Abstract
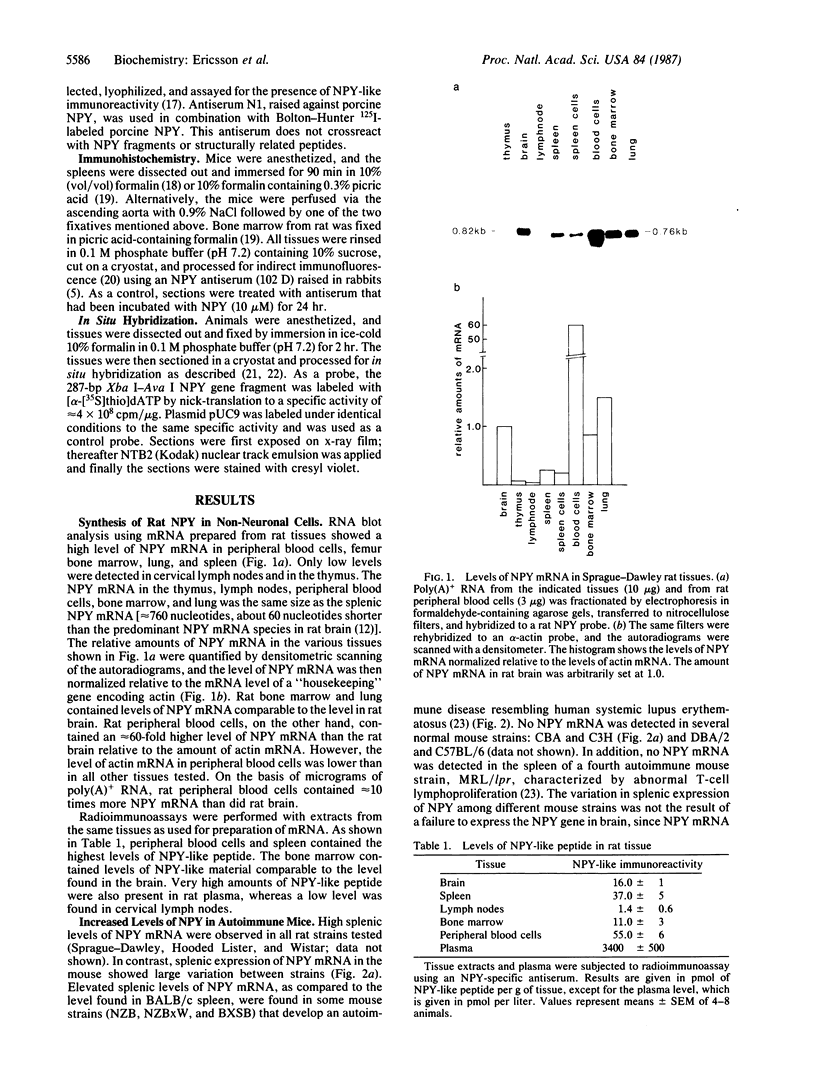
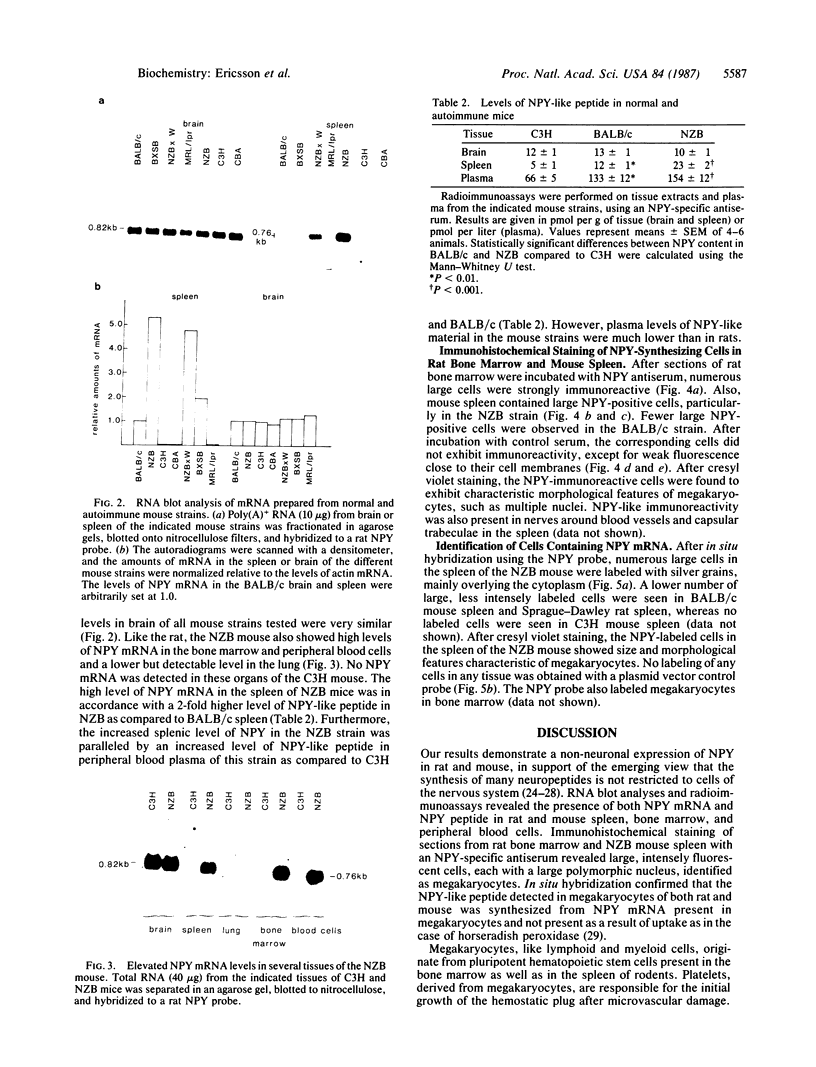
Neuropeptide tyrosine (neuropeptide Y, NPY) is a potent vasoconstrictor with a wide distribution in the central and peripheral nervous systems. Here we show that high levels of rat NPY mRNA are also found in peripheral blood cells, bone marrow, lung, and spleen. Furthermore, radioimmunoassay revealed high levels of NPY-like peptide in these tissues. In mice, the levels of splenic NPY mRNA and immunoreactive peptide differed extensively between strains and were greatly elevated in several strains (NZB, NZBxW, and BXSB) that develop a disease resembling human systemic lupus erythematosus. Like the rat, the NZB mouse showed a high content of NPY mRNA in peripheral blood cells and bone marrow. Immunohistochemical staining revealed NPY-like immunoreactivity in large cells morphologically identifiable as megakaryocytes in rat bone marrow and in the spleen of the NZB mouse strain. Expression of NPY mRNA in megakaryocytes in rat bone marrow and NZB mouse spleen was confirmed by in situ hybridization. These results indicate that NPY is synthesized in megakaryocytes, implying that NPY can be released from platelets and function as a vasoconstrictor during blood-vessel damage. In addition, the increase in splenic NPY in certain autoimmune mouse strains adds to the list of abnormalities associated with these strains.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adrian T. E., Allen J. M., Bloom S. R., Ghatei M. A., Rossor M. N., Roberts G. W., Crow T. J., Tatemoto K., Polak J. M. Neuropeptide Y distribution in human brain. Nature. 1983 Dec 8;306(5943):584–586. doi: 10.1038/306584a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allen Y. S., Adrian T. E., Allen J. M., Tatemoto K., Crow T. J., Bloom S. R., Polak J. M. Neuropeptide Y distribution in the rat brain. Science. 1983 Aug 26;221(4613):877–879. doi: 10.1126/science.6136091. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COONS A. H. Fluorescent antibody methods. Gen Cytochem Methods. 1958;1:399–422. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen C. L., Mather J. P., Morris P. L., Bardin C. W. Expression of pro-opiomelanocortin-like gene in the testis and epididymis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Sep;81(18):5672–5675. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.18.5672. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chronwall B. M., DiMaggio D. A., Massari V. J., Pickel V. M., Ruggiero D. A., O'Donohue T. L. The anatomy of neuropeptide-Y-containing neurons in rat brain. Neuroscience. 1985 Aug;15(4):1159–1181. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(85)90260-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Everitt B. J., Hökfelt T., Terenius L., Tatemoto K., Mutt V., Goldstein M. Differential co-existence of neuropeptide Y (NPY)-like immunoreactivity with catecholamines in the central nervous system of the rat. Neuroscience. 1984 Feb;11(2):443–462. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(84)90036-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Handagama P. J., George J. N., Shuman M. A., McEver R. P., Bainton D. F. Incorporation of a circulating protein into megakaryocyte and platelet granules. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Feb;84(3):861–865. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.3.861. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen M., Pedersen N. T. Circulating megakaryocytes in blood from the antecubital vein in healthy, adult humans. Scand J Haematol. 1978 Apr;20(4):371–376. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0609.1978.tb02469.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kilpatrick D. L., Millette C. F. Expression of proenkephalin messenger RNA by mouse spermatogenic cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(14):5015–5018. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.14.5015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kincade P. W., Lee G., Fernandes G., Moore M. A., Williams N., Good R. A. Abnormalities in clonable B lymphocytes and myeloid progenitors in autoimmune NZB mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jul;76(7):3464–3468. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.7.3464. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larhammar D., Ericsson A., Persson H. Structure and expression of the rat neuropeptide Y gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Apr;84(7):2068–2072. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.7.2068. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundberg J. M., Anggård A., Theodorsson-Norheim E., Pernow J. Guanethidine-sensitive release of neuropeptide Y-like immunoreactivity in the cat spleen by sympathetic nerve stimulation. Neurosci Lett. 1984 Nov 23;52(1-2):175–180. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(84)90370-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundberg J. M., Hökfelt T., Hemsén A., Theodorsson-Norheim E., Pernow J., Hamberger B., Goldstein M. Neuropeptide Y-like immunoreactivity in adrenaline cells of adrenal medulla and in tumors and plasma of pheochromocytoma patients. Regul Pept. 1986 Jan;13(2):169–182. doi: 10.1016/0167-0115(86)90224-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundberg J. M., Martinsson A., Hemsén A., Theodorsson-Norheim E., Svedenhag J., Ekblom B., Hjemdahl P. Co-release of neuropeptide Y and catecholamines during physical exercise in man. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Nov 27;133(1):30–36. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)91837-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundberg J. M., Tatemoto K. Pancreatic polypeptide family (APP, BPP, NPY and PYY) in relation to sympathetic vasoconstriction resistant to alpha-adrenoceptor blockade. Acta Physiol Scand. 1982 Dec;116(4):393–402. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1982.tb07157.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundberg J. M., Terenius L., Hökfelt T., Martling C. R., Tatemoto K., Mutt V., Polak J., Bloom S., Goldstein M. Neuropeptide Y (NPY)-like immunoreactivity in peripheral noradrenergic neurons and effects of NPY on sympathetic function. Acta Physiol Scand. 1982 Dec;116(4):477–480. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1982.tb07171.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundberg J. M., Terenius L., Hökfelt T., Tatemoto K. Comparative immunohistochemical and biochemical analysis of pancreatic polypeptide-like peptides with special reference to presence of neuropeptide Y in central and peripheral neurons. J Neurosci. 1984 Sep;4(9):2376–2386. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.04-09-02376.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minth C. D., Andrews P. C., Dixon J. E. Characterization, sequence, and expression of the cloned human neuropeptide Y gene. J Biol Chem. 1986 Sep 15;261(26):11974–11979. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minth C. D., Bloom S. R., Polak J. M., Dixon J. E. Cloning, characterization, and DNA sequence of a human cDNA encoding neuropeptide tyrosine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jul;81(14):4577–4581. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.14.4577. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minty A. J., Caravatti M., Robert B., Cohen A., Daubas P., Weydert A., Gros F., Buckingham M. E. Mouse actin messenger RNAs. Construction and characterization of a recombinant plasmid molecule containing a complementary DNA transcript of mouse alpha-actin mRNA. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jan 25;256(2):1008–1014. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedersen N. T. Occurrence of megakaryocytes in various vessels and their retention in the pulmonary capillaries in man. Scand J Haematol. 1978 Nov;21(5):369–375. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0609.1978.tb00381.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedersen N. T. The pulmonary vessels as a filter for circulating megakaryocytes in rats. Scand J Haematol. 1974;13(3):225–231. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0609.1974.tb00263.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pintar J. E., Schachter B. S., Herman A. B., Durgerian S., Krieger D. T. Characterization and localization of proopiomelanocortin messenger RNA in the adult rat testis. Science. 1984 Aug 10;225(4662):632–634. doi: 10.1126/science.6740329. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schalling M., Hökfelt T., Wallace B., Goldstein M., Filer D., Yamin C., Schlesinger D. H. Tyrosine 3-hydroxylase in rat brain and adrenal medulla: hybridization histochemistry and immunohistochemistry combined with retrograde tracing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(16):6208–6212. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.16.6208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tatemoto K., Carlquist M., Mutt V. Neuropeptide Y--a novel brain peptide with structural similarities to peptide YY and pancreatic polypeptide. Nature. 1982 Apr 15;296(5858):659–660. doi: 10.1038/296659a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theodorsson-Norheim E., Hemsén A., Lundberg J. M. Radioimmunoassay for neuropeptide Y (NPY): chromatographic characterization of immunoreactivity in plasma and tissue extracts. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1985 Jun;45(4):355–365. doi: 10.3109/00365518509161019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theofilopoulos A. N., Dixon F. J. Etiopathogenesis of murine SLE. Immunol Rev. 1981;55:179–216. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1981.tb00343.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whittemore S. R., Ebendal T., Lärkfors L., Olson L., Seiger A., Strömberg I., Persson H. Development and regional expression of beta nerve growth factor messenger RNA and protein in the rat central nervous system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Feb;83(3):817–821. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.3.817. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zurawski G., Benedik M., Kamb B. J., Abrams J. S., Zurawski S. M., Lee F. D. Activation of mouse T-helper cells induces abundant preproenkephalin mRNA synthesis. Science. 1986 May 9;232(4751):772–775. doi: 10.1126/science.2938259. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Quidt M. E., Emson P. C. Distribution of neuropeptide Y-like immunoreactivity in the rat central nervous system--II. Immunohistochemical analysis. Neuroscience. 1986 Jul;18(3):545–618. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(86)90057-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]