Abstract
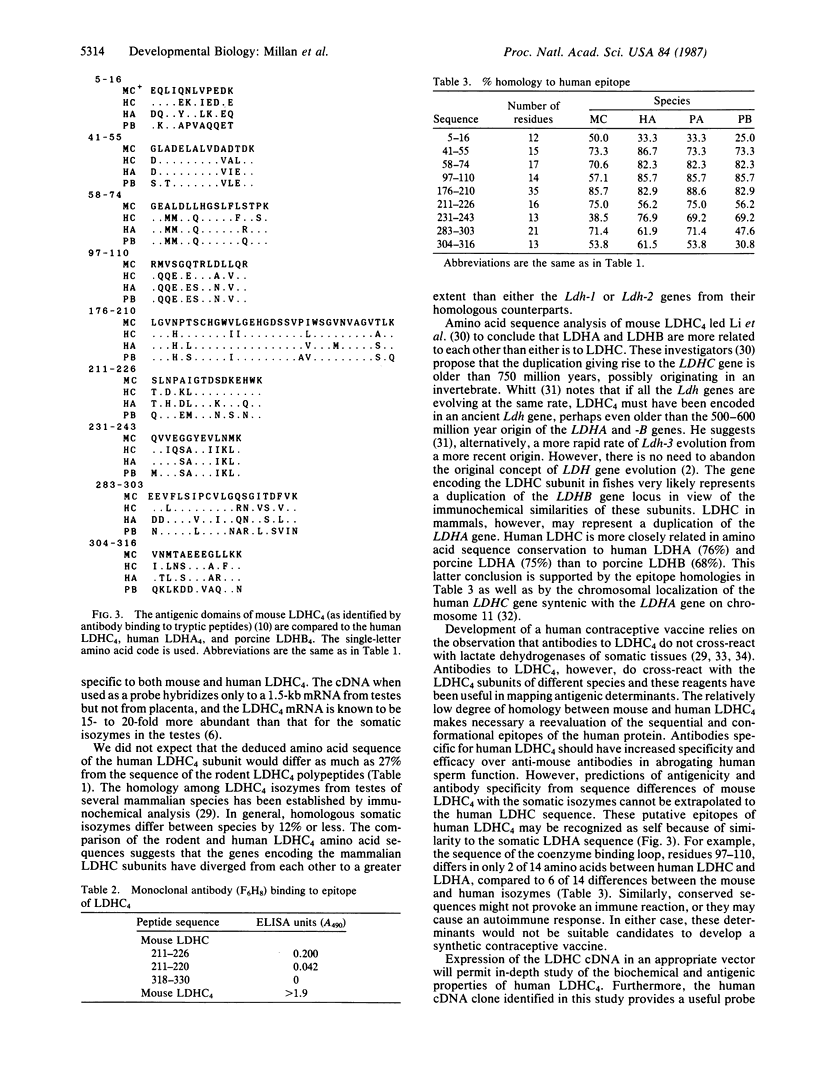
The sequence and structure of human testis-specific L-lactate dehydrogenase [LDHC4, LDHX; (L)-lactate: NAD+ oxidoreductase, EC 1.1.1.27] has been derived from analysis of a complementary DNA (cDNA) clone comprising the complete protein coding region of the enzyme. From the deduced amino acid sequence, human LDHC4 is as different from rodent LDHC4 (73% homology) as it is from human LDHA4 (76% homology) and porcine LDHB4 (68% homology). Subunit homologies are consistent with the conclusion that the LDHC gene arose by at least two independent duplication events. Furthermore, the lower degree of homology between mouse and human LDHC4 and the appearance of this isozyme late in evolution suggests a higher rate of mutation in the mammalian LDHC genes than in the LDHA and -B genes. Comparison of exposed amino acid residues of discrete antigenic determinants of mouse and human LDHC4 reveals significant differences. Knowledge of the human LDHC4 sequence will help design human-specific peptides useful in the development of a contraceptive vaccine.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alwine J. C., Kemp D. J., Stark G. R. Method for detection of specific RNAs in agarose gels by transfer to diazobenzyloxymethyl-paper and hybridization with DNA probes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5350–5354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beyler S. A., Wheat T. E., Goldberg E. Binding of antibodies against antigenic domains of murine lactate dehydrogenase-C4 to human and mouse spermatozoa. Biol Reprod. 1985 Jun;32(5):1201–1210. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod32.5.1201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biggin M. D., Gibson T. J., Hong G. F. Buffer gradient gels and 35S label as an aid to rapid DNA sequence determination. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(13):3963–3965. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.13.3963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blanco A. On the functional significance of LDH X. Johns Hopkins Med J. 1980 Jun;146(6):231–235. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engvall E., Perlmann P. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Quantitative assay of immunoglobulin G. Immunochemistry. 1971 Sep;8(9):871–874. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(71)90454-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eventoff W., Rossmann M. G., Taylor S. S., Torff H. J., Meyer H., Keil W., Kiltz H. H. Structural adaptations of lactate dehydrogenase isozymes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jul;74(7):2677–2681. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.7.2677. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glisin V., Crkvenjakov R., Byus C. Ribonucleic acid isolated by cesium chloride centrifugation. Biochemistry. 1974 Jun 4;13(12):2633–2637. doi: 10.1021/bi00709a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg E. Immunochemical specificity of lactate dehydrogenase-X. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Feb;68(2):349–352. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.2.349. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman-Leikin R. E., Goldberg E. Characterization of monoclonal antibodies to the sperm-specific lactate dehydrogenase isozyme. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(12):3774–3778. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.12.3774. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hintz M., Goldberg E. Immunohistochemical localization of LDH-x during spermatogenesis in mouse testes. Dev Biol. 1977 Jun;57(2):375–384. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(77)90222-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyte J., Doolittle R. F. A simple method for displaying the hydropathic character of a protein. J Mol Biol. 1982 May 5;157(1):105–132. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90515-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li S. S., Fitch W. M., Pan Y. C., Sharief F. S. Evolutionary relationships of vertebrate lactate dehydrogenase isozymes A4 (muscle), B4 (heart), and C4 (testis). J Biol Chem. 1983 Jun 10;258(11):7029–7032. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liang Z. G., Shelton J. A., Goldberg E. Non-cross-reactivity of antibodies to murine LDH-C4 with LDH-A4 and LDH-B4. J Exp Zool. 1986 Dec;240(3):377–384. doi: 10.1002/jez.1402400312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markert C. L., Shaklee J. B., Whitt G. S. Evolution of a gene. Multiple genes for LDH isozymes provide a model of the evolution of gene structure, function and regulation. Science. 1975 Jul 11;189(4197):102–114. doi: 10.1126/science.1138367. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Millán J. L. Molecular cloning and sequence analysis of human placental alkaline phosphatase. J Biol Chem. 1986 Mar 5;261(7):3112–3115. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Musick W. D., Rossmann M. G. The structure of mouse testicular lactate dehydrogenase isoenzyme C4 at 2.9 A resolution. J Biol Chem. 1979 Aug 25;254(16):7611–7620. doi: 10.2210/pdb1ldx/pdb. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki S., Oldberg A., Hayman E. G., Pierschbacher M. D., Ruoslahti E. Complete amino acid sequence of human vitronectin deduced from cDNA. Similarity of cell attachment sites in vitronectin and fibronectin. EMBO J. 1985 Oct;4(10):2519–2524. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03965.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka S., Fujimoto H. A postmeiotically expressed clone encodes lactate dehydrogenase isozyme X. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Apr 29;136(2):760–766. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(86)90504-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wheat T. E., Goldberg E. Antigenic domains of the sperm-specific lactate dehydrogenase C4 isozyme. Mol Immunol. 1985 Jun;22(6):643–649. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(85)90093-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wheat T. E., Goldberg E. Immunochemical dissection of the testes-specific isozyme lactate dehydrogenase C4. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1984;438:156–170. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1984.tb38284.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wheat T. E., Shelton J. A., Gonzales-Prevatt V., Goldberg E. The antigenicity of synthetic peptide fragments of lactate dehydrogenase C4. Mol Immunol. 1985 Oct;22(10):1195–1199. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(85)90008-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitt G. S. Genetic, developmental and evolutionary aspects of the lactate dehydrogenase isozyme system. Cell Biochem Funct. 1984 Jul;2(3):134–139. doi: 10.1002/cbf.290020303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wieben E. D. Regulation of the synthesis of lactate dehydrogenase-X during spermatogenesis in the mouse. J Cell Biol. 1981 Mar;88(3):492–498. doi: 10.1083/jcb.88.3.492. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young R. A., Bloom B. R., Grosskinsky C. M., Ivanyi J., Thomas D., Davis R. W. Dissection of Mycobacterium tuberculosis antigens using recombinant DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(9):2583–2587. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.9.2583. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young R. A., Davis R. W. Yeast RNA polymerase II genes: isolation with antibody probes. Science. 1983 Nov 18;222(4625):778–782. doi: 10.1126/science.6356359. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]