Abstract
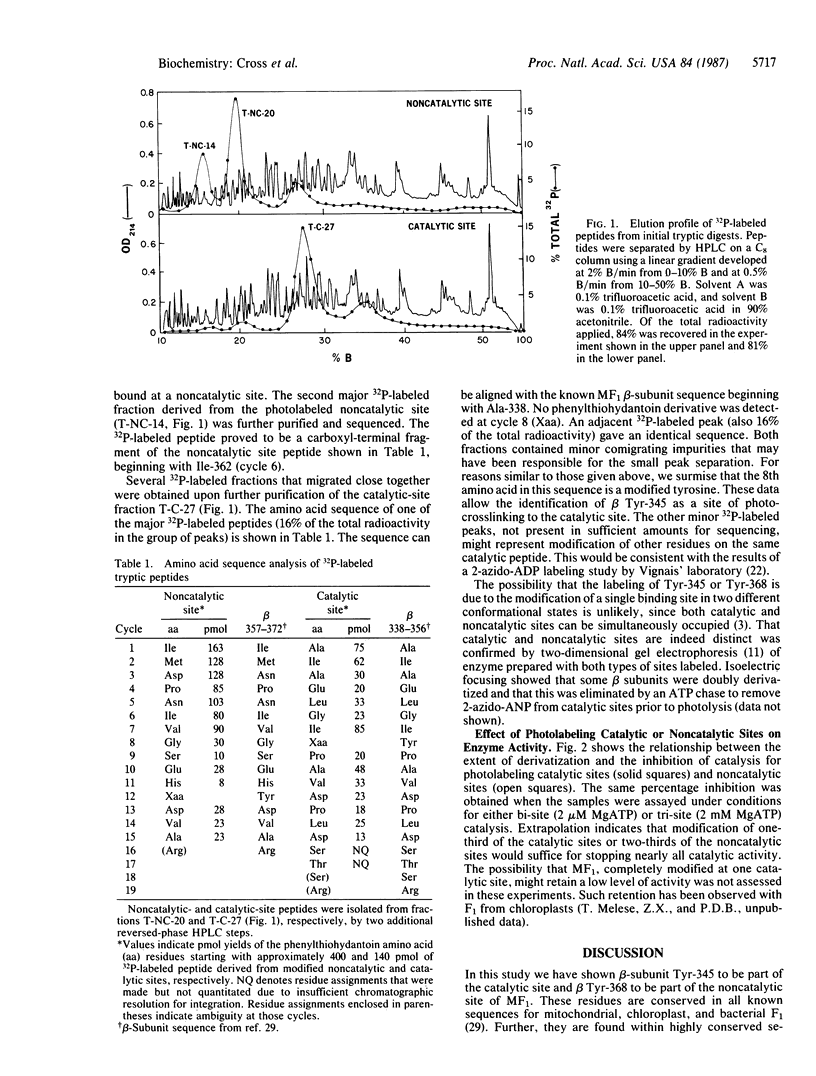
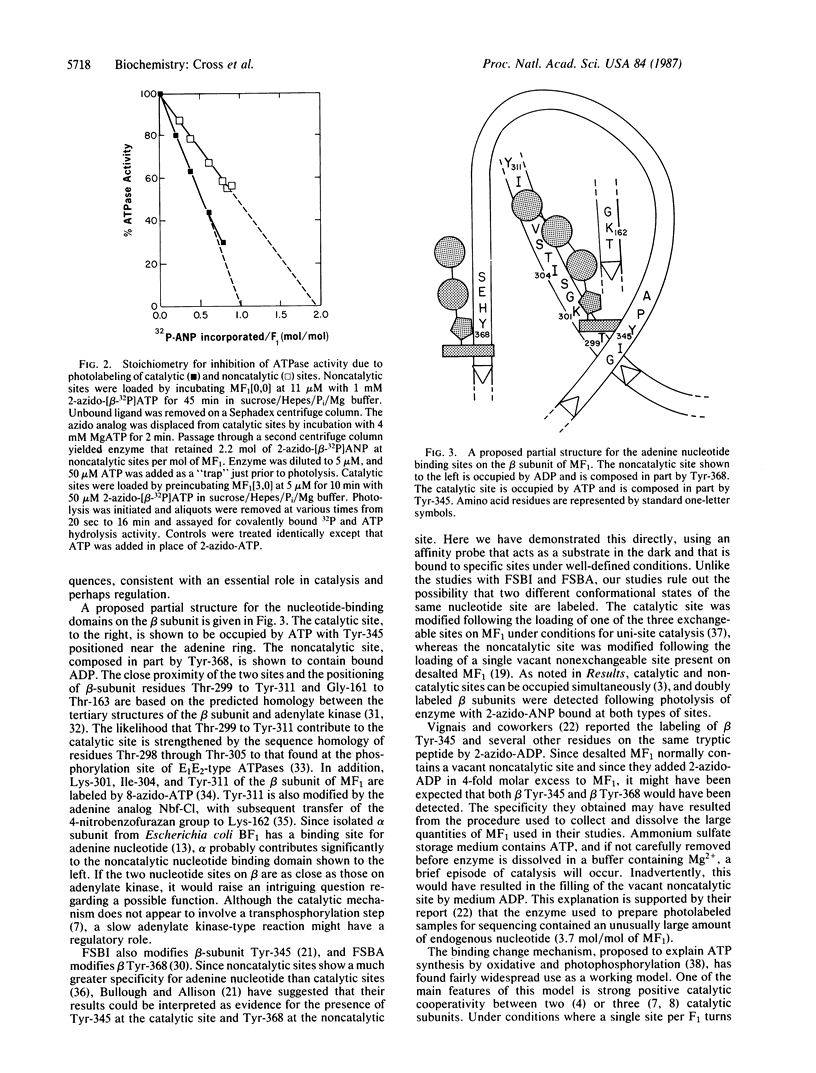
2-Azidoadenine [32P]nucleotide was bound specifically at catalytic or noncatalytic nucleotide binding sites on beef heart mitochondrial F1 ATPase. In both cases, photolysis resulted in nearly exclusive labeling of the beta subunit. The modified enzyme was digested with trypsin, and labeled peptides were purified by reversed-phase high-pressure liquid chromatography. Amino acid sequence analysis of the major 32P-labeled tryptic fragments showed beta-subunit Tyr-368 to be present at noncatalytic sites and beta Tyr-345 to be present at catalytic sites. From the relationship between the degree of inhibition and extent of modification, it is estimated that one-third of the catalytic sites or two-thirds of the noncatalytic sites must be modified to give near-complete inhibition of catalytic activity.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abbott M. S., Czarnecki J. J., Selman B. R. Localization of the high-affinity binding site for ATP on the membrane-bound chloroplast ATP synthase. J Biol Chem. 1984 Oct 10;259(19):12271–12278. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andrews W. W., Hill F. C., Allison W. S. Identification of the lysine residue to which the 4-nitrobenzofurazan group migrates after the bovine mitochondrial F1-ATPase is inactivated with 7-chloro-4-nitro[14C]benzofurazan. J Biol Chem. 1984 Dec 10;259(23):14378–14382. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boulay F., Dalbon P., Vignais P. V. Photoaffinity labeling of mitochondrial adenosinetriphosphatase by 2-azidoadenosine 5'-[alpha-32P]diphosphate. Biochemistry. 1985 Dec 3;24(25):7372–7379. doi: 10.1021/bi00346a052. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bullough D. A., Allison W. S. Inactivation of the bovine heart mitochondrial F1-ATPase by 5'-p-fluorosulfonylbenzoyl[3H]inosine is accompanied by modification of tyrosine 345 in a single beta subunit. J Biol Chem. 1986 Oct 25;261(30):14171–14177. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bullough D. A., Allison W. S. Three copies of the beta subunit must be modified to achieve complete inactivation of the bovine mitochondrial F1-ATPase by 5'-p-fluorosulfonylbenzoyladenosine. J Biol Chem. 1986 May 5;261(13):5722–5730. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choate G. L., Hutton R. L., Boyer P. D. Occurrence and significance of oxygen exchange reactions catalyzed by mitochondrial adenosine triphosphatase preparations. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jan 25;254(2):286–290. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross R. L., Cunningham D., Tamura J. K. Binding change mechanism for ATP synthesis by oxidative phosphorylation and photophosphorylation. Curr Top Cell Regul. 1984;24:335–344. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-152824-9.50036-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross R. L., Grubmeyer C., Penefsky H. S. Mechanism of ATP hydrolysis by beef heart mitochondrial ATPase. Rate enhancements resulting from cooperative interactions between multiple catalytic sites. J Biol Chem. 1982 Oct 25;257(20):12101–12105. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross R. L., Nalin C. M. Adenine nucleotide binding sites on beef heart F1-ATPase. Evidence for three exchangeable sites that are distinct from three noncatalytic sites. J Biol Chem. 1982 Mar 25;257(6):2874–2881. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross R. L. The mechanism and regulation of ATP synthesis by F1-ATPases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:681–714. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.003341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czarnecki J. J., Abbott M. S., Selman B. R. Photoaffinity labeling with 2-azidoadenosine diphosphate of a tight nucleotide binding site on chloroplast coupling factor 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(24):7744–7748. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.24.7744. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czarnecki J. J. Tautomerism of 2-azidoadenine nucleotides. Effects on enzyme kinetics and photoaffinity labeling. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Jul 16;800(1):41–51. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(84)90092-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Pietro A., Penin F., Godinot C., Gautheron D. C. "Hysteric" behavior and nucleotide binding sites of pig heart mitochondrial F1 adenosine 5'-triphosphatase. Biochemistry. 1980 Dec 9;19(25):5671–5678. doi: 10.1021/bi00566a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duncan T. M., Parsonage D., Senior A. E. Structure of the nucleotide-binding domain in the beta-subunit of Escherichia coli F1-ATPase. FEBS Lett. 1986 Nov 10;208(1):1–6. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)81519-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunn S. D., Futai M. Reconstitution of a functional coupling factor from the isolated subunits of Escherichia coli F1 ATPase. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jan 10;255(1):113–118. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esch F. S., Allison W. S. Identification of a tyrosine residue at a nucleotide binding site in the beta subunit of the mitochondrial ATPase with p-fluorosulfonyl[14C]-benzoyl-5'-adenosine. J Biol Chem. 1978 Sep 10;253(17):6100–6106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fry D. C., Kuby S. A., Mildvan A. S. ATP-binding site of adenylate kinase: mechanistic implications of its homology with ras-encoded p21, F1-ATPase, and other nucleotide-binding proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Feb;83(4):907–911. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.4.907. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garin J., Boulay F., Issartel J. P., Lunardi J., Vignais P. V. Identification of amino acid residues photolabeled with 2-azido[alpha-32P]adenosine diphosphate in the beta subunit of beef heart mitochondrial F1-ATPase. Biochemistry. 1986 Jul 29;25(15):4431–4437. doi: 10.1021/bi00363a039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garrett N. E., Penefsky H. S. Interaction of adenine nucleotides with multiple binding sites on beef heart mitochondrial adenosine triphosphatase. J Biol Chem. 1975 Sep 10;250(17):6640–6647. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gresser M. J., Myers J. A., Boyer P. D. Catalytic site cooperativity of beef heart mitochondrial F1 adenosine triphosphatase. Correlations of initial velocity, bound intermediate, and oxygen exchange measurements with an alternating three-site model. J Biol Chem. 1982 Oct 25;257(20):12030–12038. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grubmeyer C., Cross R. L., Penefsky H. S. Mechanism of ATP hydrolysis by beef heart mitochondrial ATPase. Rate constants for elementary steps in catalysis at a single site. J Biol Chem. 1982 Oct 25;257(20):12092–12100. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grubmeyer C., Penefsky H. S. The presence of two hydrolytic sites on beef heart mitochondrial adenosine triphosphatase. J Biol Chem. 1981 Apr 25;256(8):3718–3727. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris D. A., Gomez-Fernandez J. C., Klungsøyr L., Radda G. K. Specificity of nucleotide binding and coupled reactions utilising the mitochondrial ATPase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Dec 7;504(3):364–383. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(78)90060-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawke D. H., Harris D. C., Shively J. E. Microsequence analysis of peptides and proteins. V. Design and performance of a novel gas-liquid-solid phase instrument. Anal Biochem. 1985 Jun;147(2):315–330. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(85)90278-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawke D., Yuan P. M., Shively J. E. Microsequence analysis of peptides and proteins. II. Separation of amino acid phenylthiohydantoin derivatives by high-performance liquid chromatography on octadecylsilane supports. Anal Biochem. 1982 Mar 1;120(2):302–311. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90351-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollemans M., Runswick M. J., Fearnley I. M., Walker J. E. The sites of labeling of the beta-subunit of bovine mitochondrial F1-ATPase with 8-azido-ATP. J Biol Chem. 1983 Aug 10;258(15):9307–9313. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Issartel J. P., Lunardi J., Vignais P. V. Characterization of exchangeable and nonexchangeable bound adenine nucleotides in F1-ATPase from Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jan 15;261(2):895–901. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kayalar C., Rosing J., Boyer P. D. An alternating site sequence for oxidative phosphorylation suggested by measurement of substrate binding patterns and exchange reaction inhibitions. J Biol Chem. 1977 Apr 25;252(8):2486–2491. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kironde F. A., Cross R. L. Adenine nucleotide binding sites on beef heart F1-ATPase. Asymmetry and subunit location. J Biol Chem. 1987 Mar 15;262(8):3488–3495. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kironde F. A., Cross R. L. Adenine nucleotide-binding sites on beef heart F1-ATPase. Conditions that affect occupancy of catalytic and noncatalytic sites. J Biol Chem. 1986 Sep 25;261(27):12544–12549. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knowles A. F., Penefsky H. S. The subunit structure of beef heart mitochondrial adenosine triphosphatase. Isolation procedures. J Biol Chem. 1972 Oct 25;247(20):6617–6623. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melese T., Boyer P. D. Derivatization of the catalytic subunits of the chloroplast ATPase by 2-azido-ATP and dicyclohexylcarbodiimide. Evidence for catalytically induced interchange of the subunits. J Biol Chem. 1985 Dec 15;260(29):15398–15401. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nalin C. M., Cross R. L. Adenine nucleotide binding sites on beef heart F1-ATPase. Specificity of cooperative interactions between catalytic sites. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jul 25;257(14):8055–8060. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penefsky H. S. Reversible binding of Pi by beef heart mitochondrial adenosine triphosphatase. J Biol Chem. 1977 May 10;252(9):2891–2899. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Senior A. E., Wise J. G. The proton-ATPase of bacteria and mitochondria. J Membr Biol. 1983;73(2):105–124. doi: 10.1007/BF01870434. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vignais P. V., Lunardi J. Chemical probes of the mitochondrial ATP synthesis and translocation. Annu Rev Biochem. 1985;54:977–1014. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.54.070185.004553. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker J. E., Fearnley I. M., Gay N. J., Gibson B. W., Northrop F. D., Powell S. J., Runswick M. J., Saraste M., Tybulewicz V. L. Primary structure and subunit stoichiometry of F1-ATPase from bovine mitochondria. J Mol Biol. 1985 Aug 20;184(4):677–701. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90313-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong S. Y., Matsuno-Yagi A., Hatefi Y. Kinetics of ATP hydrolysis by F1-ATPase and the effects of anion activation, removal of tightly bound nucleotides, and partial inhibition of the ATPase by covalent modification. Biochemistry. 1984 Oct 9;23(21):5004–5009. doi: 10.1021/bi00316a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Dongen M. B., de Geus J. P., Korver T., Hartog A. F., Berden J. A. Binding and hydrolysis of 2-azido-ATP and 8-azido-ATP by isolated mitochondrial F1: characterisation of high-affinity binding sites. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Jul 2;850(2):359–368. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(86)90192-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



