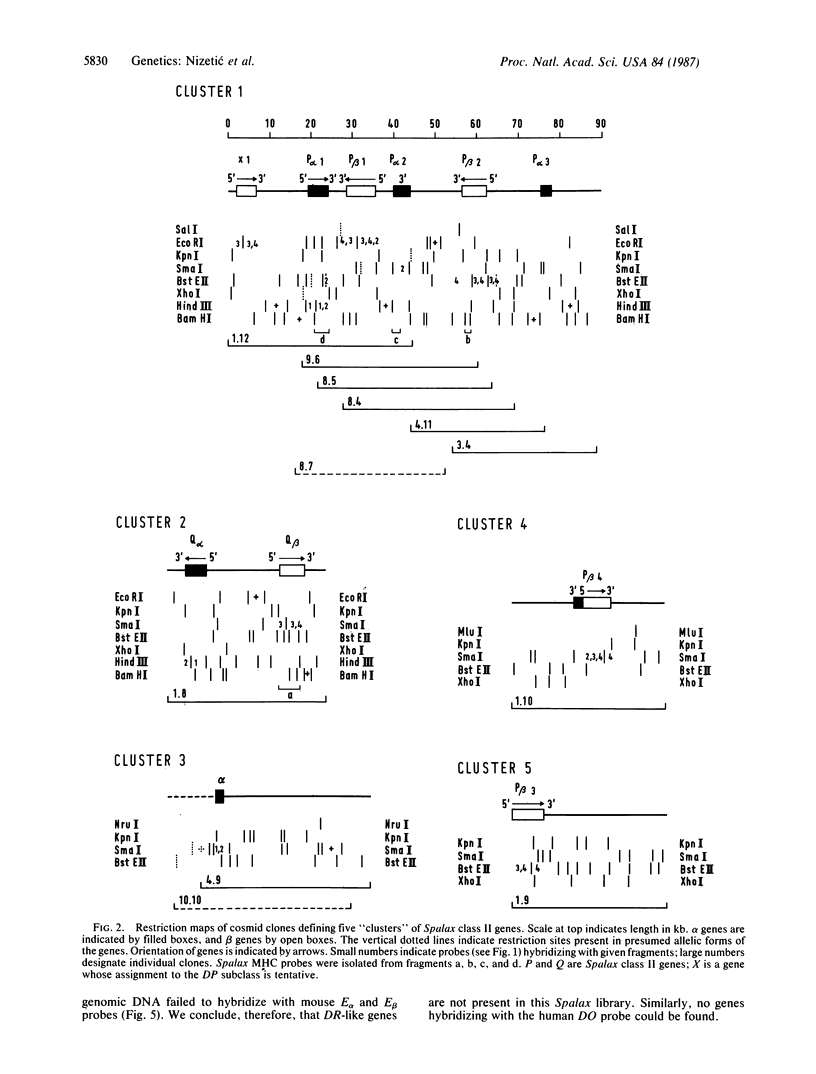
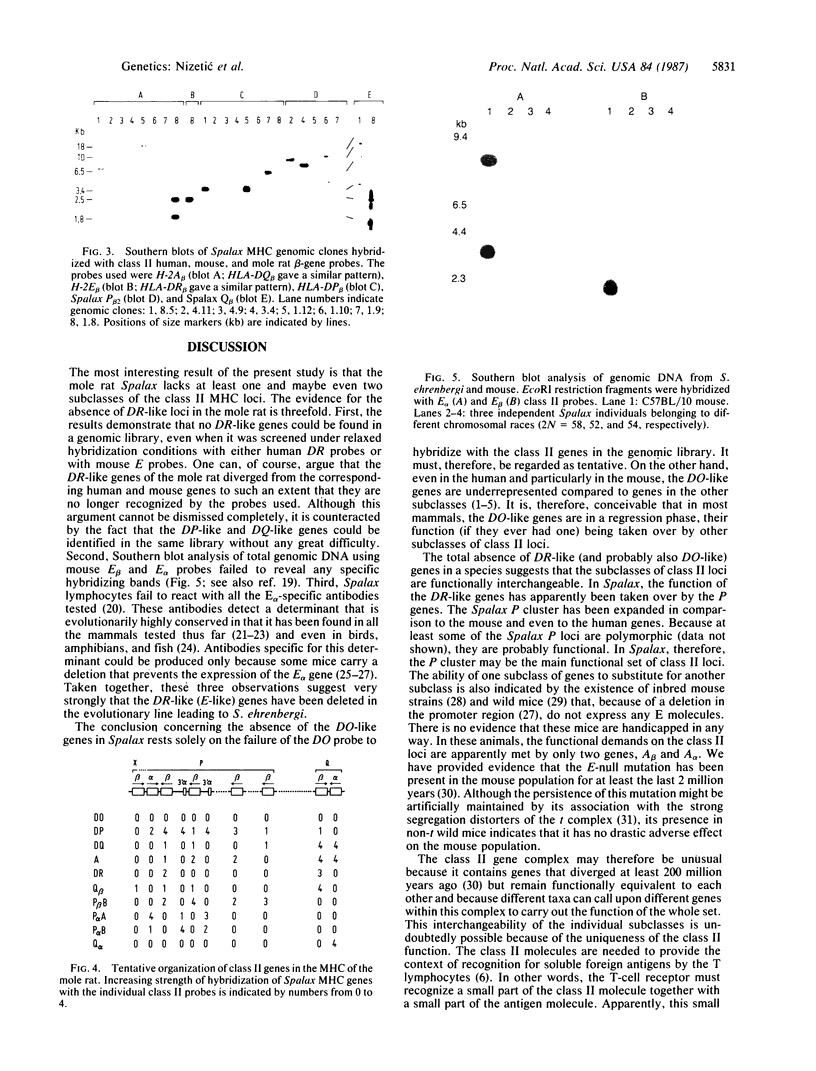
Abstract
A genomic DNA library prepared from the kidney of the mole rat Spalax ehrenbergi was screened with mouse probes representing major histocompatibility complex genes that encode alpha and beta polypeptide chains of class II molecules (alpha and beta genes). Restriction maps were constructed for the cross-hybridizing clones, and the class II genes borne by these clones were identified. By this procedure, five main regions containing class II genes were established. One region contained four genes and two gene fragments, the second region contained two genes, the third region contained one gene and one gene fragment, and the remaining two regions contained one gene each. Altogether, six beta genes, two alpha genes, and three alpha-gene fragments were identified. Two of the genes (one alpha and one beta) were established as belonging to the DQ subclass, and all other genes were found to be members of the DP subclass. (Subclass designations are based on the human HLA class II genes). No genes belonging to the DR and DO (DZ) subclasses were found in the library. The absence of DR genes in S. ehrenbergi was also indicated when other experimental methods were used. At least some of the DP loci are polymorphic and most likely also functional. Thus, in the evolution of the mole rat, the DR (and probably also the DO) loci have been deleted and their function(s) has been taken over by the DP loci, which have expanded to a great extent. These findings argue for functional interchangeability of the individual subclasses of class II loci.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Auffray C., Korman A. J., Roux-Dosseto M., Bono R., Strominger J. L. cDNA clone for the heavy chain of the human B cell alloantigen DC1: strong sequence homology to the HLA-DR heavy chain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Oct;79(20):6337–6341. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.20.6337. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Auffray C., Lillie J. W., Arnot D., Grossberger D., Kappes D., Strominger J. L. Isotypic and allotypic variation of human class II histocompatibility antigen alpha-chain genes. Nature. 1984 Mar 22;308(5957):327–333. doi: 10.1038/308327a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell J. I., Denny D. W., Jr, McDevitt H. O. Structure and polymorphism of murine and human class II major histocompatibility antigens. Immunol Rev. 1985 Jul;84:51–71. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1985.tb01125.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis M. M., Cohen D. I., Nielsen E. A., Steinmetz M., Paul W. E., Hood L. Cell-type-specific cDNA probes and the murine I region: the localization and orientation of Ad alpha. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):2194–2198. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.2194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dembic Z., Ayane M., Klein J., Steinmetz M., Benoist C. O., Mathis D. J. Inbred and wild mice carry identical deletions in their E alpha MHC genes. EMBO J. 1985 Jan;4(1):127–131. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb02326.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dembić Z., Singer P. A., Klein J. Eo: a history of a mutation. EMBO J. 1984 Jul;3(7):1647–1654. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02025.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flavell R. A., Allen H., Huber B., Wake C., Widera G. Organization and expression of the MHC of the C57 black/10 mouse. Immunol Rev. 1985 Jul;84:29–50. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1985.tb01124.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grosveld F. G., Lund T., Murray E. J., Mellor A. L., Dahl H. H., Flavell R. A. The construction of cosmid libraries which can be used to transform eukaryotic cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Nov 11;10(21):6715–6732. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.21.6715. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones P. P., Murphy D. B., McDevitt H. O. Two-gene control of the expression of a murine Ia antigen. J Exp Med. 1978 Oct 1;148(4):925–939. doi: 10.1084/jem.148.4.925. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kappes D. J., Arnot D., Okada K., Strominger J. L. Structure and polymorphism of the HLA class II SB light chain genes. EMBO J. 1984 Dec 1;3(12):2985–2993. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02245.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein J., Figueroa F. Evolution of the major histocompatibility complex. Crit Rev Immunol. 1986;6(4):295–386. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korman A. J., Auffray C., Schamboeck A., Strominger J. L. The amino acid sequence and gene organization of the heavy chain of the HLA-DR antigen: homology to immunoglobulins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Oct;79(19):6013–6017. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.19.6013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korman A. J., Boss J. M., Spies T., Sorrentino R., Okada K., Strominger J. L. Genetic complexity and expression of human class II histocompatibility antigens. Immunol Rev. 1985 Jul;85:45–86. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1985.tb01130.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Long E. O., Strubin M., Wake C. T., Gross N., Carrel S., Goodfellow P., Accolla R. S., Mach B. Isolation of cDNA clones for the p33 invariant chain associated with HLA-DR antigens. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Sep;80(18):5714–5718. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.18.5714. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lunney J. K., Mann D. L., Sachs D. H. Sharing Ia antigens between species. III. Ia specificities shared between mice and human beings. Scand J Immunol. 1979;10(5):403–413. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1979.tb01369.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathis D. J., Benoist C., Williams V. E., 2nd, Kanter M., McDevitt H. O. Several mechanisms can account for defective E alpha gene expression in different mouse haplotypes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jan;80(1):273–277. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.1.273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nizetić D., Figueroa F., Klein J. Evolutionary relationships between the t and H-2 haplotypes in the house mouse. Immunogenetics. 1984;19(4):311–320. doi: 10.1007/BF00345404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nizetić D., Figueroa F., Müller H. J., Arden B., Nevo E., Klein J. Major histocompatibility complex of the mole-rat. I. Serological and biochemical analysis. Immunogenetics. 1984;20(4):443–451. doi: 10.1007/BF00345618. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nizetić D., Figueroa F., Nevo E., Klein J. Major histocompatibility complex of the mole-rat. II. Restriction fragment polymorphism. Immunogenetics. 1985;22(1):55–67. doi: 10.1007/BF00430594. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roux-Dosseto M., Auffray C., Lillie J. W., Boss J. M., Cohen D., DeMars R., Mawas C., Seidman J. G., Strominger J. L. Genetic mapping of a human class II antigen beta-chain cDNA clone to the SB region of the HLA complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Oct;80(19):6036–6040. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.19.6036. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinohara N., Sachs D. H. Evidence for homologues of the murine I-A and I-E loci in the rat MHC. J Immunol. 1981 Mar;126(3):934–937. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinohara N., Sachs D. H., Nonaka N., Yamamoto H. Phylogenetic tracing of Ia genes. Nature. 1981 Jul 23;292(5821):362–363. doi: 10.1038/292362a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinmetz M., Minard K., Horvath S., McNicholas J., Srelinger J., Wake C., Long E., Mach B., Hood L. A molecular map of the immune response region from the major histocompatibility complex of the mouse. Nature. 1982 Nov 4;300(5887):35–42. doi: 10.1038/300035a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tonnelle C., DeMars R., Long E. O. DO beta: a new beta chain gene in HLA-D with a distinct regulation of expression. EMBO J. 1985 Nov;4(11):2839–2847. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04012.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trowsdale J., Young J. A., Kelly A. P., Austin P. J., Carson S., Meunier H., So A., Erlich H. A., Spielman R. S., Bodmer J. Structure, sequence and polymorphism in the HLA-D region. Immunol Rev. 1985 Jul;85:5–43. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1985.tb01129.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vieira J., Messing J. The pUC plasmids, an M13mp7-derived system for insertion mutagenesis and sequencing with synthetic universal primers. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):259–268. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90015-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]





