagami T., Cohen S. The primary structure of epidermal growth factor. J Biol Chem. 1972 Dec 10;247(23):7612–7621. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J., Cook E., Fotheringham I., Pheby S., Derbyshire R., Eaton M. A., Doel M., Lilley D. M., Pardon J. F., Patel T. Chemical synthesis and cloning of a gene for human beta-urogastrone. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Aug 11;10(15):4467–4482. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.15.4467. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sporn M. B., Roberts A. B. Autocrine growth factors and cancer. 1985 Feb 28-Mar 6Nature. 313(6005):745–747. doi: 10.1038/313745a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sporn M. B., Todaro G. J. Autocrine secretion and malignant transformation of cells. N Engl J Med. 1980 Oct 9;303(15):878–880. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198010093031511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thannhauser T. W., Scheraga H. A. Reversible blocking of half-cystine residues of proteins and an irreversible specific deamidation of asparagine-67 of S-sulforibonuclease under mild conditions. Biochemistry. 1985 Dec 17;24(26):7681–7688. doi: 10.1021/bi00347a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urdea M. S., Merryweather J. P., Mullenbach G. T., Coit D., Heberlein U., Valenzuela P., Barr P. J. Chemical synthesis of a gene for human epidermal growth factor urogastrone and its expression in yeast. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Dec;80(24):7461–7465. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.24.7461. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williamson M. P., Havel T. F., Wüthrich K. Solution conformation of proteinase inhibitor IIA from bull seminal plasma by 1H nuclear magnetic resonance and distance geometry. J Mol Biol. 1985 Mar 20;182(2):295–315. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90347-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wüthrich K., Billeter M., Braun W. Polypeptide secondary structure determination by nuclear magnetic resonance observation of short proton-proton distances. J Mol Biol. 1984 Dec 15;180(3):715–740. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90034-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wüthrich K., Billeter M., Braun W. Pseudo-structures for the 20 common amino acids for use in studies of protein conformations by measurements of intramolecular proton-proton distance constraints with nuclear magnetic resonance. J Mol Biol. 1983 Oct 5;169(4):949–961. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80144-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wüthrich K., Wider G., Wagner G., Braun W. Sequential resonance assignments as a basis for determination of spatial protein structures by high resolution proton nuclear magnetic resonance. J Mol Biol. 1982 Mar 5;155(3):311–319. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90007-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmerman S. S., Pottle M. S., Némethy G., Scheraga H. A. Conformational analysis of the 20 naturally occurring amino acid residues using ECEPP. Macromolecules. 1977 Jan-Feb;10(1):1–9. doi: 10.1021/ma60055a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


