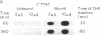Abstract
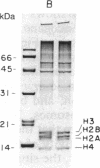
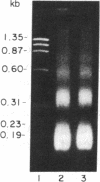
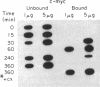
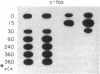
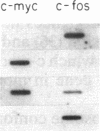
A procedure for the isolation of transcriptionally active nucleosomes was used to monitor changes in chromatin structure during the activation, repression, and superinduction of the protooncogenes c-fos and c-myc. Nuclei were isolated from murine fibroblasts at successive times after stimulation of quiescent cell cultures with serum or platelet-derived growth factor. The nucleosomes released by a brief micrococcal nuclease digestion were fractionated by HgII-affinity chromatography to separate the unfolded nucleosomes of transcriptionally active genes (in which the sulfhydryl groups of histone H3 are accessible for binding to HgII) from the compactly beaded nucleosomes of transcriptionally inert DNA sequences (in which the H3 sulfhydryl groups are not accessible). The DNA sequence contents of the HgII-bound and unbound nucleosome fractions were compared by slot-blot hybridizations to 32P-labeled cloned probes for c-fos and c-myc. The binding of the c-fos and c-myc nucleosomes to the HgII column accurately reflected both the timing and the degree of their expression, as determined by run-off transcription assays with the isolated nuclei. The superinduction of c-fos and c-myc expression by an inhibitor of protein synthesis (cycloheximide) was reflected in the persistence of the unfolded, transcriptionally active state of their component nucleosomes. These results provide direct evidence that rapid and reversible changes in nucleosome topography accompany the program of oncogene expression, and they suggest a way to monitor aberrant gene activity during malignant transformation.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bloom K. S., Anderson J. N. Fractionation of hen oviduct chromatin into transcriptionally active and inactive regions after selective micrococcal nuclease digestion. Cell. 1978 Sep;15(1):141–150. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90090-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bode J., Henco K., Wingender E. Modulation of the nucleosome structure by histone acetylation. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Sep;110(1):143–152. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb04849.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bravo R., Burckhardt J., Curran T., Müller R. Expression of c-fos in NIH3T3 cells is very low but inducible throughout the cell cycle. EMBO J. 1986 Apr;5(4):695–700. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04269.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burlingame R. W., Love W. E., Wang B. C., Hamlin R., Nguyen H. X., Moudrianakis E. N. Crystallographic structure of the octameric histone core of the nucleosome at a resolution of 3.3 A. Science. 1985 May 3;228(4699):546–553. doi: 10.1126/science.3983639. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camerini-Otero R. D., Felsenfeld G. Histone H3 disulfide dimers and nucleosome structure. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5519–5523. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5519. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campisi J., Gray H. E., Pardee A. B., Dean M., Sonenshein G. E. Cell-cycle control of c-myc but not c-ras expression is lost following chemical transformation. Cell. 1984 Feb;36(2):241–247. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90217-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chung J., Sinn E., Reed R. R., Leder P. Trans-acting elements modulate expression of the human c-myc gene in Burkitt lymphoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Oct;83(20):7918–7922. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.20.7918. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cochran B. H., Zullo J., Verma I. M., Stiles C. D. Expression of the c-fos gene and of an fos-related gene is stimulated by platelet-derived growth factor. Science. 1984 Nov 30;226(4678):1080–1082. doi: 10.1126/science.6093261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dani C., Blanchard J. M., Piechaczyk M., El Sabouty S., Marty L., Jeanteur P. Extreme instability of myc mRNA in normal and transformed human cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Nov;81(22):7046–7050. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.22.7046. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dieterich A. E., Axel R., Cantor C. R. Dynamics of nucleosome structure studied by fluorescence. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1978;42(Pt 1):199–206. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1978.042.01.022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dyson P. J., Littlewood T. D., Forster A., Rabbitts T. H. Chromatin structure of transcriptionally active and inactive human c-myc alleles. EMBO J. 1985 Nov;4(11):2885–2891. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04018.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eick D., Piechaczyk M., Henglein B., Blanchard J. M., Traub B., Kofler E., Wiest S., Lenoir G. M., Bornkamm G. W. Aberrant c-myc RNAs of Burkitt's lymphoma cells have longer half-lives. EMBO J. 1985 Dec 30;4(13B):3717–3725. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04140.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eshaghpour H., Dieterich A. E., Cantor C. R., Crothers D. M. Singlet-singlet energy transfer studies of the internal organization of nucleosomes. Biochemistry. 1980 Apr 29;19(9):1797–1805. doi: 10.1021/bi00550a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fahrlander P. D., Piechaczyk M., Marcu K. B. Chromatin structure of the murine c-myc locus: implications for the regulation of normal and chromosomally translocated genes. EMBO J. 1985 Dec 1;4(12):3195–3202. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04065.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feo S., ar-Rushdi A., Huebner K., Finan J., Nowell P. C., Clarkson B., Croce C. M. Suppression of the normal mouse c-myc oncogene in human lymphoma cells. Nature. 1985 Feb 7;313(6002):493–495. doi: 10.1038/313493a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg M. E., Hermanowski A. L., Ziff E. B. Effect of protein synthesis inhibitors on growth factor activation of c-fos, c-myc, and actin gene transcription. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Apr;6(4):1050–1057. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.4.1050. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg M. E., Ziff E. B. Stimulation of 3T3 cells induces transcription of the c-fos proto-oncogene. Nature. 1984 Oct 4;311(5985):433–438. doi: 10.1038/311433a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groudine M., Peretz M., Weintraub H. Transcriptional regulation of hemoglobin switching in chicken embryos. Mol Cell Biol. 1981 Mar;1(3):281–288. doi: 10.1128/mcb.1.3.281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly K., Cochran B. H., Stiles C. D., Leder P. Cell-specific regulation of the c-myc gene by lymphocyte mitogens and platelet-derived growth factor. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(3 Pt 2):603–610. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90092-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kruijer W., Cooper J. A., Hunter T., Verma I. M. Platelet-derived growth factor induces rapid but transient expression of the c-fos gene and protein. Nature. 1984 Dec 20;312(5996):711–716. doi: 10.1038/312711a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maniatis T., Jeffrey A., van deSande H. Chain length determination of small double- and single-stranded DNA molecules by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Biochemistry. 1975 Aug 26;14(17):3787–3794. doi: 10.1021/bi00688a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCormack J. E., Pepe V. H., Kent R. B., Dean M., Marshak-Rothstein A., Sonenshein G. E. Specific regulation of c-myc oncogene expression in a murine B-cell lymphoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Sep;81(17):5546–5550. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.17.5546. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mirzabekov A. D., Shick V. V., Belyavsky A. V., Bavykin S. G. Primary organization of nucleosome core particle of chromatin: sequence of histone arrangement along DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Sep;75(9):4184–4188. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.9.4184. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell R. L., Zokas L., Schreiber R. D., Verma I. M. Rapid induction of the expression of proto-oncogene fos during human monocytic differentiation. Cell. 1985 Jan;40(1):209–217. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90324-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller R., Bravo R., Burckhardt J., Curran T. Induction of c-fos gene and protein by growth factors precedes activation of c-myc. Nature. 1984 Dec 20;312(5996):716–720. doi: 10.1038/312716a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson D., Covault J., Chalkley R. Segregation of rapidly acetylated histones into a chromatin fraction released from intact nuclei by the action of micrococcal nuclease. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Apr 25;8(8):1745–1763. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.8.1745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piechaczyk M., Yang J. Q., Blanchard J. M., Jeanteur P., Marcu K. B. Posttranscriptional mechanisms are responsible for accumulation of truncated c-myc RNAs in murine plasma cell tumors. Cell. 1985 Sep;42(2):589–597. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90116-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prior C. P., Cantor C. R., Johnson E. M., Allfrey V. G. Incorporation of exogenous pyrene-labeled histone into Physarum chromatin: a system for studying changes in nucleosomes assembled in vivo. Cell. 1980 Jul;20(3):597–608. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90306-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prior C. P., Cantor C. R., Johnson E. M., Littau V. C., Allfrey V. G. Reversible changes in nucleosome structure and histone H3 accessibility in transcriptionally active and inactive states of rDNA chromatin. Cell. 1983 Oct;34(3):1033–1042. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90561-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabbitts P. H., Forster A., Stinson M. A., Rabbitts T. H. Truncation of exon 1 from the c-myc gene results in prolonged c-myc mRNa stability. EMBO J. 1985 Dec 30;4(13B):3727–3733. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04141.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Renz M., Neuberg M., Kurz C., Bravo R., Müller R. Regulation of c-fos transcription in mouse fibroblasts: identification of DNase I-hypersensitive sites and regulatory upstream sequences. EMBO J. 1985 Dec 30;4(13B):3711–3716. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04139.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richmond T. J., Finch J. T., Rushton B., Rhodes D., Klug A. Structure of the nucleosome core particle at 7 A resolution. Nature. 1984 Oct 11;311(5986):532–537. doi: 10.1038/311532a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saito H., Hayday A. C., Wiman K., Hayward W. S., Tonegawa S. Activation of the c-myc gene by translocation: a model for translational control. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Dec;80(24):7476–7480. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.24.7476. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schubach W., Groudine M. Alteration of c-myc chromatin structure by avian leukosis virus integration. Nature. 1984 Feb 23;307(5953):702–708. doi: 10.1038/307702a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siebenlist U., Hennighausen L., Battey J., Leder P. Chromatin structure and protein binding in the putative regulatory region of the c-myc gene in Burkitt lymphoma. Cell. 1984 Jun;37(2):381–391. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90368-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treisman R. Identification of a protein-binding site that mediates transcriptional response of the c-fos gene to serum factors. Cell. 1986 Aug 15;46(4):567–574. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90882-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treisman R. Transient accumulation of c-fos RNA following serum stimulation requires a conserved 5' element and c-fos 3' sequences. Cell. 1985 Oct;42(3):889–902. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90285-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuan D., London I. M. Mapping of DNase I-hypersensitive sites in the upstream DNA of human embryonic epsilon-globin gene in K562 leukemia cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 May;81(9):2718–2722. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.9.2718. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiman K. G., Clarkson B., Hayday A. C., Saito H., Tonegawa S., Hayward W. S. Activation of a translocated c-myc gene: role of structural alterations in the upstream region. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Nov;81(21):6798–6802. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.21.6798. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong N. T., Candido E. P. Histone H3 thiol reactivity as a probe of nucleosome structure. J Biol Chem. 1978 Nov 25;253(22):8263–8268. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zama M., Olins D. E., Wilkinson-Singley E., Olins A. L. Reversibility of nucleosome conformation perturbed by urea. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Dec 29;85(4):1446–1452. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)91165-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]