Abstract
The poliovirus genome is replicated by a virus-encoded RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RNA polymerase). The RNA polymerase is first synthesized as a larger precursor polypeptide, which is subsequently processed by a viral proteinase, 3Cpro, to give the mature polymerase molecule, 3Dpol. To further characterize the poliovirus RNA polymerase, we have constructed plasmids that expressed this protein in Escherichia coli. The plasmids consisted of fusions between the E. coli DNA encoding the first 13 amino acids of the trp operon leader protein and viral genes encoding the 3Cpro and 3Dpol polypeptides. E. coli harboring such plasmids gave significant, inducible levels of enzymatically active RNA polymerase as determined by the poly(A).oligo(U) poly(U) polymerase assay. The purified RNA polymerase activity from E. coli corresponded to a protein with the approximate molecular weight of the mature 3Dpol protein. The availability of a recombinant, enzymatically active poliovirus RNA polymerase provides a system in which we can precisely delineate the role this enzyme plays in the regulation of poliovirus replication.
Full text
PDF

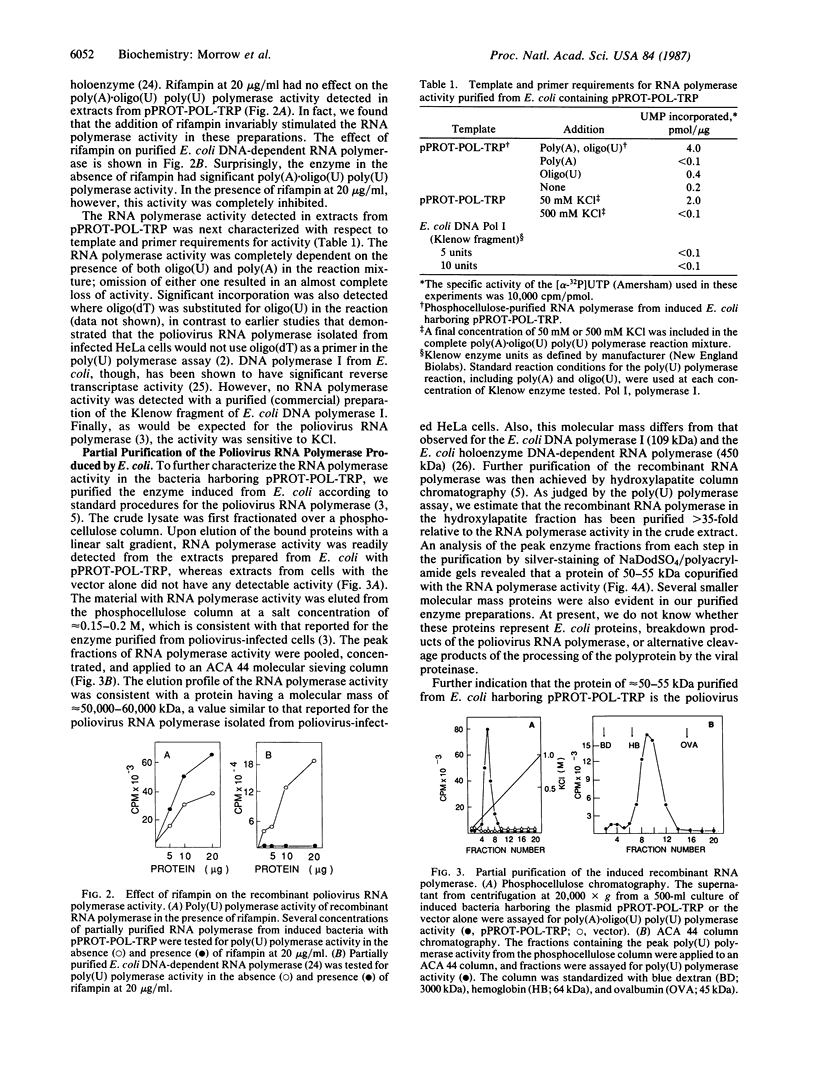


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BALTIMORE D., EGGERS H. J., FRANKLIN R. M., TAMM I. Poliovirus-induced RNA polymerase and the effects of virus-specific inhibitors on its production. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1963 Jun;49:843–849. doi: 10.1073/pnas.49.6.843. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chamberlin M., Kingston R., Gilman M., Wiggs J., deVera A. Isolation of bacterial and bacteriophage RNA polymerases and their use in synthesis of RNA in vitro. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:540–568. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01037-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dasgupta A., Baron M. H., Baltimore D. Poliovirus replicase: a soluble enzyme able to initiate copying of poliovirus RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jun;76(6):2679–2683. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.6.2679. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farmerie W. G., Loeb D. D., Casavant N. C., Hutchison C. A., 3rd, Edgell M. H., Swanstrom R. Expression and processing of the AIDS virus reverse transcriptase in Escherichia coli. Science. 1987 Apr 17;236(4799):305–308. doi: 10.1126/science.2436298. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flanegan J. B., Baltimore D. Poliovirus polyuridylic acid polymerase and RNA replicase have the same viral polypeptide. J Virol. 1979 Jan;29(1):352–360. doi: 10.1128/jvi.29.1.352-360.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flanegan J. B., Baltimore D. Poliovirus-specific primer-dependent RNA polymerase able to copy poly(A). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Sep;74(9):3677–3680. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.9.3677. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREENWOOD F. C., HUNTER W. M., GLOVER J. S. THE PREPARATION OF I-131-LABELLED HUMAN GROWTH HORMONE OF HIGH SPECIFIC RADIOACTIVITY. Biochem J. 1963 Oct;89:114–123. doi: 10.1042/bj0890114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanecak R., Semler B. L., Anderson C. W., Wimmer E. Proteolytic processing of poliovirus polypeptides: antibodies to polypeptide P3-7c inhibit cleavage at glutamine-glycine pairs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jul;79(13):3973–3977. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.13.3973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanecak R., Semler B. L., Ariga H., Anderson C. W., Wimmer E. Expression of a cloned gene segment of poliovirus in E. coli: evidence for autocatalytic production of the viral proteinase. Cell. 1984 Jul;37(3):1063–1073. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90441-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hey T. D., Richards O. C., Ehrenfeld E. Synthesis of plus- and minus-strand RNA from poliovirion RNA template in vitro. J Virol. 1986 Jun;58(3):790–796. doi: 10.1128/jvi.58.3.790-796.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ivanoff L. A., Towatari T., Ray J., Korant B. D., Petteway S. R., Jr Expression and site-specific mutagenesis of the poliovirus 3C protease in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(15):5392–5396. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.15.5392. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karkas J. D. Reverse transcription by Escherichia coli DNA polymerase I. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Dec;70(12):3834–3838. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.12.3834. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klempnauer K. H., Ramsay G., Bishop J. M., Moscovici M. G., Moscovici C., McGrath J. P., Levinson A. D. The product of the retroviral transforming gene v-myb is a truncated version of the protein encoded by the cellular oncogene c-myb. Cell. 1983 Jun;33(2):345–355. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90416-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrow C. D., Navab M., Peterson C., Hocko J., Dasgupta A. Antibody to poliovirus genome-linked protein (VPg) precipitates in vitro synthesized RNA attached to VPg-precursor polypeptide(s). Virus Res. 1984;1(2):89–100. doi: 10.1016/0168-1702(84)90066-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nichols B. P., Yanofsky C. Plasmids containing the trp promoters of Escherichia coli and Serratia marcescens and their use in expressing cloned genes. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:155–164. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01011-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nomoto A., Omata T., Toyoda H., Kuge S., Horie H., Kataoka Y., Genba Y., Nakano Y., Imura N. Complete nucleotide sequence of the attenuated poliovirus Sabin 1 strain genome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Oct;79(19):5793–5797. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.19.5793. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oakley B. R., Kirsch D. R., Morris N. R. A simplified ultrasensitive silver stain for detecting proteins in polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1980 Jul 1;105(2):361–363. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90470-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Racaniello V. R., Baltimore D. Molecular cloning of poliovirus cDNA and determination of the complete nucleotide sequence of the viral genome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Aug;78(8):4887–4891. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.8.4887. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rueckert R. R., Wimmer E. Systematic nomenclature of picornavirus proteins. J Virol. 1984 Jun;50(3):957–959. doi: 10.1128/jvi.50.3.957-959.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Semler B. L., Anderson C. W., Kitamura N., Rothberg P. G., Wishart W. L., Wimmer E. Poliovirus replication proteins: RNA sequence encoding P3-1b and the sites of proteolytic processing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jun;78(6):3464–3468. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3464. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Semler B. L., Hanecak R., Anderson C. W., Wimmer E. Cleavage sites in the polypeptide precursors of poliovirus protein P2-X. Virology. 1981 Oct 30;114(2):589–594. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90242-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Dyke T. A., Flanegan J. B. Identification of poliovirus polypeptide P63 as a soluble RNA-dependent RNA polymerase. J Virol. 1980 Sep;35(3):732–740. doi: 10.1128/jvi.35.3.732-740.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walgate R. Armadillos fight leprosy. Nature. 1981 Jun 18;291(5816):527–527. doi: 10.1038/291527a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanisch-Perron C., Vieira J., Messing J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene. 1985;33(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]