Abstract
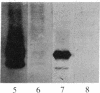
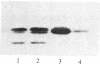
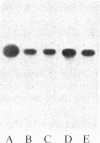
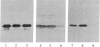
In vitro-transcribed human interferon-beta (IFN-beta) mRNA, which contains all the sequence of the natural molecule, is poorly translated in a reticulocyte lysate or when injected in Xenopus oocytes. This low level of translation is due to an inhibition by the 5' and 3' untranslated regions (UTRs). Indeed, the replacement of these sequences by those of Xenopus beta-globin mRNA dramatically increases the translational efficiency of the mRNA, especially in oocytes. This phenomenon is not due to a difference in mRNA stability since both native and chimeric mRNAs remain undegraded, at least during the translation period considered. Construction of different chimeric molecules having various combinations of 5' and 3' UTRs from IFN-beta or Xenopus beta-globin mRNA or a small sequence of SP6 polylinker as 5' UTR has revealed that the 3' UTR of IFN-beta in itself has a pronounced inhibitory effect on translation in the two translation systems from animal cells. Indeed, the addition of this 3' UTR at the 3' end of the coding region of a chicken lysozyme mRNA also causes a large decrease of its translational capacity in both systems. However, the nature of the 5' noncoding sequence influences the degree of translation inhibition exerted by the 3' UTR. Remarkably, we observed no difference in translation level when the different mRNAs were tested in a wheat germ extract.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Caput D., Beutler B., Hartog K., Thayer R., Brown-Shimer S., Cerami A. Identification of a common nucleotide sequence in the 3'-untranslated region of mRNA molecules specifying inflammatory mediators. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(6):1670–1674. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.6.1670. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Derynck R., Content J., DeClercq E., Volckaert G., Tavernier J., Devos R., Fiers W. Isolation and structure of a human fibroblast interferon gene. Nature. 1980 Jun 19;285(5766):542–547. doi: 10.1038/285542a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drummond D. R., Armstrong J., Colman A. The effect of capping and polyadenylation on the stability, movement and translation of synthetic messenger RNAs in Xenopus oocytes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Oct 25;13(20):7375–7394. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.20.7375. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gurdon J. B., Lane C. D., Woodland H. R., Marbaix G. Use of frog eggs and oocytes for the study of messenger RNA and its translation in living cells. Nature. 1971 Sep 17;233(5316):177–182. doi: 10.1038/233177a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huez G., Cleuter Y., Bruck C., Van Vloten-Doting L., Goldbach R., Verduin B. Translational stability of plant viral RNAs microinjected into living cells. Influence of a 3'-poly(A) segment. Eur J Biochem. 1983 Jan 17;130(1):205–209. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07137.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johansen H., Schümperli D., Rosenberg M. Affecting gene expression by altering the length and sequence of the 5' leader. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(24):7698–7702. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.24.7698. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konarska M. M., Padgett R. A., Sharp P. A. Recognition of cap structure in splicing in vitro of mRNA precursors. Cell. 1984 Oct;38(3):731–736. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90268-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Influences of mRNA secondary structure on initiation by eukaryotic ribosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 May;83(9):2850–2854. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.9.2850. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Point mutations define a sequence flanking the AUG initiator codon that modulates translation by eukaryotic ribosomes. Cell. 1986 Jan 31;44(2):283–292. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90762-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krieg P. A., Melton D. A. Functional messenger RNAs are produced by SP6 in vitro transcription of cloned cDNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 25;12(18):7057–7070. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.18.7057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marbaix G., Huez G., Burny A., Cleuter Y., Hubert E., Leclercq M., Chantrenne H., Soreq H., Nudel U., Littauer U. Z. Absence of polyadenylate segment in globin messenger RNA accelerates its degradation in Xenopus oocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Aug;72(8):3065–3067. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.8.3065. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcu K., Dudock B. Characterization of a highly efficient protein synthesizing system derived from commercial wheat germ. Nucleic Acids Res. 1974 Nov;1(11):1385–1397. doi: 10.1093/nar/1.11.1385. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meijlink F., Curran T., Miller A. D., Verma I. M. Removal of a 67-base-pair sequence in the noncoding region of protooncogene fos converts it to a transforming gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Aug;82(15):4987–4991. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.15.4987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melton D. A., Krieg P. A., Rebagliati M. R., Maniatis T., Zinn K., Green M. R. Efficient in vitro synthesis of biologically active RNA and RNA hybridization probes from plasmids containing a bacteriophage SP6 promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 25;12(18):7035–7056. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.18.7035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller A. D., Curran T., Verma I. M. c-fos protein can induce cellular transformation: a novel mechanism of activation of a cellular oncogene. Cell. 1984 Jan;36(1):51–60. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90073-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosca J. D., Pitha P. M. Transcriptional and posttranscriptional regulation of exogenous human beta interferon gene in simian cells defective in interferon synthesis. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jun;6(6):2279–2283. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.6.2279. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelham H. R., Jackson R. J. An efficient mRNA-dependent translation system from reticulocyte lysates. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Aug 1;67(1):247–256. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10656.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raj N. B., Pitha P. M. Two levels of regulation of beta-interferon gene expression in human cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(13):3923–3927. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.13.3923. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw G., Kamen R. A conserved AU sequence from the 3' untranslated region of GM-CSF mRNA mediates selective mRNA degradation. Cell. 1986 Aug 29;46(5):659–667. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90341-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soreq H., Sagar A. D., Sehgal P. B. Translational activity and functional stability of human fibroblast beta 1 and beta 2 interferon mRNAs lacking 3'-terminal RNA sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Mar;78(3):1741–1745. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.3.1741. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treisman R. Transient accumulation of c-fos RNA following serum stimulation requires a conserved 5' element and c-fos 3' sequences. Cell. 1985 Oct;42(3):889–902. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90285-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Heuvel M., Bosveld I. J., Luyten W., Trapman J., Zwarthoff E. C. Transient expression of murine interferon-alpha genes in mouse and monkey cells. Gene. 1986;45(2):159–165. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(86)90250-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]