Abstract
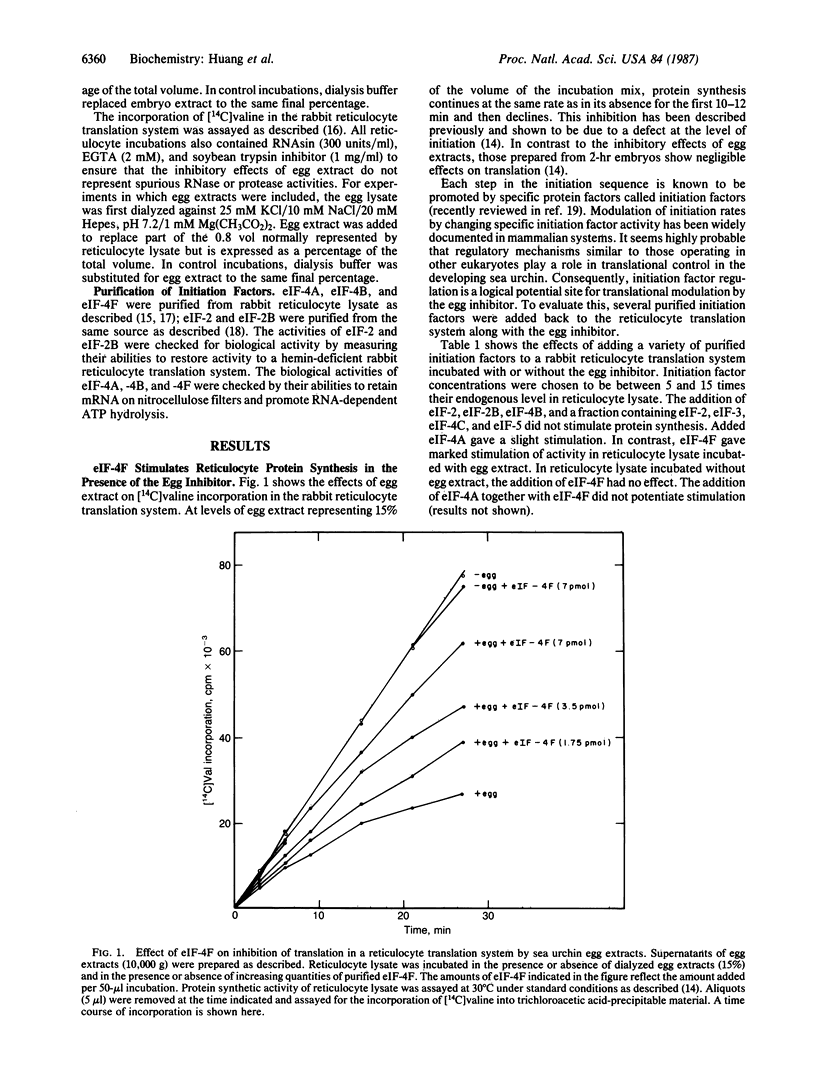
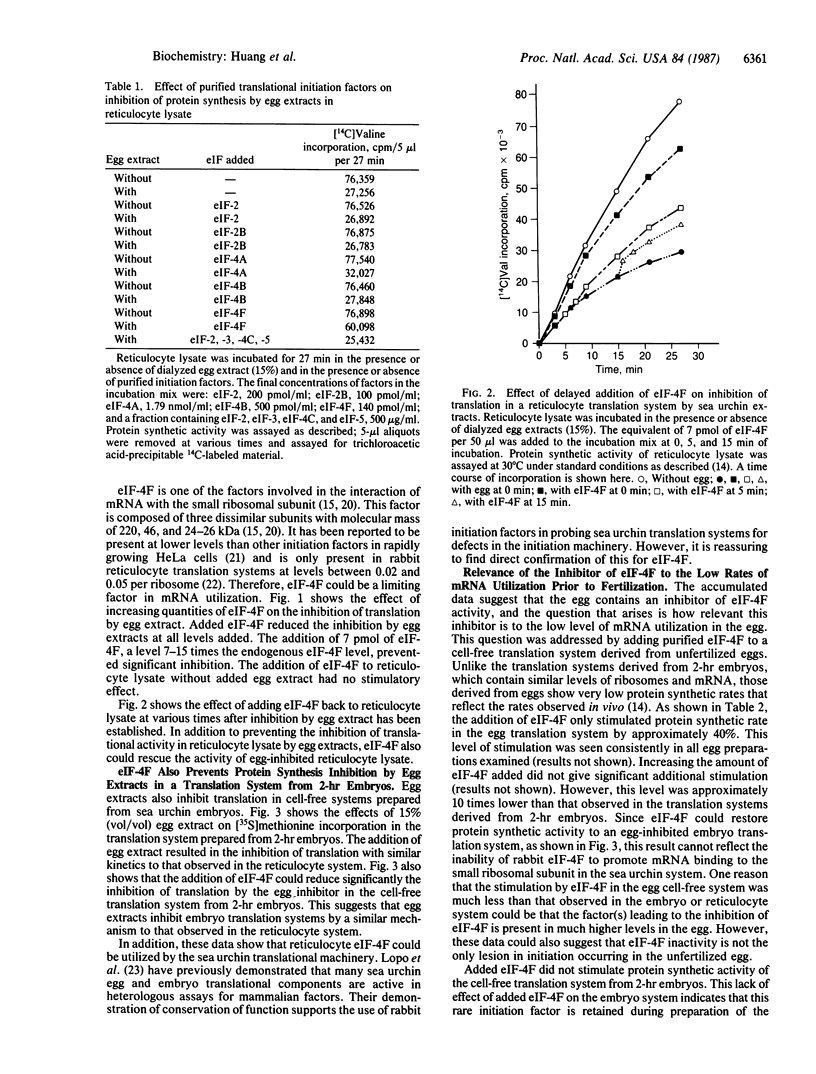
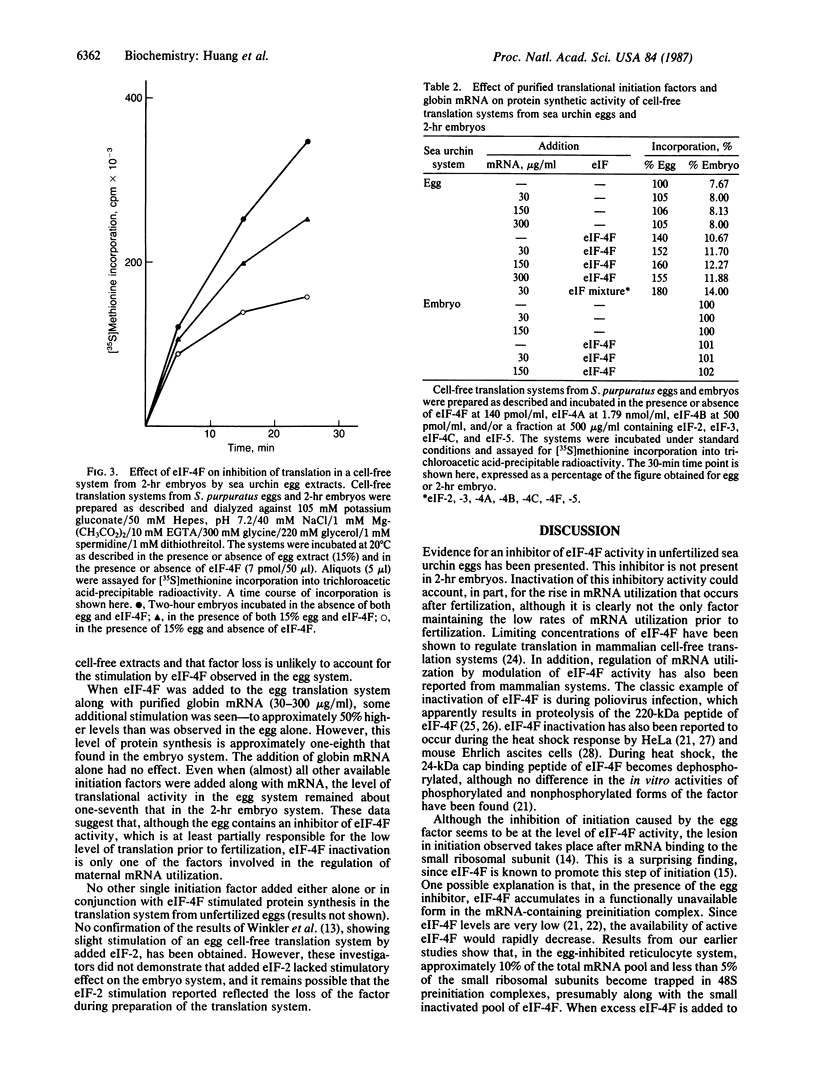
Extracts from unfertilized sea urchin eggs contain an inhibitor of translation that inhibits protein synthesis in cell-free translation systems from sea urchin embryos or rabbit reticulocytes. The inhibitory effects of egg extracts can be reversed by the addition of mammalian eukaryotic initiation factor 4F (eIF-4F) in both sea urchin embryo and reticulocyte systems, suggesting that the inhibitor inactivates this initiation factor. The accumulated data suggest that the ability of eIF-4F to recycle may be compromised. The addition of eIF-4F to cell-free translation systems from unfertilized sea urchin eggs also stimulates protein synthesis. However, the stimulation does not increase protein synthetic activity in the egg cell-free translation system to the levels observed in those produced from 2-hr embryos. This suggests that, although the unfertilized egg contains an inhibitor of eIF-4F and reduced levels of eIF-4F activity, inactivation of this component is only one of the factors involved in the low rate of maternal mRNA utilization found prior to fertilization.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Caldwell D. C., Emerson C. P., Jr The role of cap methylation in the translational activation of stored maternal histone mRNA in sea urchin embryos. Cell. 1985 Sep;42(2):691–700. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90126-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colin A. M., Hille M. B. Injected mRNA does not increase protein synthesis in unfertilized, fertilized, or ammonia-activated sea urchin eggs. Dev Biol. 1986 May;115(1):184–192. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(86)90239-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costantini F. D., Britten R. J., Davidson E. H. Message sequences and short repetitive sequences are interspersed in sea urchin egg poly(A)+ RNAs. Nature. 1980 Sep 11;287(5778):111–117. doi: 10.1038/287111a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson E. H., Hough-Evans B. R., Britten R. J. Molecular biology of the sea urchin embryo. Science. 1982 Jul 2;217(4554):17–26. doi: 10.1126/science.6178156. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duncan R., Hershey J. W. Heat shock-induced translational alterations in HeLa cells. Initiation factor modifications and the inhibition of translation. J Biol Chem. 1984 Oct 10;259(19):11882–11889. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duncan R., Humphreys T. Oligo(U) sequences present in sea urchin maternal RNA decrease following fertilization. Dev Biol. 1983 Mar;96(1):258–262. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(83)90326-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duncan R., Milburn S. C., Hershey J. W. Regulated phosphorylation and low abundance of HeLa cell initiation factor eIF-4F suggest a role in translational control. Heat shock effects on eIF-4F. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jan 5;262(1):380–388. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edery I., Hümbelin M., Darveau A., Lee K. A., Milburn S., Hershey J. W., Trachsel H., Sonenberg N. Involvement of eukaryotic initiation factor 4A in the cap recognition process. J Biol Chem. 1983 Sep 25;258(18):11398–11403. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epel D. Protein synthesis in sea urchin eggs: a "late" response to fertilization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Apr;57(4):899–906. doi: 10.1073/pnas.57.4.899. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grifo J. A., Tahara S. M., Leis J. P., Morgan M. A., Shatkin A. J., Merrick W. C. Characterization of eukaryotic initiation factor 4A, a protein involved in ATP-dependent binding of globin mRNA. J Biol Chem. 1982 May 10;257(9):5246–5252. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grifo J. A., Tahara S. M., Morgan M. A., Shatkin A. J., Merrick W. C. New initiation factor activity required for globin mRNA translation. J Biol Chem. 1983 May 10;258(9):5804–5810. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen L. J., Huang W. I., Jagus R. Inhibitor of translational initiation in sea urchin eggs prevents mRNA utilization. J Biol Chem. 1987 May 5;262(13):6114–6120. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiremath L. S., Webb N. R., Rhoads R. E. Immunological detection of the messenger RNA cap-binding protein. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jul 5;260(13):7843–7849. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jagus R., Safer B. Quantitation and localization of globin messenger RNA in rabbit reticulocyte lysate. J Biol Chem. 1979 Aug 10;254(15):6865–6868. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenkins N. A., Kaumeyer J. F., Young E. M., Raff R. A. A test for masked message: the template activity of messenger ribonucleoprotein particles isolated from sea urchine eggs. Dev Biol. 1978 Apr;63(2):279–298. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(78)90134-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaumeyer J. F., Jenkins N. A., Raff R. A. Messenger ribonucleoprotein particles in unfertilized sea urchin eggs. Dev Biol. 1978 Apr;63(2):266–278. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(78)90133-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konieczny A., Safer B. Purification of the eukaryotic initiation factor 2-eukaryotic initiation factor 2B complex and characterization of its guanine nucleotide exchange activity during protein synthesis initiation. J Biol Chem. 1983 Mar 10;258(5):3402–3408. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopo A. C., Lashbrook C. C., Infante D., Infante A. A., Hershey J. W. Translational initiation factors from sea urchin eggs and embryos: functional properties are highly conserved. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1986 Oct;250(1):162–170. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(86)90713-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moon R. T., Danilchik M. V., Hille M. B. An assessment of the masked message hypothesis: sea urchin egg messenger ribonucleoprotein complexes are efficient templates for in vitro protein synthesis. Dev Biol. 1982 Oct;93(2):389–403. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(82)90126-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moon R. T., Nicosia R. F., Olsen C., Hille M. B., Jeffery W. R. The cytoskeletal framework of sea urchin eggs and embryos: developmental changes in the association of messenger RNA. Dev Biol. 1983 Feb;95(2):447–458. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(83)90046-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pain V. M. Initiation of protein synthesis in mammalian cells. Biochem J. 1986 May 1;235(3):625–637. doi: 10.1042/bj2350625. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panniers R., Stewart E. B., Merrick W. C., Henshaw E. C. Mechanism of inhibition of polypeptide chain initiation in heat-shocked Ehrlich cells involves reduction of eukaryotic initiation factor 4F activity. J Biol Chem. 1985 Aug 15;260(17):9648–9653. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ray B. K., Brendler T. G., Adya S., Daniels-McQueen S., Miller J. K., Hershey J. W., Grifo J. A., Merrick W. C., Thach R. E. Role of mRNA competition in regulating translation: further characterization of mRNA discriminatory initiation factors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Feb;80(3):663–667. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.3.663. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Safer B., Jagus R., Kemper W. M. Analysis of initiation factor function in highly fractionated and unfractionated reticulocyte lysate systems. Methods Enzymol. 1979;60:61–87. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(79)60008-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tahara S. M., Morgan M. A., Shatkin A. J. Two forms of purified m7G-cap binding protein with different effects on capped mRNA translation in extracts of uninfected and poliovirus-infected HeLa cells. J Biol Chem. 1981 Aug 10;256(15):7691–7694. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


