Abstract
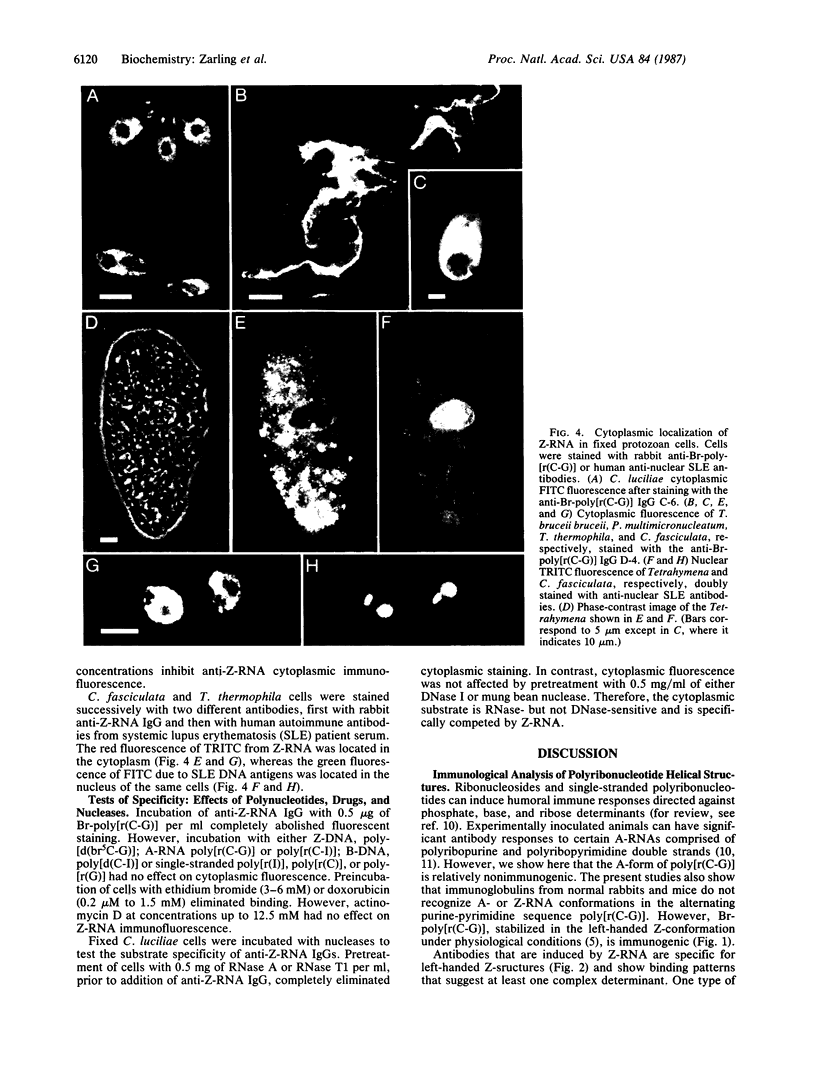
Specific immunochemical probes for Z-RNA were generated and characterized to search for possible Z-RNA-like double helices in cells. Z-RNA was detected in the cytoplasm of fixed protozoan cells by immunofluorescence microscopy using these anti-Z-RNA IgGs. In contrast, autoimmune or experimentally elicited anti-DNA antibodies, specifically reactive with B-DNA or Z-DNA, stained the nuclei. Pre-or nonimmune IgGs did not bind to the cells. RNase A or T1 digestion eliminated anti-Z-RNA IgG binding to cytoplasmic determinants; however, DNase I or mung bean nuclease had no effect. Doxorubicin and ethidium bromide prevented anti-Z-RNA antibody binding; however, actinomycin D, which does not bind double-stranded RNA, did not. Anti-Z-RNA immunofluorescence was specifically blocked in competition assays by synthetic Z-RNA but not Z-DNA, A-RNA, or single-stranded RNAs. Thus, some cytoplasmic sequences in fixed cells exist in the left-handed Z-RNA conformation.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Gaffiero G. V., Robin P., Nahon E. The mouse immune response to the double stranded polyribonucleotide complex poly(G) . poly(C). Clin Exp Immunol. 1984 Feb;55(2):264–272. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HASELKORN R. ACTINOMYCIN D AS A PROBE FOR NUCLEIC ACID SECONDARY STRUCTURE. Science. 1964 Feb 14;143(3607):682–684. doi: 10.1126/science.143.3607.682. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagen F. K., Zarling D. A., Jovin T. M. Electron microscopy of SV40 DNA cross-linked by anti-Z DNA IgG. EMBO J. 1985 Mar;4(3):837–844. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03706.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jovin T. M., McIntosh L. P., Arndt-Jovin D. J., Zarling D. A., Robert-Nicoud M., van de Sande J. H., Jorgenson K. F., Eckstein F. Left-handed DNA: from synthetic polymers to chromosomes. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 1983 Oct;1(1):21–57. doi: 10.1080/07391102.1983.10507425. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reich E., Goldberg I. H. Actinomycin and nucleic acid function. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1964;3:183–234. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60742-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Revet B., Zarling D. A., Jovin T. M., Delain E. Different Z DNA forming sequences are revealed in phi X174 RFI by high resolution darkfield immuno-electron microscopy. EMBO J. 1984 Dec 20;3(13):3353–3358. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02303.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rich A., Nordheim A., Wang A. H. The chemistry and biology of left-handed Z-DNA. Annu Rev Biochem. 1984;53:791–846. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.53.070184.004043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robert-Nicoud M., Arndt-Jovin D. J., Zarling D. A., Jovin T. M. Immunological detection of left-handed Z DNA in isolated polytene chromosomes. Effects of ionic strength, pH, temperature and topological stress. EMBO J. 1984 Apr;3(4):721–731. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01875.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silberklang M., Gillum A. M., RajBhandary U. L. Use of in vitro 32P labeling in the sequence analysis of nonradioactive tRNAs. Methods Enzymol. 1979;59:58–109. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)59072-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stollar B. D. The experimental induction of antibodies to nucleic acids. Methods Enzymol. 1980;70(A):70–85. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)70042-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zarling D. A., Arndt-Jovin D. J., McIntosh L. P., Robert-Nicoud M., Jovin T. M. Interactions of anti-poly[d(G-br5C)] IgG with synthetic, viral and cellular Z DNAs. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 1984 Mar;1(5):1081–1107. doi: 10.1080/07391102.1984.10507506. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zarling D. A., Arndt-Jovin D. J., Robert-Nicoud M., McIntosh L. P., Thomae R., Jovin T. M. Immunoglobulin recognition of synthetic and natural left-handed Z DNA conformations and sequences. J Mol Biol. 1984 Jul 5;176(3):369–415. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90495-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]