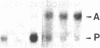Abstract
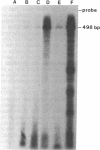
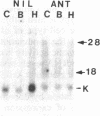
A glandular-like kallikrein enzyme, a member of a well-characterized family of specific arginyl endopeptidases that may be involved in prohormone processing, has previously been shown to be present in the anterior and neurointermediate lobes of the rat pituitary. We isolated glandular-like kallikrein cDNAs from cDNA libraries prepared from these two tissues. By nucleotide sequence, restriction endonuclease, solution hybridization/nuclease protection, and blot analyses, we showed that, of the 8-10 rat kallikrein-encoding genes, it is the true glandular kallikrein mRNA that is expressed in both pituitary lobes. RNA blot-hybridization analysis of anterior and neurointermediate lobe pituitary RNA revealed a kallikrein mRNA of approximately equal to 900 base pairs. As analyzed by blot-hybridization and solution hybridization/nuclease protection analyses, the true glandular kallikrein mRNA was present at low levels: approximately equal to 0.05% of total mRNA in both male and female neurointermediate lobes. Similar low levels of the glandular kallikrein mRNA were found in the male anterior lobe, whereas the levels were 10- to 15-fold higher in the female anterior lobe. In vivo administration of a dopamine agonist (bromocryptine) or antagonist (haloperidol) caused a decrease or increase, respectively, in the amount of true glandular kallikrein mRNA in the neurointermediate lobe of both sexes that closely paralleled changes in proopiomelanocortin mRNA levels. Bromocryptine decreased and haloperidol increased true glandular kallikrein mRNA levels in the female anterior lobe but had no effect in the male anterior lobe. Nuclear transcription run-on studies showed that the changes in mRNA were due, at least in part, to parallel effects of haloperidol on kallikrein gene transcription. Thus, these studies have demonstrated that the pituitary expresses the glandular-type member of the kallikrein gene family and that dopaminergic compounds elicit changes in kallikrein mRNA, at least in part, by modulating transcription. In the intermediate lobe, regulation of true glandular kallikrein gene expression is parallel to that of proopiomelanocortin gene expression, suggesting that the enzyme may play a physiological role in the production and/or secretion of the proopiomelanocortin peptides in this tissue.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ashley P. L., MacDonald R. J. Kallikrein-related mRNAs of the rat submaxillary gland: nucleotide sequences of four distinct types including tonin. Biochemistry. 1985 Aug 13;24(17):4512–4520. doi: 10.1021/bi00338a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashley P. L., MacDonald R. J. Tissue-specific expression of kallikrein-related genes in the rat. Biochemistry. 1985 Aug 13;24(17):4520–4527. doi: 10.1021/bi00338a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benton W. D., Davis R. W. Screening lambdagt recombinant clones by hybridization to single plaques in situ. Science. 1977 Apr 8;196(4286):180–182. doi: 10.1126/science.322279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blum M., McEwen B. S., Roberts J. L. Transcriptional analysis of tyrosine hydroxylase gene expression in the tuberoinfundibular dopaminergic neurons of the rat arcuate nucleus after estrogen treatment. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jan 15;262(2):817–821. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cathala G., Savouret J. F., Mendez B., West B. L., Karin M., Martial J. A., Baxter J. D. A method for isolation of intact, translationally active ribonucleic acid. DNA. 1983;2(4):329–335. doi: 10.1089/dna.1983.2.329. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen C. L., Dionne F. T., Roberts J. L. Regulation of the pro-opiomelanocortin mRNA levels in rat pituitary by dopaminergic compounds. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Apr;80(8):2211–2215. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.8.2211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clements J. A., Fuller P. J., McNally M., Nikolaidis I., Funder J. W. Estrogen regulation of kallikrein gene expression in the rat anterior pituitary. Endocrinology. 1986 Jul;119(1):268–273. doi: 10.1210/endo-119-1-268. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans M. I., Hager L. J., McKnight G. S. A somatomedin-like peptide hormone is required during the estrogen-mediated induction of ovalbumin gene transcription. Cell. 1981 Jul;25(1):187–193. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90243-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuller P. J., Clements J. A., Whitfeld P. L., Funder J. W. Kallikrein gene expression in the rat anterior pituitary. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1985 Feb;39(2):99–105. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(85)90125-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray A., Dull T. J., Ullrich A. Nucleotide sequence of epidermal growth factor cDNA predicts a 128,000-molecular weight protein precursor. Nature. 1983 Jun 23;303(5919):722–725. doi: 10.1038/303722a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loh Y. P., Gainer H. Characterization of pro-opiocortin-converting activity in purified secretory granules from rat pituitary neurointermediate lobe. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jan;79(1):108–112. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.1.108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mains R. E., Myers A. C., Eipper B. A. Hormonal, drug, and dietary factors affecting peptidyl glycine alpha-amidating monooxygenase activity in various tissues of the adult male rat. Endocrinology. 1985 Jun;116(6):2505–2515. doi: 10.1210/endo-116-6-2505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason A. J., Evans B. A., Cox D. R., Shine J., Richards R. I. Structure of mouse kallikrein gene family suggests a role in specific processing of biologically active peptides. Nature. 1983 May 26;303(5915):300–307. doi: 10.1038/303300a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Millington W. R., O'Donohue T. L., Chappell M. C., Roberts J. L., Mueller G. P. Coordinate regulation of peptide acetyltransferase activity and proopiomelanocortin gene expression in the intermediate lobe of the rat pituitary. Endocrinology. 1986 May;118(5):2024–2033. doi: 10.1210/endo-118-5-2024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powers C. A. Anterior pituitary glandular kallikrein: trypsin activation and estrogen regulation. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1986 Jul;46(2):163–174. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(86)90095-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powers C. A. Dopamine receptor blockade increases glandular kallikrein-like activity in the neurointermediate lobe of the rat pituitary. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Mar 15;127(2):668–672. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(85)80213-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powers C. A. Dopaminergic regulation of glandular kallikrein in the intermediate lobe of the rat pituitary. Neuroendocrinology. 1986;43(3):368–376. doi: 10.1159/000124564. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powers C. A., Nasjletti A. A kininogenase resembling glandular kallikrein in the rat pituitary pars intermedia. Endocrinology. 1983 Apr;112(4):1194–1200. doi: 10.1210/endo-112-4-1194. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powers C. A., Nasjletti A. A major sex difference in kallikrein-like activity in the rat anterior pituitary. Endocrinology. 1984 May;114(5):1841–1844. doi: 10.1210/endo-114-5-1841. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powers C. A. Trypsin activation, partial characterization, and distribution of kallikrein-like and thrombin-like proteases in the neurointermediate lobe of the rat pituitary. J Neurochem. 1986 Jul;47(1):145–153. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1986.tb02842.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pélaprat D., Seidah N. G., Sikstrom R. A., Lambelin P., Hamelin J., Lazure C., Cromlish J. A., Chrétien M. Subcellular fractionation of pituitary neurointermediate lobes: revelation of various basic proteases. Endocrinology. 1984 Aug;115(2):581–590. doi: 10.1210/endo-115-2-581. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shine J., Mason A. J., Evans B. A., Richards R. I. The kallikrein multigene family: specific processing of biologically active peptides. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1983;48(Pt 1):419–426. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1983.048.01.046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swift G. H., Dagorn J. C., Ashley P. L., Cummings S. W., MacDonald R. J. Rat pancreatic kallikrein mRNA: nucleotide sequence and amino acid sequence of the encoded preproenzyme. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(23):7263–7267. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.23.7263. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA and small DNA fragments transferred to nitrocellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5201–5205. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahl G. M., Stern M., Stark G. R. Efficient transfer of large DNA fragments from agarose gels to diazobenzyloxymethyl-paper and rapid hybridization by using dextran sulfate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Aug;76(8):3683–3687. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.8.3683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood W. I., Gitschier J., Lasky L. A., Lawn R. M. Base composition-independent hybridization in tetramethylammonium chloride: a method for oligonucleotide screening of highly complex gene libraries. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Mar;82(6):1585–1588. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.6.1585. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zinn K., DiMaio D., Maniatis T. Identification of two distinct regulatory regions adjacent to the human beta-interferon gene. Cell. 1983 Oct;34(3):865–879. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90544-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]