Abstract
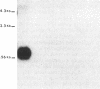
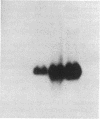
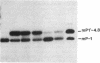
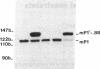
Protamines are abundant basic proteins involved in the condensation of sperm chromatin. In the mouse, protamine genes are transcribed postmeiotically in round spermatids. We have cloned and sequenced the mouse protamine 1 gene. Ten lines of transgenic mice harboring marked protamine 1 sequences were generated by microinjection of fertilized eggs. Transcription of the transgene is restricted to round spermatids and in several cases exceeds that of the endogenous gene. The cis-acting sequences required for tissue-specific protamine expression reside on a 2.4-kilobase restriction fragment. Prospects for using transgenic mice to address fundamental questions of male germ-cell development are discussed.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aiken J. M., McKenzie D., Zhao H. Z., States J. C., Dixon G. H. Sequence homologies in the protamine gene family of rainbow trout. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Jul 25;11(14):4907–4922. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.14.4907. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balhorn R., Weston S., Thomas C., Wyrobek A. J. DNA packaging in mouse spermatids. Synthesis of protamine variants and four transition proteins. Exp Cell Res. 1984 Feb;150(2):298–308. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(84)90572-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brinster R. L., Chen H. Y., Trumbauer M. E., Yagle M. K., Palmiter R. D. Factors affecting the efficiency of introducing foreign DNA into mice by microinjecting eggs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jul;82(13):4438–4442. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.13.4438. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cathala G., Savouret J. F., Mendez B., West B. L., Karin M., Martial J. A., Baxter J. D. A method for isolation of intact, translationally active ribonucleic acid. DNA. 1983;2(4):329–335. doi: 10.1089/dna.1983.2.329. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durnam D. M., Palmiter R. D. A practical approach for quantitating specific mRNAs by solution hybridization. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jun;131(2):385–393. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90188-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erickson R. P., Lewis S. E., Butley M. Is Haploid gene expression possible for sperm antigens? J Reprod Immunol. 1981 Sep;3(4):195–217. doi: 10.1016/0165-0378(81)90042-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hecht N. B., Bower P. A., Waters S. H., Yelick P. C., Distel R. J. Evidence for haploid expression of mouse testicular genes. Exp Cell Res. 1986 May;164(1):183–190. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(86)90465-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleene K. C., Distel R. J., Hecht N. B. Nucleotide sequence of a cDNA clone encoding mouse protamine 1. Biochemistry. 1985 Jan 29;24(3):719–722. doi: 10.1021/bi00324a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleene K. C., Distel R. J., Hecht N. B. Translational regulation and deadenylation of a protamine mRNA during spermiogenesis in the mouse. Dev Biol. 1984 Sep;105(1):71–79. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(84)90262-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleene K. C., Distel R. J., Hecht N. B. cDNA clones encoding cytoplasmic poly(A)+ RNAs which first appear at detectable levels in haploid phases of spermatogenesis in the mouse. Dev Biol. 1983 Aug;98(2):455–464. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(83)90375-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krawetz S. A., Connor W., Dixon G. H. Cloning of bovine P1 protamine cDNA and the evolution of vertebrate P1 protamines. DNA. 1987 Feb;6(1):47–57. doi: 10.1089/dna.1987.6.47. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehrach H., Diamond D., Wozney J. M., Boedtker H. RNA molecular weight determinations by gel electrophoresis under denaturing conditions, a critical reexamination. Biochemistry. 1977 Oct 18;16(21):4743–4751. doi: 10.1021/bi00640a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKay D. J., Renaux B. S., Dixon G. H. Human sperm protamines. Amino-acid sequences of two forms of protamine P2. Eur J Biochem. 1986 Apr 1;156(1):5–8. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb09540.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mount S. M. A catalogue of splice junction sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Jan 22;10(2):459–472. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.2.459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norrander J., Kempe T., Messing J. Construction of improved M13 vectors using oligodeoxynucleotide-directed mutagenesis. Gene. 1983 Dec;26(1):101–106. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90040-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ornitz D. M., Palmiter R. D., Hammer R. E., Brinster R. L., Swift G. H., MacDonald R. J. Specific expression of an elastase-human growth hormone fusion gene in pancreatic acinar cells of transgenic mice. Nature. 1985 Feb 14;313(6003):600–602. doi: 10.1038/313600a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmiter R. D., Chen H. Y., Brinster R. L. Differential regulation of metallothionein-thymidine kinase fusion genes in transgenic mice and their offspring. Cell. 1982 Jun;29(2):701–710. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90186-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sinclair G. D., Dixon G. H. Purification and characterization of cytoplasmic protamine messenger ribonucleoprotein particles from rainbow trout testis cells. Biochemistry. 1982 Apr 13;21(8):1869–1877. doi: 10.1021/bi00537a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- States J. C., Connor W., Wosnick M. A., Aiken J. M., Gedamu L., Dixon G. H. Nucleotide sequence of a protamine component CII gene of Salmo gairdnerii. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Aug 11;10(15):4551–4563. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.15.4551. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkie T. M., Brinster R. L., Palmiter R. D. Germline and somatic mosaicism in transgenic mice. Dev Biol. 1986 Nov;118(1):9–18. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(86)90068-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]