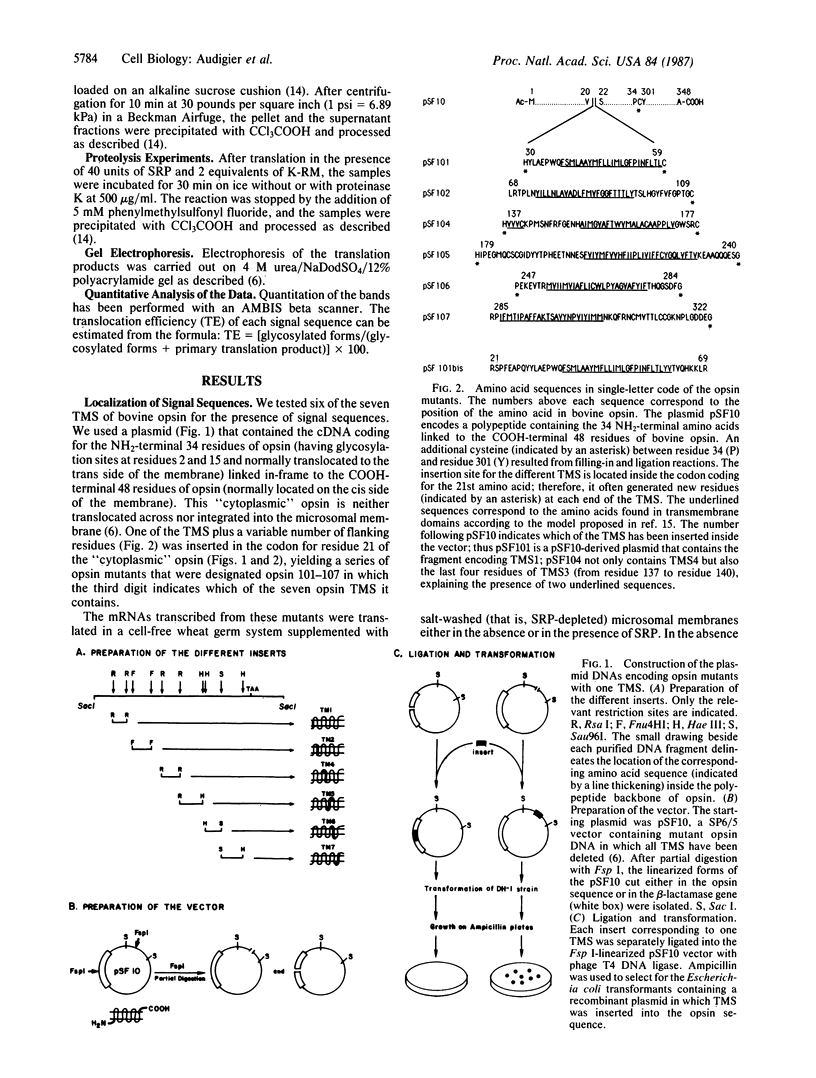
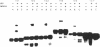Abstract
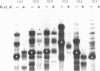
Bovine opsin, a polytopic integral membrane protein, contains seven transmembrane segments connecting eight hydrophilic domains alternating on each side of the membrane. To localize topogenic sequences that might specify the distinct topology of opsin in the membrane, we constructed various opsin mutants, each containing only one transmembrane segment. Messenger RNAs transcribed from these mutants were translated in a cell-free system supplemented with microsomal membranes. Among six of the seven transmembrane segments of opsin that were analyzed, five were able to function as signal sequences and also expressed stop-transfer sequences of variable strength. By the criteria of extractability at pH 11 and protease sensitivity, the presence of a signal sequence in combination with a "strong" stop-transfer sequence yielded integration into the lipid bilayer of the majority of chains. However, in combination with a "weak" stop-transfer sequence, we observed integration into the lipid bilayer of only some chains, with the others either completely translocated across the membrane or retained in a water-accessible space in the membrane.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson D. J., Blobel G. Immunoprecipitation of proteins from cell-free translations. Methods Enzymol. 1983;96:111–120. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(83)96012-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson D. J., Walter P., Blobel G. Signal recognition protein is required for the integration of acetylcholine receptor delta subunit, a transmembrane glycoprotein, into the endoplasmic reticulum membrane. J Cell Biol. 1982 May;93(2):501–506. doi: 10.1083/jcb.93.2.501. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blobel G., Dobberstein B. Transfer of proteins across membranes. I. Presence of proteolytically processed and unprocessed nascent immunoglobulin light chains on membrane-bound ribosomes of murine myeloma. J Cell Biol. 1975 Dec;67(3):835–851. doi: 10.1083/jcb.67.3.835. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blobel G., Dobberstein B. Transfer of proteins across membranes. II. Reconstitution of functional rough microsomes from heterologous components. J Cell Biol. 1975 Dec;67(3):852–862. doi: 10.1083/jcb.67.3.852. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blobel G. Intracellular protein topogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Mar;77(3):1496–1500. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.3.1496. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonatti S., Blobel G. Absence of a cleavable signal sequence in Sindbis virus glycoprotein PE2. J Biol Chem. 1979 Dec 25;254(24):12261–12264. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bos T. J., Davis A. R., Nayak D. P. NH2-terminal hydrophobic region of influenza virus neuraminidase provides the signal function in translocation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(8):2327–2331. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.8.2327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiRienzo J. M., Nakamura K., Inouye M. The outer membrane proteins of Gram-negative bacteria: biosynthesis, assembly, and functions. Annu Rev Biochem. 1978;47:481–532. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.47.070178.002405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erickson A. H., Blobel G. Cell-free translation of messenger RNA in a wheat germ system. Methods Enzymol. 1983;96:38–50. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(83)96007-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans E. A., Gilmore R., Blobel G. Purification of microsomal signal peptidase as a complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Feb;83(3):581–585. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.3.581. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedlander M., Blobel G. Bovine opsin has more than one signal sequence. 1985 Nov 28-Dec 4Nature. 318(6044):338–343. doi: 10.1038/318338a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujiki Y., Hubbard A. L., Fowler S., Lazarow P. B. Isolation of intracellular membranes by means of sodium carbonate treatment: application to endoplasmic reticulum. J Cell Biol. 1982 Apr;93(1):97–102. doi: 10.1083/jcb.93.1.97. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilmore R., Blobel G. Translocation of secretory proteins across the microsomal membrane occurs through an environment accessible to aqueous perturbants. Cell. 1985 Sep;42(2):497–505. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90107-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilmore R., Walter P., Blobel G. Protein translocation across the endoplasmic reticulum. II. Isolation and characterization of the signal recognition particle receptor. J Cell Biol. 1982 Nov;95(2 Pt 1):470–477. doi: 10.1083/jcb.95.2.470. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holland E. C., Drickamer K. Signal recognition particle mediates the insertion of a transmembrane protein which has a cytoplasmic NH2 terminus. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jan 25;261(3):1286–1292. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz F. N., Rothman J. E., Lingappa V. R., Blobel G., Lodish H. F. Membrane assembly in vitro: synthesis, glycosylation, and asymmetric insertion of a transmembrane protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Aug;74(8):3278–3282. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.8.3278. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lerner R. A. Tapping the immunological repertoire to produce antibodies of predetermined specificity. Nature. 1982 Oct 14;299(5884):593–596. doi: 10.1038/299592a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lingappa V. R., Chaidez J., Yost C. S., Hedgpeth J. Determinants for protein localization: beta-lactamase signal sequence directs globin across microsomal membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jan;81(2):456–460. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.2.456. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lingappa V. R., Katz F. N., Lodish H. F., Blobel G. A signal sequence for the insertion of a transmembrane glycoprotein. Similarities to the signals of secretory proteins in primary structure and function. J Biol Chem. 1978 Dec 25;253(24):8667–8670. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lingappa V. R., Shields D., Woo S. L., Blobel G. Nascent chicken ovalbumin contains the functional equivalent of a signal sequence. J Cell Biol. 1978 Nov;79(2 Pt 1):567–572. doi: 10.1083/jcb.79.2.567. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipp J., Dobberstein B. The membrane-spanning segment of invariant chain (I gamma) contains a potentially cleavable signal sequence. Cell. 1986 Sep 26;46(7):1103–1112. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90710-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melton D. A., Krieg P. A., Rebagliati M. R., Maniatis T., Zinn K., Green M. R. Efficient in vitro synthesis of biologically active RNA and RNA hybridization probes from plasmids containing a bacteriophage SP6 promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 25;12(18):7035–7056. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.18.7035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer D. I., Krause E., Dobberstein B. Secretory protein translocation across membranes-the role of the "docking protein'. Nature. 1982 Jun 24;297(5868):647–650. doi: 10.1038/297647a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milstein C., Brownlee G. G., Harrison T. M., Mathews M. B. A possible precursor of immunoglobulin light chains. Nat New Biol. 1972 Sep 27;239(91):117–120. doi: 10.1038/newbio239117a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathans J., Hogness D. S. Isolation, sequence analysis, and intron-exon arrangement of the gene encoding bovine rhodopsin. Cell. 1983 Oct;34(3):807–814. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90537-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ovchinnikov YuA Rhodopsin and bacteriorhodopsin: structure-function relationships. FEBS Lett. 1982 Nov 8;148(2):179–191. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(82)80805-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmiter R. D., Gagnon J., Walsh K. A. Ovalbumin: a secreted protein without a transient hydrophobic leader sequence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jan;75(1):94–98. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.1.94. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spiess M., Lodish H. F. An internal signal sequence: the asialoglycoprotein receptor membrane anchor. Cell. 1986 Jan 17;44(1):177–185. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90496-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toneguzzo F., Ghosh H. P. In vitro synthesis of vesicular stomatitis virus membrane glycoprotein and insertion into membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Feb;75(2):715–719. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.2.715. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walter P., Blobel G. Preparation of microsomal membranes for cotranslational protein translocation. Methods Enzymol. 1983;96:84–93. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(83)96010-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walter P., Blobel G. Signal recognition particle contains a 7S RNA essential for protein translocation across the endoplasmic reticulum. Nature. 1982 Oct 21;299(5885):691–698. doi: 10.1038/299691a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yost C. S., Hedgpeth J., Lingappa V. R. A stop transfer sequence confers predictable transmembrane orientation to a previously secreted protein in cell-free systems. Cell. 1983 Oct;34(3):759–766. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90532-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu J., Fischman D. A., Steck T. L. Selective solubilization of proteins and phospholipids from red blood cell membranes by nonionic detergents. J Supramol Struct. 1973;1(3):233–248. doi: 10.1002/jss.400010308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zerial M., Melancon P., Schneider C., Garoff H. The transmembrane segment of the human transferrin receptor functions as a signal peptide. EMBO J. 1986 Jul;5(7):1543–1550. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04395.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Heijne G. Towards a comparative anatomy of N-terminal topogenic protein sequences. J Mol Biol. 1986 May 5;189(1):239–242. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90394-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]