Abstract
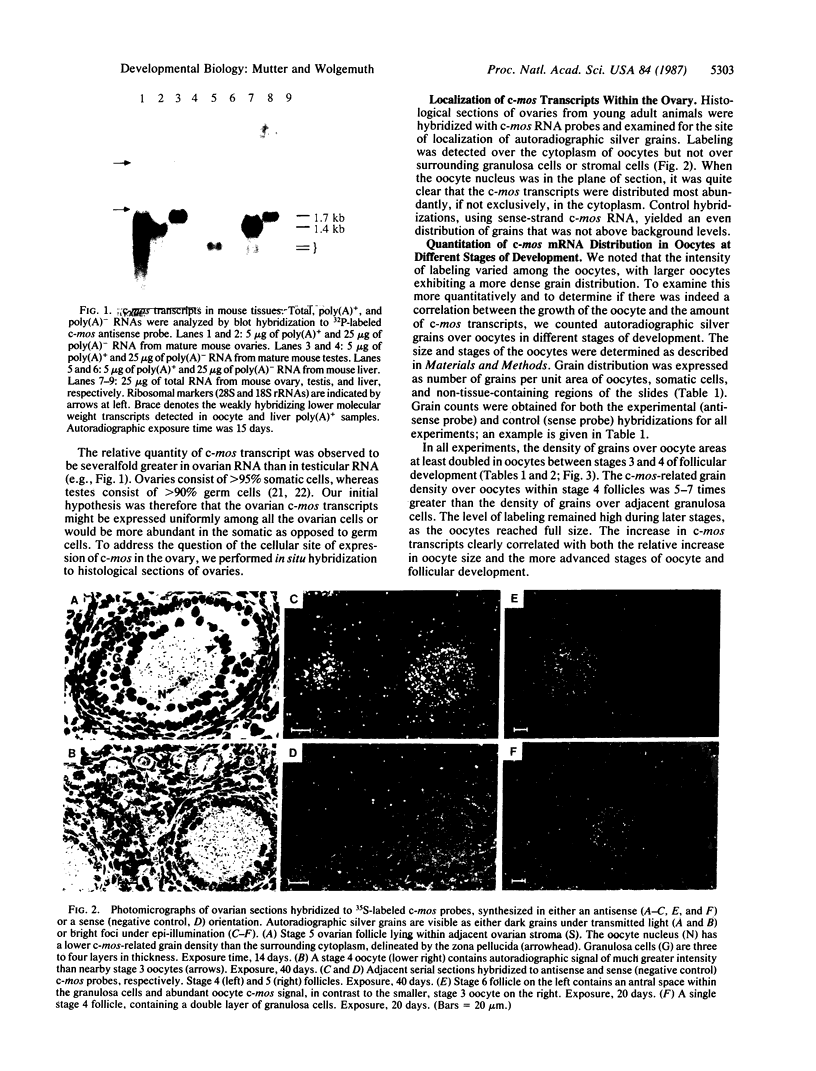
The protooncogene c-mos is expressed in murine reproductive tissues, producing transcripts of 1.7 and 1.4 kilobases in testis and ovary, respectively. In situ hybridization analysis of c-mos expression in histological sections of mouse ovaries revealed that oocytes are the predominant if not exclusive source of c-mos transcripts. c-mos transcripts accumulate in growing oocytes, increasing 40- to 90-fold during oocyte and follicular development. c-mos transcripts were also detected in male germ cells and are most abundant after the cells have entered the haploid stage of spermatogenesis. This developmentally regulated pattern of c-mos expression in oocytes and spermatogenic cells suggests that the c-mos gene product may have a function in normal germ-cell differentiation or early embryogenesis.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aviv H., Leder P. Purification of biologically active globin messenger RNA by chromatography on oligothymidylic acid-cellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jun;69(6):1408–1412. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.6.1408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bachvarova R., De Leon V., Johnson A., Kaplan G., Paynton B. V. Changes in total RNA, polyadenylated RNA, and actin mRNA during meiotic maturation of mouse oocytes. Dev Biol. 1985 Apr;108(2):325–331. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(85)90036-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bachvarova R., De Leon V. Polyadenylated RNA of mouse ova and loss of maternal RNA in early development. Dev Biol. 1980 Jan;74(1):1–8. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(80)90048-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brower P. T., Gizang E., Boreen S. M., Schultz R. M. Biochemical studies of mammalian oogenesis: synthesis and stability of various classes of RNA during growth of the mouse oocyte in vitro. Dev Biol. 1981 Sep;86(2):373–383. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(81)90195-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cathala G., Savouret J. F., Mendez B., West B. L., Karin M., Martial J. A., Baxter J. D. A method for isolation of intact, translationally active ribonucleic acid. DNA. 1983;2(4):329–335. doi: 10.1089/dna.1983.2.329. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman D. S., Kiessling A. A., Millette C. F., Cooper G. M. Expression of c-mos RNA in germ cells of male and female mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jul;84(13):4509–4513. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.13.4509. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goustin A. S., Betsholtz C., Pfeifer-Ohlsson S., Persson H., Rydnert J., Bywater M., Holmgren G., Heldin C. H., Westermark B., Ohlsson R. Coexpression of the sis and myc proto-oncogenes in developing human placenta suggests autocrine control of trophoblast growth. Cell. 1985 May;41(1):301–312. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90083-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jakobovits A., Shackleford G. M., Varmus H. E., Martin G. R. Two proto-oncogenes implicated in mammary carcinogenesis, int-1 and int-2, are independently regulated during mouse development. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Oct;83(20):7806–7810. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.20.7806. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan G., Abreu S. L., Bachvarova R. rRNA accumulation and protein synthetic patterns in growing mouse oocytes. J Exp Zool. 1982 May 1;220(3):361–370. doi: 10.1002/jez.1402200311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meistrich M. L., Bruce W. R., Clermont Y. Cellular composition of fractions of mouse testis cells following velocity sedimentation separation. Exp Cell Res. 1973 Apr;79(1):213–227. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller R., Slamon D. J., Tremblay J. M., Cline M. J., Verma I. M. Differential expression of cellular oncogenes during pre- and postnatal development of the mouse. Nature. 1982 Oct 14;299(5884):640–644. doi: 10.1038/299640a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller R., Tremblay J. M., Adamson E. D., Verma I. M. Tissue and cell type-specific expression of two human c-onc genes. Nature. 1983 Aug 4;304(5925):454–456. doi: 10.1038/304454a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller R., Verma I. M., Adamson E. D. Expression of c-onc genes: c-fos transcripts accumulate to high levels during development of mouse placenta, yolk sac and amnion. EMBO J. 1983;2(5):679–684. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01484.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogiso Y., Matsumoto M., Morita T., Nishino H., Iwashima A., Matsushiro A. Expression of c-mos proto-oncogene in undifferentiated teratocarcinoma cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Oct 30;140(2):477–484. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(86)90757-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oskarsson M., McClements W. L., Blair D. G., Maizel J. V., Vande Woude G. F. Properties of a normal mouse cell DNA sequence (sarc) homologous to the src sequence of Moloney sarcoma virus. Science. 1980 Mar 14;207(4436):1222–1224. doi: 10.1126/science.6243788. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedersen T., Peters H. Proposal for a classification of oocytes and follicles in the mouse ovary. J Reprod Fertil. 1968 Dec;17(3):555–557. doi: 10.1530/jrf.0.0170555. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters H. The development of the mouse ovary from birth to maturity. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1969 Sep;62(1):98–116. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.0620098. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeifer-Ohlsson S., Goustin A. S., Rydnert J., Wahlström T., Bjersing L., Stehelin D., Ohlsson R. Spatial and temporal pattern of cellular myc oncogene expression in developing human placenta: implications for embryonic cell proliferation. Cell. 1984 Sep;38(2):585–596. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90513-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pikó L., Clegg K. B. Quantitative changes in total RNA, total poly(A), and ribosomes in early mouse embryos. Dev Biol. 1982 Feb;89(2):362–378. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(82)90325-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pikó L., Hammons M. D., Taylor K. D. Amounts, synthesis, and some properties of intracisternal A particle-related RNA in early mouse embryos. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jan;81(2):488–492. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.2.488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ponzetto C., Wolgemuth D. J. Haploid expression of a unique c-abl transcript in the mouse male germ line. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Jul;5(7):1791–1794. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.7.1791. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Propst F., Rosenberg M. P., Iyer A., Kaul K., Vande Woude G. F. c-mos proto-oncogene RNA transcripts in mouse tissues: structural features, developmental regulation, and localization in specific cell types. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 May;7(5):1629–1637. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.5.1629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Propst F., Vande Woude G. F. Expression of c-mos proto-oncogene transcripts in mouse tissues. Nature. 1985 Jun 6;315(6019):516–518. doi: 10.1038/315516a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slamon D. J., Cline M. J. Expression of cellular oncogenes during embryonic and fetal development of the mouse. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Nov;81(22):7141–7145. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.22.7141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sternlicht A. L., Schultz R. M. Biochemical studies of mammalian oogenesis: kinetics of accumulation of total and poly(A)-containing RNA during growth of the mouse oocyte. J Exp Zool. 1981 Feb;215(2):191–200. doi: 10.1002/jez.1402150209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahl G. M., Stern M., Stark G. R. Efficient transfer of large DNA fragments from agarose gels to diazobenzyloxymethyl-paper and rapid hybridization by using dextran sulfate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Aug;76(8):3683–3687. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.8.3683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolgemuth D. J., Gizang-Ginsberg E., Engelmyer E., Gavin B. J., Ponzetto C. Separation of mouse testis cells on a Celsep (TM) apparatus and their usefulness as a source of high molecular weight DNA or RNA. Gamete Res. 1985;12:1–10. doi: 10.1002/mrd.1120120102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]