Abstract
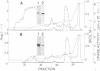
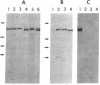
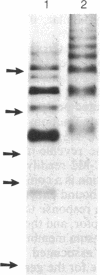
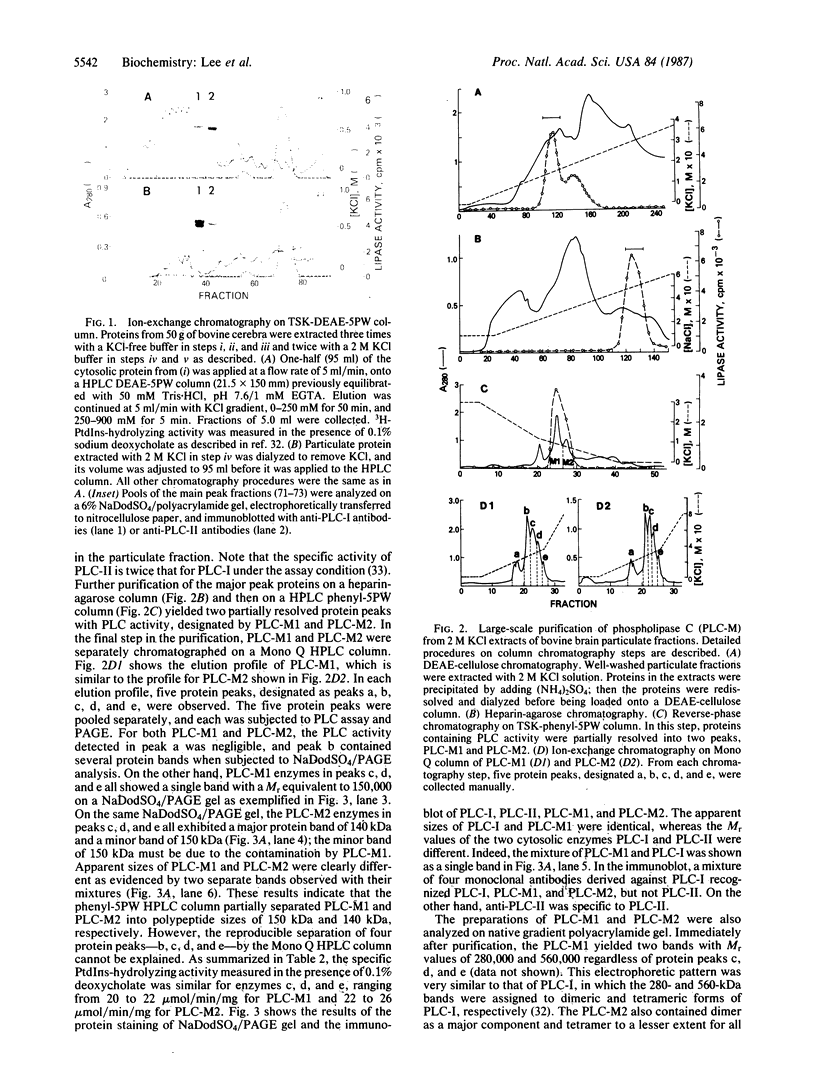
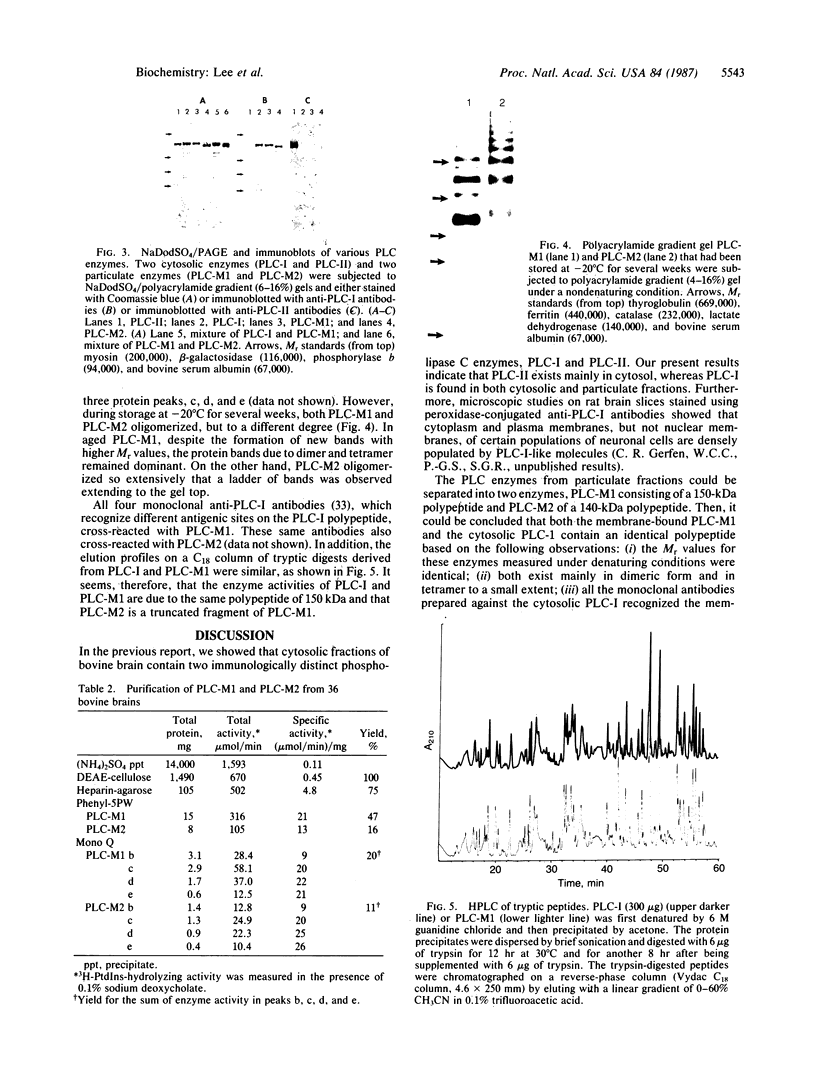
We previously reported that cytosolic fractions of bovine brain contain two immunologically distinct phosphoinositide-specific phospholipases C (PLCs), PLC-I and PLC-II. In this report the subcellular distribution of PLC-I and PLC-II in brain homogenates was measured using RIA. Significant differences were found in the distribution of the two forms of PLC in 100,000 X g supernatants (cytosolic fraction) of brain homogenized in hypotonic buffer and 2 M KCl extracts of washed pellets (particulate fraction). More than 90% of PLC-II was found in the cytosolic fractions, whereas the PLC-I-like molecules were equally distributed between cytosolic and particulate fractions. Purification of PLC enzyme to near homogeneity from the particulate fractions yielded two PLC enzymes, both of which could be recognized by anti-PLC-I antibodies but not by anti-PLC-II antibodies. Their Mr values, determined under denaturing conditions, were 150,000 and 140,000. The polypeptide of the enzyme of Mr 150,000 seems to be the same as that of the cytosolic enzyme PLC-I: their Mr values were identical, and their trypsin-digested peptides yielded a similar elution profile on a C18 reverse-phase column. We propose, therefore, that PLC-I and its truncated form are weakly associated with membranes.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aub D. L., Frey E. A., Sekura R. D., Cote T. E. Coupling of the thyrotropin-releasing hormone receptor to phospholipase C by a GTP-binding protein distinct from the inhibitory or stimulatory GTP-binding protein. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jul 15;261(20):9333–9340. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banno Y., Nakashima S., Nozawa Y. Partial purification of phosphoinositide phospholipase C from human platelet cytosol; characterization of its three forms. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Apr 29;136(2):713–721. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(86)90498-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J., Irvine R. F. Inositol trisphosphate, a novel second messenger in cellular signal transduction. Nature. 1984 Nov 22;312(5992):315–321. doi: 10.1038/312315a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford P. G., Rubin R. P. Guanine nucleotide regulation of phospholipase C activity in permeabilized rabbit neutrophils. Inhibition by pertussis toxin and sensitization to submicromolar calcium concentrations. Biochem J. 1986 Oct 1;239(1):97–102. doi: 10.1042/bj2390097. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burch R. M., Luini A., Axelrod J. Phospholipase A2 and phospholipase C are activated by distinct GTP-binding proteins in response to alpha 1-adrenergic stimulation in FRTL5 thyroid cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Oct;83(19):7201–7205. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.19.7201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgess G. M., Irvine R. F., Berridge M. J., McKinney J. S., Putney J. W., Jr Actions of inositol phosphates on Ca2+ pools in guinea-pig hepatocytes. Biochem J. 1984 Dec 15;224(3):741–746. doi: 10.1042/bj2240741. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cockcroft S., Gomperts B. D. Role of guanine nucleotide binding protein in the activation of polyphosphoinositide phosphodiesterase. Nature. 1985 Apr 11;314(6011):534–536. doi: 10.1038/314534a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedel R. O., Brown J. D., Durell J. The enzymic hydrolysis of phosphatidyl inositol by guinea pig brain: Sub-cellular distribution and hydrolysis products. J Neurochem. 1969 Mar;16(3):371–378. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1969.tb10376.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilman A. G. G proteins and dual control of adenylate cyclase. Cell. 1984 Mar;36(3):577–579. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90336-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzales R. A., Crews F. T. Guanine nucleotides stimulate production of inositol trisphosphate in rat cortical membranes. Biochem J. 1985 Dec 15;232(3):799–804. doi: 10.1042/bj2320799. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hakata H., Kambayashi J., Kosaki G. Purification and characterization of phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C from bovine platelets. J Biochem. 1982 Sep;92(3):929–935. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a134008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hepler J. R., Harden T. K. Guanine nucleotide-dependent pertussis-toxin-insensitive stimulation of inositol phosphate formation by carbachol in a membrane preparation from human astrocytoma cells. Biochem J. 1986 Oct 1;239(1):141–146. doi: 10.1042/bj2390141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higashida H., Streaty R. A., Klee W., Nirenberg M. Bradykinin-activated transmembrane signals are coupled via No or Ni to production of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate, a second messenger in NG108-15 neuroblastoma-glioma hybrid cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Feb;83(4):942–946. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.4.942. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofmann S. L., Majerus P. W. Identification and properties of two distinct phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C enzymes from sheep seminal vesicular glands. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jun 10;257(11):6461–6469. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofmann S. L., Majerus P. W. Modulation of phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C activity by phospholipid interactions, diglycerides, and calcium ions. J Biol Chem. 1982 Dec 10;257(23):14359–14364. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irvine R. F., Dawson R. M. The distribution of calcium-dependent phosphatidylinositol-specific phosphodiesterase in rat brain. J Neurochem. 1978 Dec;31(6):1427–1434. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1978.tb06568.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamisaka Y., Toyoshima S., Osawa T. Phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C of murine lymphocytes. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1986 Sep;249(2):569–578. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(86)90035-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keough K. M., Thompson W. Soluble and particulate forms of phosphoinositide phosphodiesterase in ox brain. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Jul 7;270(3):324–336. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(72)90197-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lapetina E. G., Michell R. H. A membrane-bound activity catalysing phosphatidylinositol breakdown to 1,2-diacylglycerol, D-myoinositol 1:2-cyclic phosphate an D-myoinositol 1-phosphate. Properties and subcellular distribution in rat cerebral cortex. Biochem J. 1973 Mar;131(3):433–442. doi: 10.1042/bj1310433. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Litosch I., Fain J. N. 5-Methyltryptamine stimulates phospholipase C-mediated breakdown of exogenous phosphoinositides by blowfly salivary gland membranes. J Biol Chem. 1985 Dec 25;260(30):16052–16055. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Litosch I., Wallis C., Fain J. N. 5-Hydroxytryptamine stimulates inositol phosphate production in a cell-free system from blowfly salivary glands. Evidence for a role of GTP in coupling receptor activation to phosphoinositide breakdown. J Biol Chem. 1985 May 10;260(9):5464–5471. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Low M. G., Carroll R. C., Cox A. C. Characterization of multiple forms of phosphoinositide-specific phospholipase C purified from human platelets. Biochem J. 1986 Jul 1;237(1):139–145. doi: 10.1042/bj2370139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin T. F., Lucas D. O., Bajjalieh S. M., Kowalchyk J. A. Thyrotropin-releasing hormone activates a Ca2+-dependent polyphosphoinositide phosphodiesterase in permeable GH3 cells. GTP gamma S potentiation by a cholera and pertussis toxin-insensitive mechanism. J Biol Chem. 1986 Feb 25;261(6):2918–2927. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melin P. M., Sundler R., Jergil B. Phospholipase C in rat liver plasma membranes. Phosphoinositide specificity and regulation by guanine nucleotides and calcium. FEBS Lett. 1986 Mar 17;198(1):85–88. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)81189-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merritt J. E., Taylor C. W., Rubin R. P., Putney J. W., Jr Evidence suggesting that a novel guanine nucleotide regulatory protein couples receptors to phospholipase C in exocrine pancreas. Biochem J. 1986 Jun 1;236(2):337–343. doi: 10.1042/bj2360337. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michell B., Kirk C. G-protein control of inositol phosphate hydrolysis. Nature. 1986 Sep 11;323(6084):112–113. doi: 10.1038/323112b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishizuka Y. Turnover of inositol phospholipids and signal transduction. Science. 1984 Sep 21;225(4668):1365–1370. doi: 10.1126/science.6147898. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothenberg R. J., Moskowitz R. W., Malemud C. J. Phospholipase C activity in plasma membranes isolated from lapine synovial cells in monolayer culture. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Aug 30;115(1):331–338. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)91008-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryu S. H., Cho K. S., Lee K. Y., Suh P. G., Rhee S. G. Two forms of phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C from bovine brain. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Nov 26;141(1):137–144. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(86)80345-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siess W., Lapetina E. G. Properties and distribution of phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C in human and horse platelets. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Jul 12;752(2):329–338. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(83)90131-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C. D., Cox C. C., Snyderman R. Receptor-coupled activation of phosphoinositide-specific phospholipase C by an N protein. Science. 1986 Apr 4;232(4746):97–100. doi: 10.1126/science.3006254. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sternweis P. C. The purified alpha subunits of Go and Gi from bovine brain require beta gamma for association with phospholipid vesicles. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jan 15;261(2):631–637. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takenawa T., Nagai Y. Purification of phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C from rat liver. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jul 10;256(13):6769–6775. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uhing R. J., Prpic V., Jiang H., Exton J. H. Hormone-stimulated polyphosphoinositide breakdown in rat liver plasma membranes. Roles of guanine nucleotides and calcium. J Biol Chem. 1986 Feb 15;261(5):2140–2146. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wakelam M. J., Davies S. A., Houslay M. D., McKay I., Marshall C. J., Hall A. Normal p21N-ras couples bombesin and other growth factor receptors to inositol phosphate production. Nature. 1986 Sep 11;323(6084):173–176. doi: 10.1038/323173a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]