Abstract
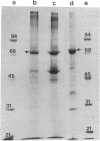
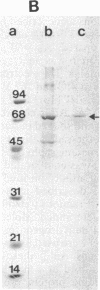
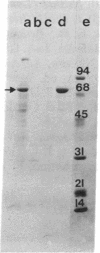
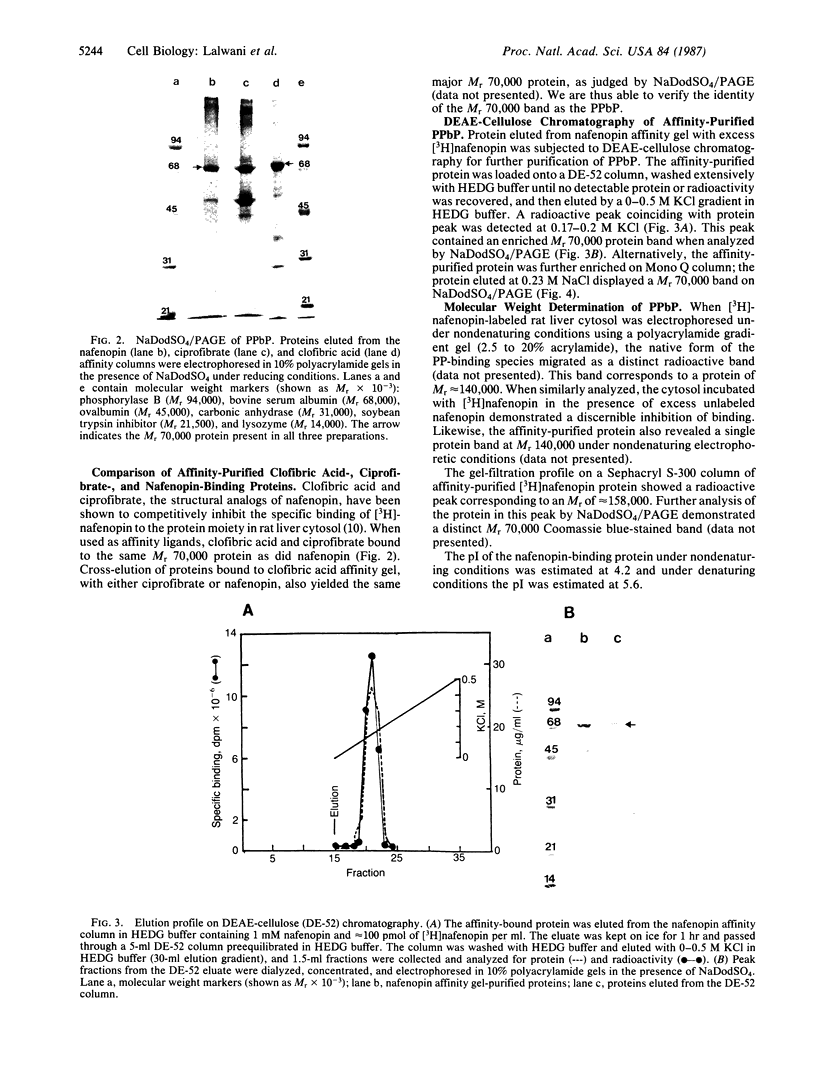
Peroxisome proliferators (PP) induce a highly predictable pleiotropic response in rat and mouse liver that is characterized by hepatomegaly, increase in peroxisome number in hepatocytes, and induction of certain peroxisomal enzymes. The PP-binding protein (PPbP) was purified from rat liver cytosol by a two-step procedure involving affinity chromatography and ion-exchange chromatography. Three PP, nafenopin and its structural analogs clofibric acid and ciprofibrate, were used as affinity ligands and eluting agents. This procedure yields a major protein with an apparent Mr of 70,000 on NaDodSO4/PAGE in the presence of reducing agent and Mr 140,000 (Mr 140,000-160,000) on gel filtration and polyacrylamide gradient gel electrophoresis under nondenaturing conditions, indicating that the active protein is a dimer. This protein has an acidic pI of 4.2 under nondenaturing conditions, which rises to 5.6 under denaturing conditions. The isolation of the same Mr 70,000 protein with three different, but structurally related, agents as affinity ligands and the immunological identity of the isolated proteins constitute strong evidence that this protein is the PPbP capable of recognizing PP that are structurally related to clofibrate. The PPbP probably plays an important role in the regulation of PP-induced pleiotropic response.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown M. S., Goldstein J. L. A receptor-mediated pathway for cholesterol homeostasis. Science. 1986 Apr 4;232(4746):34–47. doi: 10.1126/science.3513311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erickson J. S., Mathews C. K. T4 bacteriophage-specific dihydrofolate reductase: purification to homogeneity by affinity chromatography. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1971 Jun 4;43(5):1164–1170. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(71)90585-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hashimoto T. Individual peroxisomal beta-oxidation enzymes. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1982;386:5–12. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1982.tb21403.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hess R., Stäubli W., Riess W. Nature of the hepatomegalic effect produced by ethyl-chlorophenoxy-isobutyrate in the rat. Nature. 1965 Nov 27;208(5013):856–858. doi: 10.1038/208856a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lalwani N. D., Fahl W. E., Reddy J. K. Detection of a nafenopin-binding protein in rat liver cytosol associated with the induction of peroxisome proliferation by hypolipidemic compounds. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Oct 31;116(2):388–393. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)90534-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazarow P. B. Rat liver peroxisomes catalyze the beta oxidation of fatty acids. J Biol Chem. 1978 Mar 10;253(5):1522–1528. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):4007–4021. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poland A., Glover E., Ebetino F. H., Kende A. S. Photoaffinity labeling of the Ah receptor. J Biol Chem. 1986 May 15;261(14):6352–6365. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddy J. K., Azarnoff D. L., Hignite C. E. Hypolipidaemic hepatic peroxisome proliferators form a novel class of chemical carcinogens. Nature. 1980 Jan 24;283(5745):397–398. doi: 10.1038/283397a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddy J. K., Goel S. K., Nemali M. R., Carrino J. J., Laffler T. G., Reddy M. K., Sperbeck S. J., Osumi T., Hashimoto T., Lalwani N. D. Transcription regulation of peroxisomal fatty acyl-CoA oxidase and enoyl-CoA hydratase/3-hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydrogenase in rat liver by peroxisome proliferators. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(6):1747–1751. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.6.1747. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddy J. K., Krishnakantha T. P. Hepatic peroxisome proliferation: induction by two novel compounds structurally unrelated to clofibrate. Science. 1975 Nov 21;190(4216):787–789. doi: 10.1126/science.1198095. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddy J. K., Warren J. R., Reddy M. K., Lalwani N. D. Hepatic and renal effects of peroxisome proliferators: biological implications. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1982;386:81–110. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1982.tb21409.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto K. R. Steroid receptor regulated transcription of specific genes and gene networks. Annu Rev Genet. 1985;19:209–252. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.19.120185.001233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]