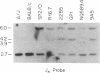
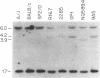
Abstract
To characterize the light chain gene segments involved in the murine immune response to keyhole limpet hemocyanin p-azophenylarsonate (Ars), we have determined the amino acid and/or nucleotide sequences of several anti-arsonate antibodies of the Ars-A family in the A/J, C.AL-20, and BALB/c strains. These structures have been compared to certain BALB/c anti-phenyloxazolone and anti-levan antibodies previously sequenced and to the A/J V kappa 10-Ars-A genomic sequence (where V kappa = kappa chain variable). These primary structural studies were complemented by Southern filter hybridization analyses utilizing V kappa and kappa chain joining (J kappa) molecular probes. We found a surprising uniformity of structure among these antibody light chains derived from different murine strains. Thus, in contrast to the heavy chain variable (Vh) regions of the Ars-A antibody family where the BALB/c strain lacks the VH gene segment utilized in the A/J Ars-A response, the light chain variable region gene segments at the V kappa 10-Ars-A locus appear to be identical between the two strains.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Azuma T., Igras V., Reilly E. B., Eisen H. N. Diversity at the variable-joining region boundary of lambda light chains has a pronounced effect on immunoglobulin ligand-binding activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Oct;81(19):6139–6143. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.19.6139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ball R. K., Chang J. Y., Alkan S. S., Braun D. G. The complete amino acid sequence of the light chain variable region of two monoclonal anti-p-azobenzene-arsonate antibodies bearing the cross-reactive idiotype. Mol Immunol. 1983 Feb;20(2):197–201. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(83)90131-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berek C., Griffiths G. M., Milstein C. Molecular events during maturation of the immune response to oxazolone. Nature. 1985 Aug 1;316(6027):412–418. doi: 10.1038/316412a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown A. R., Fried V. A. Two BALB/c anti-arsonate idiotype families: two heavy chain variable regions (Vh) shared with anti-DNP antibodies are used by one family while a Vh similar to anti-GAT antibodies is used by the other. Mol Immunol. 1987 Apr;24(4):391–398. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(87)90181-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke S. H., Claflin J. L., Potter M., Rudikoff S. Polymorphism in anti-phosphocholine antibodies reflecting evolution of immunoglobulin families. J Exp Med. 1983 Jan 1;157(1):98–113. doi: 10.1084/jem.157.1.98. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelman G. M., Gottlieb P. D. A genetic marker in the variable region of light chains of mouse immunoglobulins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Nov;67(3):1192–1199. doi: 10.1073/pnas.67.3.1192. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gearhart P. J., Bogenhagen D. F. Clusters of point mutations are found exclusively around rearranged antibody variable genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(11):3439–3443. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.11.3439. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gearhart P. J., Johnson N. D., Douglas R., Hood L. IgG antibodies to phosphorylcholine exhibit more diversity than their IgM counterparts. Nature. 1981 May 7;291(5810):29–34. doi: 10.1038/291029a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson D. Genetic polymorphism of mouse immunoglobulin light chains revealed by isoelectric focusing. J Exp Med. 1976 Jul 1;144(1):298–303. doi: 10.1084/jem.144.1.298. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottlieb P. D., Boyd R. T., Ponath P. D., Goldrick M. M. Restriction enzyme polymorphisms in V kappa and J kappa genes of inbred and wild mice. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1986;127:186–192. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-71304-0_22. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haba S., Ovary Z., Nisonoff A. Clearance of IgE from serum of normal and hybridoma-bearing mice. J Immunol. 1985 May;134(5):3291–3297. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haba S., Rosen E. M., Meek K., Nisonoff A. Primary structure of IgE monoclonal antibodies expressing an intrastrain crossreactive idiotype. J Exp Med. 1986 Jul 1;164(1):291–302. doi: 10.1084/jem.164.1.291. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartman A. B., Rudikoff S. VH genes encoding the immune response to beta-(1,6)-galactan: somatic mutation in IgM molecules. EMBO J. 1984 Dec 1;3(12):3023–3030. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02249.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeske D. J., Jarvis J., Milstein C., Capra J. D. Junctional diversity is essential to antibody activity. J Immunol. 1984 Sep;133(3):1090–1092. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaartinen M., Griffiths G. M., Markham A. F., Milstein C. mRNA sequences define an unusually restricted IgG response to 2-phenyloxazolone and its early diversification. 1983 Jul 28-Aug 3Nature. 304(5924):320–324. doi: 10.1038/304320a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamoyi E., Estess P., Capra J. D., Nisonoff A. Heterogeneity of an intrastrain cross-reactive idiotype associated with anti-p-azophenylarsonate antibodies of A/J mice. J Immunol. 1980 Jun;124(6):2834–2840. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landolfi N. F., Capra J. D., Tucker P. W. Germ-line sequence of the DH segment employed in Ars-A antibodies: implications for the generation of junctional diversity. J Immunol. 1986 Jul 1;137(1):362–365. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laskin J. A., Gray A., Nisonoff A., Klinman N. R., Gottlieb P. D. Segregation at a locus determining an immunoglobulin genetic marker for the light chain variable region affects inheritance of expression of an idiotype. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Oct;74(10):4600–4604. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.10.4600. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Legrain P., Buttin G. The VK gene expressed by BALB/c ABPC48 cross-reactive idiotypes induced by anti-idiotypic immunization is identical to that of BALB/c anti-oxazolone and A/J anti-arsonate antibodies. J Immunol. 1985 May;134(5):3468–3473. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meek K., Jeske D., Slaoui M., Leo O., Urbain J., Capra J. D. Complete amino acid sequence of heavy chain variable regions derived from two monoclonal anti-p-azophenylarsonate antibodies of BALB/c mice expressing the major cross-reactive idiotype of the A/J strain. J Exp Med. 1984 Oct 1;160(4):1070–1086. doi: 10.1084/jem.160.4.1070. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milner E. C., Capra J. D. Structural analysis of monoclonal anti-arsonate antibodies: idiotypic specificities are determined by the heavy chain. Mol Immunol. 1983 Jan;20(1):39–46. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(83)90103-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milner E. C., Capra J. D. VH families in the antibody response to p-azophenylarsonate: correlation between serology and amino acid sequence. J Immunol. 1982 Jul;129(1):193–199. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moser M., Leo O., Hiernaux J., Urbain J. Idiotypic manipulation in mice: BALB/c mice can express the crossreactive idiotype of A/J mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(14):4474–4478. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.14.4474. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pawlak L. L., Mushinski E. B., Nisonoff A., Potter M. Evidence for the linkage of the IGC H locus to a gene controlling the idiotypic specificity of anti-p-azophenylarsonate antibodies in strain A mice. J Exp Med. 1973 Jan 1;137(1):22–31. doi: 10.1084/jem.137.1.22. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potter M. History of the BALB/c family. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1985;122:1–5. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-70740-7_1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Primi D., Barbier E., Cazenave P. A. Structural polymorphism of V kappa 21 E and V kappa 21 D gene products in laboratory mice. Eur J Immunol. 1986 Mar;16(3):292–296. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830160315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Primi D., Drapier A. M., Cazenave P. A. Highly preferential VH-VL pairing in normal B cells results in antigen-independent selection of the available repertoire. J Immunol. 1987 Mar 1;138(5):1607–1612. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynaud C. A., Anquez V., Dahan A., Weill J. C. A single rearrangement event generates most of the chicken immunoglobulin light chain diversity. Cell. 1985 Feb;40(2):283–291. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90142-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robbins P. F., Rosen E. M., Haba S., Nisonoff A. Relationship of VH and VL genes encoding three idiotypic families of anti-p-azobenzenearsonate antibodies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Feb;83(4):1050–1054. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.4.1050. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanz I., Capra J. D. V kappa and J kappa gene segments of A/J Ars-A antibodies: somatic recombination generates the essential arginine at the junction of the variable and joining regions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Feb;84(4):1085–1089. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.4.1085. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharon J., Gefter M. L., Manser T., Ptashne M. Site-directed mutagenesis of an invariant amino acid residue at the variable-diversity segments junction of an antibody. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Apr;83(8):2628–2631. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.8.2628. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegelman M., Capra J. D. Complete amino acid sequence of light chain variable regions derived from five monoclonal anti-p-azophenylarsonate antibodies differing with respect to a crossreactive idiotype. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Dec;78(12):7679–7683. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.12.7679. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siekevitz M., Gefter M. L., Brodeur P., Riblet R., Marshak-Rothstein A. The genetic basis of antibody production: the dominant anti-arsonate idiotype response of the strain A mouse. Eur J Immunol. 1982 Dec;12(12):1023–1032. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830121208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slaughter C. A., Capra J. D. Amino acid sequence diversity within the family of antibodies bearing the major antiarsonate cross-reactive idiotype of the A strain mouse. J Exp Med. 1983 Nov 1;158(5):1615–1634. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.5.1615. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slaughter C. A., Jeske D. J., Kuziel W. A., Milner E. C., Capra J. D. Use of JH4 joining segment gene by an anti-arsonate antibody that bears the major A-strain cross-reactive idiotype but displays diminished antigen binding. J Immunol. 1984 Jun;132(6):3164–3171. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. A., Margolies M. N. Complete amino acid sequence of the heavy-chain variable region from an A/J mouse antigen-nonbinding monoclonal antibody bearing the predominant arsonate idiotype. Biochemistry. 1984 Sep 25;23(20):4726–4732. doi: 10.1021/bi00315a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. A., Margolies M. N. Complete amino acid sequences of the heavy and light chain variable regions from two A/J mouse antigen nonbinding monoclonal antibodies bearing the predominant p-azophenyl arsonate idiotype. Biochemistry. 1987 Jan 27;26(2):604–612. doi: 10.1021/bi00376a036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wysocki L. J., Manser T., Gridley T., Gefter M. L. Molecular limitations on variable-gene junctional diversity. J Immunol. 1986 Dec 15;137(12):3699–3701. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wysocki L. J., Margolies M. N., Huang B., Nemazee D. A., Wechsler D. S., Sato V. L., Smith J. A., Gefter M. L. Combinational diversity within variable regions bearing the predominant anti-p-azophenylarsonate idiotype of strain A mice. J Immunol. 1985 Apr;134(4):2740–2747. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]