Abstract
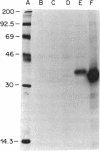
The cDNA encoding the B chain of the plant toxin ricin has been cloned and expressed in monkey kidney COS-M6 cells. The recombinant B chain was detected by labeling the transfected cells with [35S]methionine and [35S]-cysteine and demonstrating the secretion of a protein with a Mr of 30,000-32,000 that was not present in the medium of mock-transfected COS-M6 cells. This protein was specifically immunoprecipitated by an anti-ricin or anti-B-chain antibody and the amount of recombinant B chain secreted by the COS-M6 cells was determined by a radioimmunoassay. Virtually all of the recombinant B chain formed active ricin when mixed with native A chain; it could also bind to the galactose-containing glycoprotein asialofetuin as effectively as native B chain. These results indicate that the vast majority of recombinant B chains secreted into the medium of the COS-M6 cells retain biological function.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cushley W., Muirhead M. J., Silva F., Greathouse J., Tucker T., Uhr J. W., Vitetta E. S. In vivo reconstitution of ricin-like activity from its A and B chain subunits. Toxicon. 1984;22(2):265–277. doi: 10.1016/0041-0101(84)90027-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eccles S. A., McIntosh D. P., Purvies H. P., Cumber A. J., Parnell G. D., Forrester J. A., Styles J. M., Dean C. J. An ineffective monoclonal antibody-ricin A chain conjugate is converted to a tumouricidal agent in vivo by subsequent systemic administration of ricin B chain. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 1987;24(1):37–41. doi: 10.1007/BF00199830. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fulton R. J., Blakey D. C., Knowles P. P., Uhr J. W., Thorpe P. E., Vitetta E. S. Purification of ricin A1, A2, and B chains and characterization of their toxicity. J Biol Chem. 1986 Apr 25;261(12):5314–5319. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gluzman Y. SV40-transformed simian cells support the replication of early SV40 mutants. Cell. 1981 Jan;23(1):175–182. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90282-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horowitz M., Cepko C. L., Sharp P. A. Expression of chimeric genes in the early region of SV40. J Mol Appl Genet. 1983;2(2):147–159. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houston L. L. Transport of ricin A chain after prior treatment of mouse leukemia cells with ricin B chain. J Biol Chem. 1982 Feb 10;257(3):1532–1539. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamb F. I., Roberts L. M., Lord J. M. Nucleotide sequence of cloned cDNA coding for preproricin. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Apr 15;148(2):265–270. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb08834.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lappi D. A., Kapmeyer W., Beglau J. M., Kaplan N. O. The disulfide bond connecting the chains of ricin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Mar;75(3):1096–1100. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.3.1096. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCracken A. A., Fishman N. F. Secretion of rat serum albumin by COS cells transfected with a spliced cDNA gene. A system to study protein sorting. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jan 15;261(2):508–511. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McIntosh D. P., Edwards D. C., Cumber A. J., Parnell G. D., Dean C. J., Ross W. C., Forrester J. A. Ricin B chain converts a non-cytotoxic antibody-ricin A chain conjugate into a potent and specific cytotoxic agent. FEBS Lett. 1983 Nov 28;164(1):17–20. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(83)80009-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montfort W., Villafranca J. E., Monzingo A. F., Ernst S. R., Katzin B., Rutenber E., Xuong N. H., Hamlin R., Robertus J. D. The three-dimensional structure of ricin at 2.8 A. J Biol Chem. 1987 Apr 15;262(11):5398–5403. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neville D. M., Jr, Youle R. J. Monoclonal antibody-ricin or ricin A chain hybrids: kinetic analysis of cell killing for tumor therapy. Immunol Rev. 1982;62:75–91. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1982.tb00390.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okayama H., Berg P. A cDNA cloning vector that permits expression of cDNA inserts in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Feb;3(2):280–289. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.2.280. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okayama H., Berg P. High-efficiency cloning of full-length cDNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Feb;2(2):161–170. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.2.161. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsnes S., Pihl A. Chimeric toxins. Pharmacol Ther. 1981;15(3):355–381. doi: 10.1016/0163-7258(81)90050-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsnes S., Saltvedt E., Pihl A. Isolation and comparison of galactose-binding lectins from Abrus precatorius and Ricinus communis. J Biol Chem. 1974 Feb 10;249(3):803–810. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorpe P. E., Ross W. C., Brown A. N., Myers C. D., Cumber A. J., Foxwell B. M., Forrester J. T. Blockade of the galactose-binding sites of ricin by its linkage to antibody. Specific cytotoxic effects of the conjugates. Eur J Biochem. 1984 Apr 2;140(1):63–71. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb08067.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorpe P. E., Ross W. C. The preparation and cytotoxic properties of antibody-toxin conjugates. Immunol Rev. 1982;62:119–158. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1982.tb00392.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tolleshaug H., Goldstein J. L., Schneider W. J., Brown M. S. Posttranslational processing of the LDL receptor and its genetic disruption in familial hypercholesterolemia. Cell. 1982 Oct;30(3):715–724. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90276-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vitetta E. S., Cushley W., Uhr J. W. Synergy of ricin A chain-containing immunotoxins and ricin B chain-containing immunotoxins in in vitro killing of neoplastic human B cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Oct;80(20):6332–6335. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.20.6332. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vitetta E. S., Fulton R. J., Uhr J. W. Cytotoxicity of a cell-reactive immunotoxin containing ricin A chain is potentiated by an anti-immunotoxin containing ricin B chain. J Exp Med. 1984 Jul 1;160(1):341–346. doi: 10.1084/jem.160.1.341. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vitetta E. S., Krolick K. A., Miyama-Inaba M., Cushley W., Uhr J. W. Immunotoxins: a new approach to cancer therapy. Science. 1983 Feb 11;219(4585):644–650. doi: 10.1126/science.6218613. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vitetta E. S., Krolick K. A., Uhr J. W. Neoplastic B cells as targets for antibody-ricin A chain immunotoxins. Immunol Rev. 1982;62:159–183. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1982.tb00393.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vitetta E. S. Synergy between immunotoxins prepared with native ricin A chains and chemically-modified ricin B chains. J Immunol. 1986 Mar 1;136(5):1880–1887. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vitetta E. S., Uhr J. W. Immunotoxins. Annu Rev Immunol. 1985;3:197–212. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.03.040185.001213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto T., Davis C. G., Brown M. S., Schneider W. J., Casey M. L., Goldstein J. L., Russell D. W. The human LDL receptor: a cysteine-rich protein with multiple Alu sequences in its mRNA. Cell. 1984 Nov;39(1):27–38. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90188-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Youle R. J., Neville D. M., Jr Kinetics of protein synthesis inactivation by ricin-anti-Thy 1.1 monoclonal antibody hybrids. Role of the ricin B subunit demonstrated by reconstitution. J Biol Chem. 1982 Feb 25;257(4):1598–1601. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]