Abstract
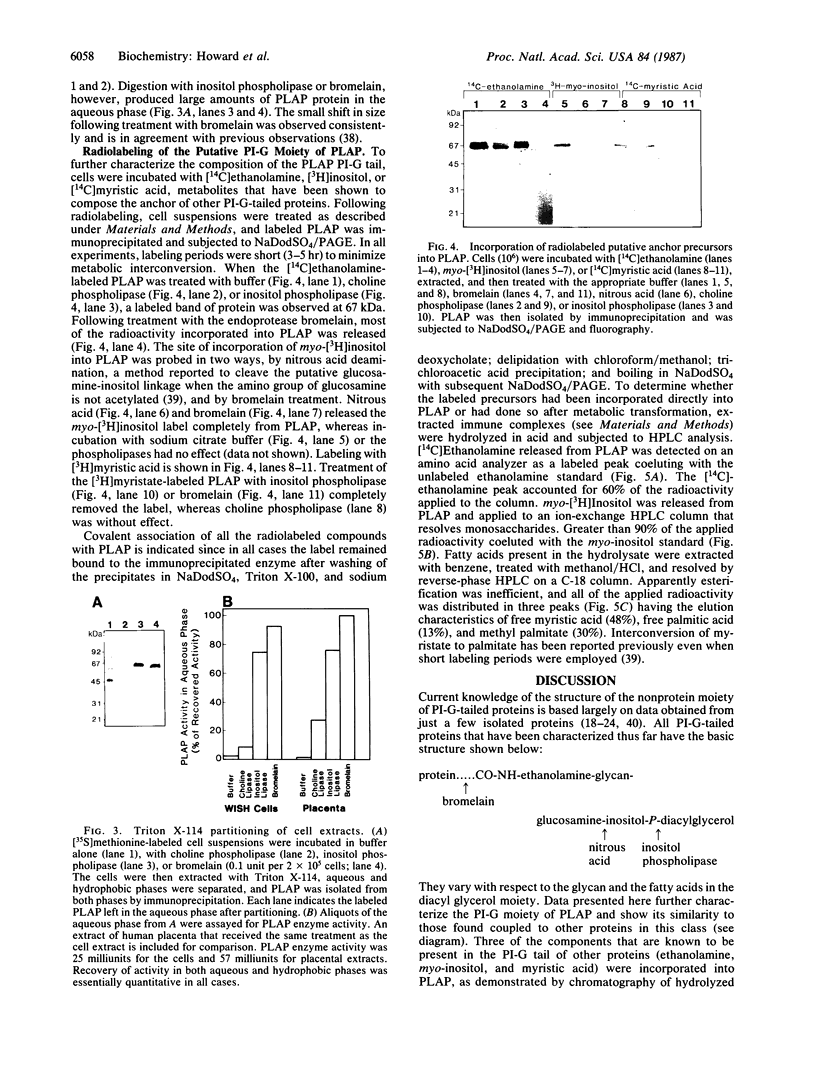
Placental alkaline phosphatase [orthophosphoric-monoester phosphohydrolase (alkaline optimum), EC 3.1.3.1] is a member of a diverse group of membrane proteins whose attachment to the lipid bilayer is mediated by a phosphatidylinositol-glycan. To investigate structural aspects of the glycolipid anchor, cultured WISH cells were used because we found that they produce the enzyme in abundant quantities. When cell suspensions were incubated with purified phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C, most of the placental alkaline phosphatase was released from membranes in a hydrophilic form. On incubation of the cells with [14C]ethanolamine, [14C]myristic acid, or myo-[3H]inositol, each was incorporated into the phosphatase near the carboxyl terminus, showing that these components, which are found in other phosphatidylinositol membrane-linked proteins, are also present in placental alkaline phosphatase.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bangs J. D., Andrews N. W., Hart G. W., Englund P. T. Posttranslational modification and intracellular transport of a trypanosome variant surface glycoprotein. J Cell Biol. 1986 Jul;103(1):255–263. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.1.255. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bangs J. D., Hereld D., Krakow J. L., Hart G. W., Englund P. T. Rapid processing of the carboxyl terminus of a trypanosome variant surface glycoprotein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(10):3207–3211. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.10.3207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berger J., Garattini E., Hua J. C., Udenfriend S. Cloning and sequencing of human intestinal alkaline phosphatase cDNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Feb;84(3):695–698. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.3.695. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berger J., Howard A. D., Gerber L., Cullen B. R., Udenfriend S. Expression of active, membrane-bound human placental alkaline phosphatase by transfected simian cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jul;84(14):4885–4889. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.14.4885. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chakrabartty A., Stinson R. A. Properties of membrane-bound and solubilized forms of alkaline phosphatase from human liver. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Apr 17;839(2):174–180. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(85)90034-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross G. A. Eukaryotic protein modification and membrane attachment via phosphatidylinositol. Cell. 1987 Jan 30;48(2):179–181. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90419-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferguson M. A., Cross G. A. Myristylation of the membrane form of a Trypanosoma brucei variant surface glycoprotein. J Biol Chem. 1984 Mar 10;259(5):3011–3015. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferguson M. A., Duszenko M., Lamont G. S., Overath P., Cross G. A. Biosynthesis of Trypanosoma brucei variant surface glycoproteins. N-glycosylation and addition of a phosphatidylinositol membrane anchor. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jan 5;261(1):356–362. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferguson M. A., Low M. G., Cross G. A. Glycosyl-sn-1,2-dimyristylphosphatidylinositol is covalently linked to Trypanosoma brucei variant surface glycoprotein. J Biol Chem. 1985 Nov 25;260(27):14547–14555. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garattini E., Margolis J., Heimer E., Felix A., Udenfriend S. Human placental alkaline phosphatase in liver and intestine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Sep;82(18):6080–6084. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.18.6080. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goz B. The induction of alkaline phosphatase activity in HeLa cells by 5-iodo-2'-deoxyuridine. Cancer Res. 1974 Sep;34(9):2393–2398. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henthorn P. S., Knoll B. J., Raducha M., Rothblum K. N., Slaughter C., Weiss M., Lafferty M. A., Fischer T., Harris H. Products of two common alleles at the locus for human placental alkaline phosphatase differ by seven amino acids. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(15):5597–5601. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.15.5597. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henthorn P. S., Raducha M., Edwards Y. H., Weiss M. J., Slaughter C., Lafferty M. A., Harris H. Nucleotide and amino acid sequences of human intestinal alkaline phosphatase: close homology to placental alkaline phosphatase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Mar;84(5):1234–1238. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.5.1234. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikezawa H., Yamanegi M., Taguchi R., Miyashita T., Ohyabu T. Studies on phosphatidylinositol phosphodiesterase (phospholipase C type) of Bacillus cereus. I. purification, properties and phosphatase-releasing activity. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Nov 19;450(2):154–164. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kam W., Clauser E., Kim Y. S., Kan Y. W., Rutter W. J. Cloning, sequencing, and chromosomal localization of human term placental alkaline phosphatase cDNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(24):8715–8719. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.24.8715. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Low M. G., Finean J. B. Release of alkaline phosphatase from membranes by a phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C. Biochem J. 1977 Oct 1;167(1):281–284. doi: 10.1042/bj1670281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malik A. S., Low M. G. Conversion of human placental alkaline phosphatase from a high Mr form to a low Mr form during butanol extraction. An investigation of the role of endogenous phosphoinositide-specific phospholipases. Biochem J. 1986 Dec 1;240(2):519–527. doi: 10.1042/bj2400519. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKenna M. J., Hamilton T. A., Sussman H. H. Comparison of human alkaline phosphatase isoenzymes. Structural evidence for three protein classes. Biochem J. 1979 Jul 1;181(1):67–73. doi: 10.1042/bj1810067. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Medof M. E., Walter E. I., Roberts W. L., Haas R., Rosenberry T. L. Decay accelerating factor of complement is anchored to cells by a C-terminal glycolipid. Biochemistry. 1986 Nov 4;25(22):6740–6747. doi: 10.1021/bi00370a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Millán J. L. Molecular cloning and sequence analysis of human placental alkaline phosphatase. J Biol Chem. 1986 Mar 5;261(7):3112–3115. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulivor R. A., Boccelli D., Harris H. Quantitative analysis of alkaline phosphatases in serum and amniotic fluid: comparison of biochemical and immunologic assays. J Lab Clin Med. 1985 Mar;105(3):342–348. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olson E. N., Towler D. A., Glaser L. Specificity of fatty acid acylation of cellular proteins. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 25;260(6):3784–3790. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ovitt C. E., Strauss A. W., Alpers D. H., Chou J. Y., Boime I. Expression of different-sized placental alkaline phosphatase mRNAs in placenta and choriocarcinoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(11):3781–3785. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.11.3781. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts W. L., Rosenberry T. L. Selective radiolabeling and isolation of the hydrophobic membrane-binding domain of human erythrocyte acetylcholinesterase. Biochemistry. 1986 Jun 3;25(11):3091–3098. doi: 10.1021/bi00359a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seargeant L. E., Stinson R. A. Evidence that three structural genes code for human alkaline phosphatases. Nature. 1979 Sep 13;281(5727):152–154. doi: 10.1038/281152a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shively J. E., Conrad H. E. Formation of anhydrosugars in the chemical depolymerization of heparin. Biochemistry. 1976 Sep 7;15(18):3932–3942. doi: 10.1021/bi00663a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein S., Brink L. Amino acid analysis of proteins and peptides at the picomole level: the fluorescamine amino acid analyzer. Methods Enzymol. 1981;79(Pt B):20–25. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(81)79008-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sundler R., Alberts A. W., Vagelos P. R. Enzymatic properties of phosphatidylinositol inositolphosphohydrolase from Bacillus cereus. Substrate dilution in detergent-phospholipid micelles and bilayer vesicles. J Biol Chem. 1978 Jun 25;253(12):4175–4179. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA and small DNA fragments transferred to nitrocellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5201–5205. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tse A. G., Barclay A. N., Watts A., Williams A. F. A glycophospholipid tail at the carboxyl terminus of the Thy-1 glycoprotein of neurons and thymocytes. Science. 1985 Nov 29;230(4729):1003–1008. doi: 10.1126/science.2865810. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss M. J., Henthorn P. S., Lafferty M. A., Slaughter C., Raducha M., Harris H. Isolation and characterization of a cDNA encoding a human liver/bone/kidney-type alkaline phosphatase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Oct;83(19):7182–7186. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.19.7182. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]