Abstract
We investigated the role of the Moloney helper virus, Moloney murine leukemia virus (Mo-MuLV), in cell transformation and tumor induction by the defective Abelson murine leukemia virus (Ab-MuLV). A molecular clone of Ab-MuLV (P160 strain) was transfected into the psi 2 packaging cell line, and helper virus-free Ab-MuLV (psi 2) was harvested from the supernatant medium. Ab-MuLV (psi 2) was as efficient as helper virus-containing Ab-MuLV (Mo-MuLV) in the transformation of primary bone marrow cells in vitro. Inoculation of weanling BALB/c mice with Ab-MuLV (psi 2) induced nonthymic pre-B-cell lymphomas with high efficiency and short latency (28 days). Adult BALB/c mice were less sensitive to tumor induction by a factor of 100. Ab-MuLV (psi 2) did not induce tumors in weanling C57BL/6 mice, unlike Ab-MuLV (Mo-MuLV). Examination of the proviral integration pattern in Ab-MuLV (psi 2)-induced tumor cell DNA revealed that each of the tumors contained a single integrated provirus. Immunoprecipitation of viral-encoded proteins in helper virus-free tumor cell lines detected the P160 Ab-MuLV-transforming protein; however, no trace of the gag, pol, and env helper virus-encoded proteins was found. Our results indicate that integration and expression of a single Ab-MuLV genome is sufficient for efficient transformation of primary bone marrow cells by Ab-MuLV in vitro and tumor induction in susceptible mice. However, the helper virus may contribute to tumor induction in weanling resistant mice.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alt F., Rosenberg N., Lewis S., Thomas E., Baltimore D. Organization and reorganization of immunoglobulin genes in A-MULV-transformed cells: rearrangement of heavy but not light chain genes. Cell. 1981 Dec;27(2 Pt 1):381–390. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90421-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baumbach W. R., Keath E. J., Cole M. D. A mouse c-myc retrovirus transforms established fibroblast lines in vitro and induces monocyte-macrophage tumors in vivo. J Virol. 1986 Aug;59(2):276–283. doi: 10.1128/jvi.59.2.276-283.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berger S. A., Sanderson N., Bernstein A., Hankins W. D. Induction of the early stages of Friend erythroleukemia with helper-free Friend spleen focus-forming virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Oct;82(20):6913–6917. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.20.6913. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bestwick R. K., Hankins W. D., Kabat D. Roles of helper and defective retroviral genomes in murine erythroleukemia: studies of spleen focus-forming virus in the absence of helper. J Virol. 1985 Dec;56(3):660–664. doi: 10.1128/jvi.56.3.660-664.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cianciolo G. J., Copeland T. D., Oroszlan S., Snyderman R. Inhibition of lymphocyte proliferation by a synthetic peptide homologous to retroviral envelope proteins. Science. 1985 Oct 25;230(4724):453–455. doi: 10.1126/science.2996136. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cianciolo G. J., Matthews T. J., Bolognesi D. P., Snyderman R. Macrophage accumulation in mice is inhibited by low molecular weight products from murine leukemia viruses. J Immunol. 1980 Jun;124(6):2900–2905. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook W. D. Rapid thymomas induced by Abelson murine leukemia virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 May;79(9):2917–2921. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.9.2917. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook W. D. Thymocyte subsets transformed by Abelson murine leukemia virus. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Feb;5(2):390–397. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.2.390. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuypers H. T., Selten G. C., Zijlstra M., de Goede R. E., Melief C. J., Berns A. J. Tumor progression in murine leukemia virus-induced T-cell lymphomas: monitoring clonal selections with viral and cellular probes. J Virol. 1986 Oct;60(1):230–241. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.1.230-241.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuypers H. T., Selten G., Quint W., Zijlstra M., Maandag E. R., Boelens W., van Wezenbeek P., Melief C., Berns A. Murine leukemia virus-induced T-cell lymphomagenesis: integration of proviruses in a distinct chromosomal region. Cell. 1984 May;37(1):141–150. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90309-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dale B., Ozanne B. Characterization of mouse cellular deoxyribonucleic acid homologous to Abelson murine leukemia virus-specific sequences. Mol Cell Biol. 1981 Aug;1(8):731–742. doi: 10.1128/mcb.1.8.731. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goff S. P., Gilboa E., Witte O. N., Baltimore D. Structure of the Abelson murine leukemia virus genome and the homologous cellular gene: studies with cloned viral DNA. Cell. 1980 Dec;22(3):777–785. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90554-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., van der Eb A. J. A new technique for the assay of infectivity of human adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1973 Apr;52(2):456–467. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green P. L., Kaehler D. A., Risser R. Clonal dominance and progression in Abelson murine leukemia virus lymphomagenesis. J Virol. 1987 Jul;61(7):2192–2197. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.7.2192-2197.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green P. L., Lamph W. W., Dudley J., Arfsten A., Risser R., Lanier L. L., Warner N. L., Tung J. S., Scheid M. P. Phenotypic variation in clonal Abelson virus lymphoma cells. J Immunol. 1985 Feb;134(2):1268–1275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grunwald D. J., Dale B., Dudley J., Lamph W., Sugden B., Ozanne B., Risser R. Loss of viral gene expression and retention of tumorigenicity by Abelson lymphoma cells. J Virol. 1982 Jul;43(1):92–103. doi: 10.1128/jvi.43.1.92-103.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartley J. W., Rowe W. P., Capps W. I., Huebner R. J. Isolation of naturally occurring viruses of the murine leukemia virus group in tissue culture. J Virol. 1969 Feb;3(2):126–132. doi: 10.1128/jvi.3.2.126-132.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartley J. W., Rowe W. P. Clonal cells lines from a feral mouse embryo which lack host-range restrictions for murine leukemia viruses. Virology. 1975 May;65(1):128–134. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(75)90013-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson I. C., Lieber M. M., Todaro G. J. Mink cell line Mv 1 Lu (CCL 64). Focus formation and the generation of "nonproducer" transformed cell lines with murine and feline sarcoma viruses. Virology. 1974 Jul;60(1):282–287. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(74)90386-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirt B. Selective extraction of polyoma DNA from infected mouse cell cultures. J Mol Biol. 1967 Jun 14;26(2):365–369. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90307-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopkins N., Besmer P., DeLeo A. B., Law L. W. High-frequency cotransfer of the transformed phenotype and a tumor-specific transplantation antigen by DNA from the 3-methylcholanthrene-induced Meth A sarcoma of BALB/c mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Dec;78(12):7555–7559. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.12.7555. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horowitz J. M., Risser R. A locus that enhances the induction of endogenous ecotropic murine leukemia viruses is distinct from genome-length ecotropic proviruses. J Virol. 1982 Dec;44(3):950–957. doi: 10.1128/jvi.44.3.950-957.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jähner D., Jaenisch R. Integration of Moloney leukaemia virus into the germ line of mice: correlation between site of integration and virus activation. Nature. 1980 Oct 2;287(5781):456–458. doi: 10.1038/287456a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessler S. W. Rapid isolation of antigens from cells with a staphylococcal protein A-antibody adsorbent: parameters of the interaction of antibody-antigen complexes with protein A. J Immunol. 1975 Dec;115(6):1617–1624. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mann R., Mulligan R. C., Baltimore D. Construction of a retrovirus packaging mutant and its use to produce helper-free defective retrovirus. Cell. 1983 May;33(1):153–159. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90344-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manning D. D., Reed N. D., Shaffer C. F. Maintenance of skin xenografts of widely divergent phylogenetic origin of congenitally athymic (nude) mice. J Exp Med. 1973 Aug 1;138(2):488–494. doi: 10.1084/jem.138.2.488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKearn J. P., Rosenberg N. Mapping cell surface antigens on mouse pre-B cell lines. Eur J Immunol. 1985 Mar;15(3):295–298. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830150316. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orosz C. G., Zinn N. E., Olsen R. G., Mathes L. E. Retrovirus-mediated immunosuppression. I. FeLV-UV and specific FeLV proteins alter T lymphocyte behavior by inducing hyporesponsiveness to lymphokines. J Immunol. 1985 May;134(5):3396–3403. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potter M., Sklar M. D., Rowe W. P. Rapid viral induction of plasmacytomas in pristane-primed BALB-c mice. Science. 1973 Nov 9;182(4112):592–594. doi: 10.1126/science.182.4112.592. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raschke W. C., Baird S., Ralph P., Nakoinz I. Functional macrophage cell lines transformed by Abelson leukemia virus. Cell. 1978 Sep;15(1):261–267. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90101-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddy E. P., Smith M. J., Srinivasan A. Nucleotide sequence of Abelson murine leukemia virus genome: structural similarity of its transforming gene product to other onc gene products with tyrosine-specific kinase activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(12):3623–3627. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.12.3623. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Risser R., Kaehler D., Lamph W. W. Different genes control the susceptibility of mice to Moloney or Abelson murine leukemia viruses. J Virol. 1985 Sep;55(3):547–553. doi: 10.1128/jvi.55.3.547-553.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
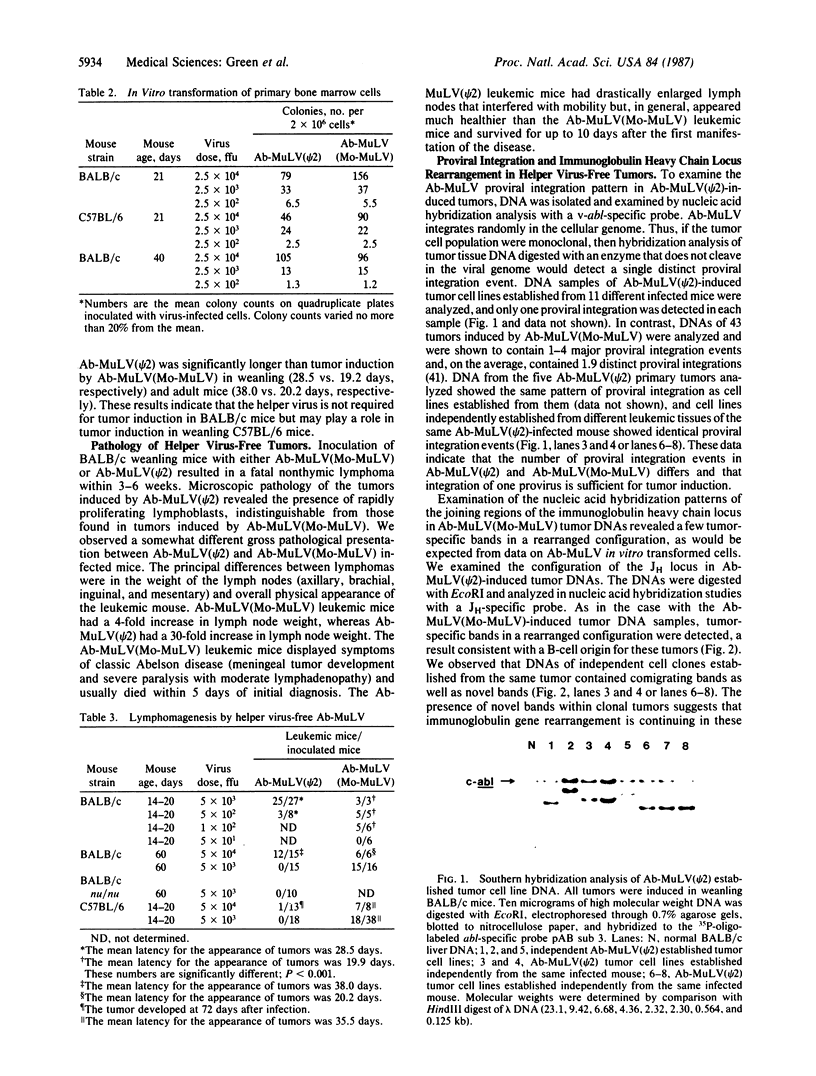
- Risser R., Potter M., Rowe W. P. Abelson virus-induced lymphomagenesis in mice. J Exp Med. 1978 Sep 1;148(3):714–726. doi: 10.1084/jem.148.3.714. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg N. E., Clark D. R., Witte O. N. Abelson murine leukemia virus mutants deficient in kinase activity and lymphoid cell transformation. J Virol. 1980 Dec;36(3):766–774. doi: 10.1128/jvi.36.3.766-774.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg N., Baltimore D. A quantitative assay for transformation of bone marrow cells by Abelson murine leukemia virus. J Exp Med. 1976 Jun 1;143(6):1453–1463. doi: 10.1084/jem.143.6.1453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg N., Baltimore D., Scher C. D. In vitro transformation of lymphoid cells by Abelson murine leukemia virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 May;72(5):1932–1936. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.5.1932. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg N., Baltimore D. The effect of helper virus on Abelson virus-induced transformation of lymphoid cells. J Exp Med. 1978 Apr 1;147(4):1126–1141. doi: 10.1084/jem.147.4.1126. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowe W. P., Pugh W. E., Hartley J. W. Plaque assay techniques for murine leukemia viruses. Virology. 1970 Dec;42(4):1136–1139. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(70)90362-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scher C. D. Effect of pseudotype on Abelson virus and Kirsten sarcoma virus-induced leukemia. J Exp Med. 1978 Apr 1;147(4):1044–1053. doi: 10.1084/jem.147.4.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scher C. D., Siegler R. Direct transformation of 3T3 cells by Abelson murine leukaemia virus. Nature. 1975 Feb 27;253(5494):729–731. doi: 10.1038/253729a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shields A., Goff S., Paskind M., Otto G., Baltimore D. Structure of the Abelson murine leukemia virus genome. Cell. 1979 Dec;18(4):955–962. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90208-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sklar M. D., Shevach E. M., Green I., Potter M. Transplantation and preliminary characterisation of lymphocyte surface markers of Abelson virus-induced lymphomas. Nature. 1975 Feb 13;253(5492):550–552. doi: 10.1038/253550a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Srinivasan A., Reddy E. P., Aaronson S. A. Abelson murine leukemia virus: molecular cloning of infectious integrated proviral DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Apr;78(4):2077–2081. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.4.2077. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang J. Y., Ledley F., Goff S., Lee R., Groner Y., Baltimore D. The mouse c-abl locus: molecular cloning and characterization. Cell. 1984 Feb;36(2):349–356. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90228-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang J. Y., Queen C., Baltimore D. Expression of an Abelson murine leukemia virus-encoded protein in Escherichia coli causes extensive phosphorylation of tyrosine residues. J Biol Chem. 1982 Nov 25;257(22):13181–13184. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe S., Temin H. M. Encapsidation sequences for spleen necrosis virus, an avian retrovirus, are between the 5' long terminal repeat and the start of the gag gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Oct;79(19):5986–5990. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.19.5986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witte O. N., Ponticelli A., Gifford A., Baltimore D., Rosenberg N., Elder J. Phosphorylation of the Abelson murine leukemia virus transforming protein. J Virol. 1981 Sep;39(3):870–878. doi: 10.1128/jvi.39.3.870-878.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolff L., Ruscetti S. Malignant transformation of erythroid cells in vivo by introduction of a nonreplicating retrovirus vector. Science. 1985 Jun 28;228(4707):1549–1552. doi: 10.1126/science.2990034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolff L., Tambourin P., Ruscetti S. Induction of the autonomous stage of transformation in erythroid cells infected with SFFV: helper virus is not required. Virology. 1986 Jul 15;152(1):272–276. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90393-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]