Abstract
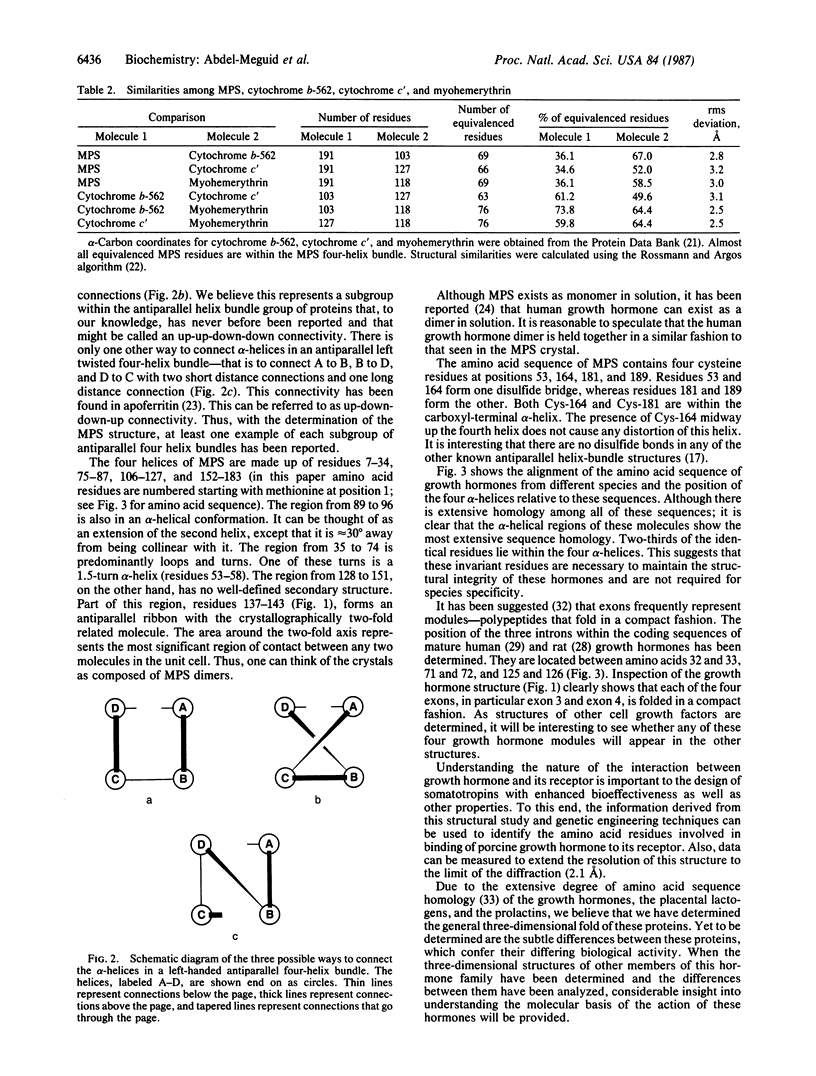
The three-dimensional structure of a genetically engineered variant of porcine growth hormone, methionyl porcine somatotropin (MPS), has been determined at 2.8-A resolution, using single crystal x-ray diffraction techniques. Phases were obtained by use of a single isomorphous K2OsCl6 derivative and were improved by use of the density modification procedure. The MPS structure is predominantly helical. It consists mainly of four antiparallel alpha-helices arranged in a left twisted helical bundle, a structural motif observed in a number of other unrelated proteins. However, the way the four helices are connected in the bundle is unusual and, to our knowledge, has never been reported before. Alignment of the amino acid sequence of MPS with that of other growth hormones reveals that residues within the alpha-helices are predominantly invariant and thus these invariant residues are necessary to maintain the structural integrity of these proteins.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abdel-Meguid S. S., Smith W. W., Violand B. N., Bentle L. A. Crystallization of methionyl porcine somatotropin, a genetically engineered variant of porcine growth hormone. J Mol Biol. 1986 Nov 5;192(1):159–160. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90472-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell J. A., Moffat K., Vonderhaar B. K., Golde D. W. Crystallization and preliminary x-ray characterization of bovine growth hormone. Purification of bovine prolactin and growth hormone. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jul 15;260(14):8520–8525. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernstein F. C., Koetzle T. F., Williams G. J., Meyer E. F., Jr, Brice M. D., Rodgers J. R., Kennard O., Shimanouchi T., Tasumi M. The Protein Data Bank: a computer-based archival file for macromolecular structures. J Mol Biol. 1977 May 25;112(3):535–542. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(77)80200-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bewley T. A., Li C. H. Conformational comparison of human pituitary growth hormone and human chorionic somatomammotropin (human placental lactogen) by second-order absorption spectroscopy. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1984 Aug 15;233(1):219–227. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(84)90620-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brewley T. A., Li C. H. Sequence comparison of human pituitary growth hormone, human chorionic somatomammotropin and ovine pituitary lactogenic hormone. Experientia. 1971;27(11):1368–1371. doi: 10.1007/BF02136745. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catt K. J., Moffat B., Niall H. D. Human growth hormone and placental lactogen: structural similarity. Science. 1967 Jul 21;157(3786):321–321. doi: 10.1126/science.157.3786.321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeNoto F. M., Moore D. D., Goodman H. M. Human growth hormone DNA sequence and mRNA structure: possible alternative splicing. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Aug 11;9(15):3719–3730. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.15.3719. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ford G. C., Harrison P. M., Rice D. W., Smith J. M., Treffry A., White J. L., Yariv J. Ferritin: design and formation of an iron-storage molecule. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1984 Feb 13;304(1121):551–565. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1984.0046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Go M. Correlation of DNA exonic regions with protein structural units in haemoglobin. Nature. 1981 May 7;291(5810):90–92. doi: 10.1038/291090a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gráf L., Li C. H. On the primary structure of pituitary bovine growth hormone. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 Jan;56(1):168–176. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(74)80330-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hendrickson W. A., Ward K. B. Pseudosymmetry in the structure of myohemerythrin. J Biol Chem. 1977 May 10;252(9):3012–3018. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunt R. E., Moffat K., Golde D. W. Purification and crystallization of the polypeptide hormone human chorionic somatomammotropin. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jul 10;256(13):7042–7045. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lederer F., Glatigny A., Bethge P. H., Bellamy H. D., Matthew F. S. Improvement of the 2.5 A resolution model of cytochrome b562 by redetermining the primary structure and using molecular graphics. J Mol Biol. 1981 Jun 5;148(4):427–448. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90185-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li C. H., Chung D., Lahm H. W., Stein S. The primary structure of monkey pituitary growth hormone. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1986 Feb 15;245(1):287–291. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(86)90216-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li C. H., Dixon J. S., Gordon D., Knorr J. Amino acid sequence of sheep pituitary growth hormone. Int J Pept Protein Res. 1972;4(2):151–153. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-3011.1972.tb03412.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Page G. S., Smith S., Goodman H. M. DNA sequence of the rat growth hormone gene: location of the 5' terminus of the growth hormone mRNA and identification of an internal transposon-like element. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 May 11;9(9):2087–2104. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.9.2087. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson J. S. The anatomy and taxonomy of protein structure. Adv Protein Chem. 1981;34:167–339. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3233(08)60520-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossmann M. G., Argos P. Exploring structural homology of proteins. J Mol Biol. 1976 Jul 25;105(1):75–95. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(76)90195-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seeburg P. H., Sias S., Adelman J., de Boer H. A., Hayflick J., Jhurani P., Goeddel D. V., Heyneker H. L. Efficient bacterial expression of bovine and porcine growth hormones. DNA. 1983;2(1):37–45. doi: 10.1089/dna.1.1983.2.37. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherwood L. M. Similarities in the chemical structure of human placental lactogen and pituitary growth hormone. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Dec;58(6):2307–2314. doi: 10.1073/pnas.58.6.2307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Souza L. M., Boone T. C., Murdock D., Langley K., Wypych J., Fenton D., Johnson S., Lai P. H., Everett R., Hsu R. Y. Application of recombinant DNA technologies to studies on chicken growth hormone. J Exp Zool. 1984 Dec;232(3):465–473. doi: 10.1002/jez.1402320313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang B. C. Resolution of phase ambiguity in macromolecular crystallography. Methods Enzymol. 1985;115:90–112. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(85)15009-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber P. C., Bartsch R. G., Cusanovich M. A., Hamlin R. C., Howard A., Jordan S. R., Kamen M. D., Meyer T. E., Weatherford D. W., Nguyen huu Xuong Structure of cytochrome c': a dimeric, high-spin haem protein. Nature. 1980 Jul 17;286(5770):302–304. doi: 10.1038/286302a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zakin M. M., Poskus E., Langton A. A., Ferrara P., Santomé J. A., Dellacha J. M., Paladini A. C. Primary structure of equine growth hormone. Int J Pept Protein Res. 1976;8(5):435–444. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-3011.1976.tb02523.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




