Abstract
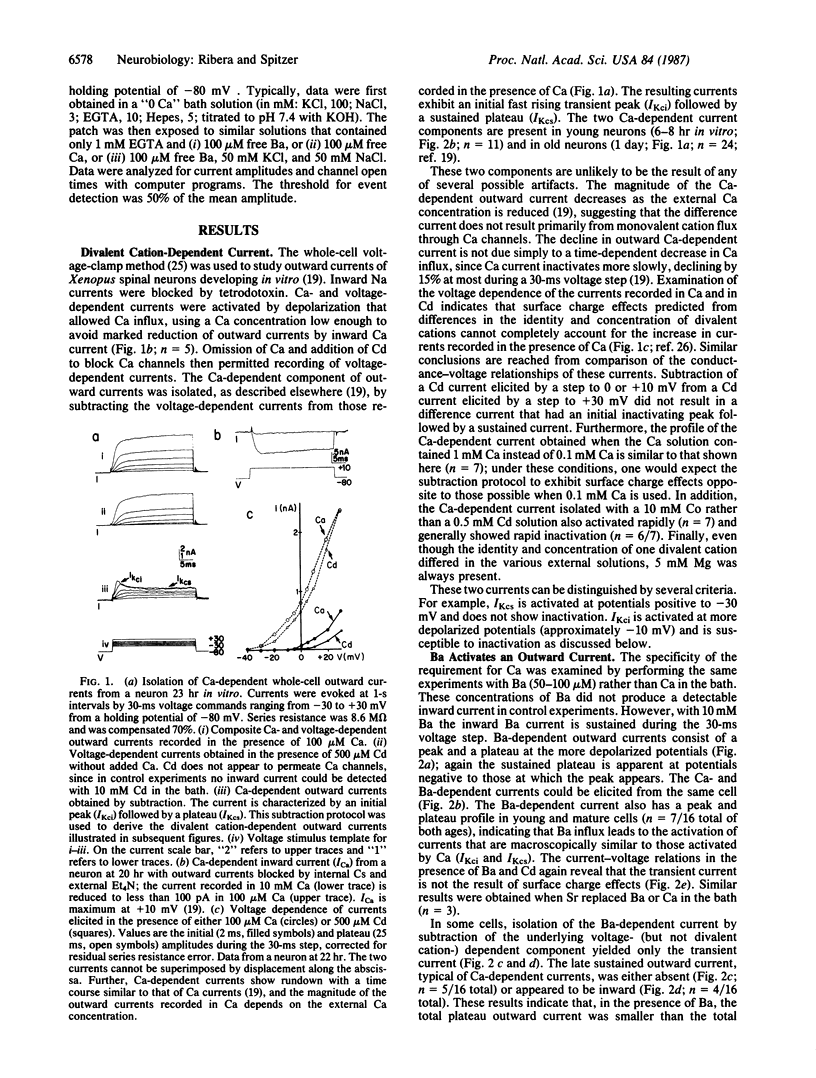
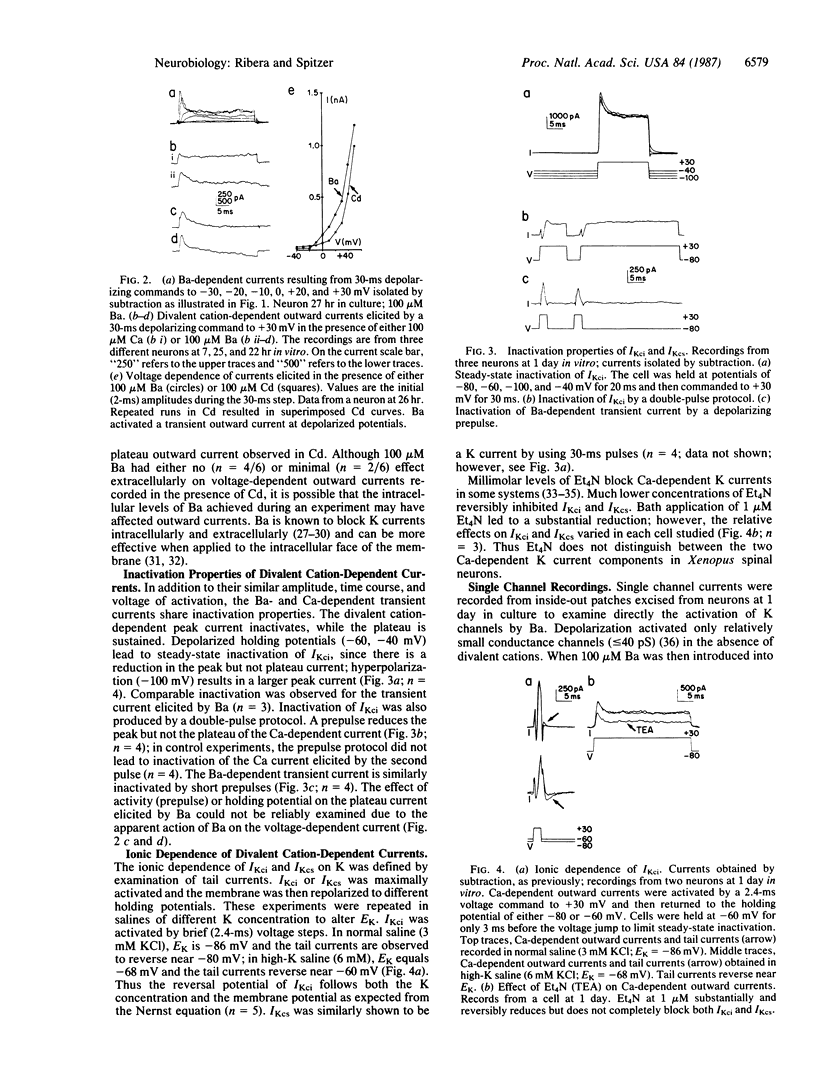
Amphibian spinal neurons in culture possess both rapidly inactivating and sustained calcium-dependent potassium current components, similar to those described for other cells. Divalent cation-dependent whole-cell outward currents were isolated by subtracting the voltage-dependent potassium currents recorded from Xenopus laevis neurons in the presence of impermeant cadmium (100-500 microM) from the currents produced without cadmium but in the presence of permeant divalent cations (50-100 microM). These concentrations of permeant ions were low enough to avoid contamination by macroscopic inward currents through calcium channels. Calcium-dependent potassium currents were reduced by 1 microM tetraethylammonium. These currents can also be activated by barium or strontium. Barium as well as calcium activated outward currents in young neurons (6-8 hr) and in relatively mature neurons (19-26 hr in vitro). However, barium influx appeared to suppress the sustained voltage-dependent potassium current in most cells. Barium also activated at least one class of potassium channels observed in excised membrane patches, while blocking others. The blocking action may have masked and hindered detection of the stimulatory action of barium in other systems.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams P. R., Constanti A., Brown D. A., Clark R. B. Intracellular Ca2+ activates a fast voltage-sensitive K+ current in vertebrate sympathetic neurones. Nature. 1982 Apr 22;296(5859):746–749. doi: 10.1038/296746a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong C. M., Swenson R. P., Jr, Taylor S. R. Block of squid axon K channels by internally and externally applied barium ions. J Gen Physiol. 1982 Nov;80(5):663–682. doi: 10.1085/jgp.80.5.663. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bader C. R., Bernheim L., Bertrand D. Sodium-activated potassium current in cultured avian neurones. Nature. 1985 Oct 10;317(6037):540–542. doi: 10.1038/317540a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrett E. F., Barret J. N. Separation of two voltage-sensitive potassium currents, and demonstration of a tetrodotoxin-resistant calcium current in frog motoneurones. J Physiol. 1976 Mar;255(3):737–774. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011306. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrett J. N., Barrett E. F., Dribin L. B. Calcium-dependent slow potassium conductance in rat skeletal myotubes. Dev Biol. 1981 Mar;82(2):258–266. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(81)90450-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrett J. N., Magleby K. L., Pallotta B. S. Properties of single calcium-activated potassium channels in cultured rat muscle. J Physiol. 1982 Oct;331:211–230. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014370. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bixby J. L., Spitzer N. C. The appearance and development of neurotransmitter sensitivity in Xenopus embryonic spinal neurones in vitro. J Physiol. 1984 Aug;353:143–155. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015328. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blair L. A., Dionne V. E. Developmental acquisition of Ca2+-sensitivity by K+ channels in spinal neurones. Nature. 1985 May 23;315(6017):329–331. doi: 10.1038/315329a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blair L. A. The timing of protein synthesis required for the development of the sodium action potential in embryonic spinal neurons. J Neurosci. 1983 Jul;3(7):1430–1436. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.03-07-01430.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgess G. M., Claret M., Jenkinson D. H. Effects of quinine and apamin on the calcium-dependent potassium permeability of mammalian hepatocytes and red cells. J Physiol. 1981 Aug;317:67–90. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1981.sp013814. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eaton D. C., Brodwick M. S. Effects of barium on the potassium conductance of squid axon. J Gen Physiol. 1980 Jun;75(6):727–750. doi: 10.1085/jgp.75.6.727. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golowasch J., Kirkwood A., Miller C. Allosteric effects of Mg2+ on the gating of Ca2+-activated K+ channels from mammalian skeletal muscle. J Exp Biol. 1986 Sep;124:5–13. doi: 10.1242/jeb.124.1.5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagiwara S., Miyazaki S., Moody W., Patlak J. Blocking effects of barium and hydrogen ions on the potassium current during anomalous rectification in the starfish egg. J Physiol. 1978 Jun;279:167–185. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012338. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamill O. P., Marty A., Neher E., Sakmann B., Sigworth F. J. Improved patch-clamp techniques for high-resolution current recording from cells and cell-free membrane patches. Pflugers Arch. 1981 Aug;391(2):85–100. doi: 10.1007/BF00656997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hermann A., Gorman A. L. Blockade of voltage-dependent and Ca2+-dependent K+ current components by internal Ba2+ in molluscan pacemaker neurons. Experientia. 1979 Feb 15;35(2):229–231. doi: 10.1007/BF01920633. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hermann A., Gorman A. L. Effects of tetraethylammonium on potassium currents in a molluscan neurons. J Gen Physiol. 1981 Jul;78(1):87–110. doi: 10.1085/jgp.78.1.87. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hille B., Woodhull A. M., Shapiro B. I. Negative surface charge near sodium channels of nerve: divalent ions, monovalent ions, and pH. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1975 Jun 10;270(908):301–318. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1975.0011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hosoi S., Slayman C. L. Membrane voltage, resistance, and channel switching in isolated mouse fibroblasts (L cells): a patch-electrode analysis. J Physiol. 1985 Oct;367:267–290. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015824. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwatsuki N., Petersen O. H. Inhibition of Ca2+-activated K+ channels in pig pancreatic acinar cells by Ba2+, Ca2+, quinine and quinidine. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Oct 10;819(2):249–257. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(85)90180-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krnjević K., Lisiewicz A. Injections of calcium ions into spinal motoneurones. J Physiol. 1972 Sep;225(2):363–390. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009945. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamborghini J. E., Iles A. Development of a high-affinity GABA uptake system in embryonic amphibian spinal neurons. Dev Biol. 1985 Nov;112(1):167–176. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(85)90130-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lux H. D., Neher E., Marty A. Single channel activity associated with the calcium dependent outward current in Helix pomatia. Pflugers Arch. 1981 Mar;389(3):293–295. doi: 10.1007/BF00584792. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDermott A. B., Weight F. F. Action potential repolarization may involve a transient, Ca2+-sensitive outward current in a vertebrate neurone. Nature. 1982 Nov 11;300(5888):185–188. doi: 10.1038/300185a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marty A. Blocking of large unitary calcium-dependent potassium currents by internal sodium ions. Pflugers Arch. 1983 Feb;396(2):179–181. doi: 10.1007/BF00615524. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marty A. Ca-dependent K channels with large unitary conductance in chromaffin cell membranes. Nature. 1981 Jun 11;291(5815):497–500. doi: 10.1038/291497a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer M. L., Westbrook G. L., Guthrie P. B. Voltage-dependent block by Mg2+ of NMDA responses in spinal cord neurones. Nature. 1984 May 17;309(5965):261–263. doi: 10.1038/309261a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meech R. W. Intracellular calcium injection causes increased potassium conductance in Aplysia nerve cells. Comp Biochem Physiol A Comp Physiol. 1972 Jun 1;42(2):493–499. doi: 10.1016/0300-9629(72)90128-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meech R. W., Standen N. B. Potassium activation in Helix aspersa neurones under voltage clamp: a component mediated by calcium influx. J Physiol. 1975 Jul;249(2):211–239. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp011012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meech R. W. The sensitivity of Helix aspersa neurones to injected calcium ions. J Physiol. 1974 Mar;237(2):259–277. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1974.sp010481. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller C., Moczydlowski E., Latorre R., Phillips M. Charybdotoxin, a protein inhibitor of single Ca2+-activated K+ channels from mammalian skeletal muscle. Nature. 1985 Jan 24;313(6000):316–318. doi: 10.1038/313316a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mounier Y., Vassort G. Evidence for a transient potassium membrane current dependent on calcium influx in crab muscle fibre. J Physiol. 1975 Oct;251(3):609–625. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp011111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nowak L., Bregestovski P., Ascher P., Herbet A., Prochiantz A. Magnesium gates glutamate-activated channels in mouse central neurones. Nature. 1984 Feb 2;307(5950):462–465. doi: 10.1038/307462a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pallotta B. S., Magleby K. L., Barrett J. N. Single channel recordings of Ca2+-activated K+ currents in rat muscle cell culture. Nature. 1981 Oct 8;293(5832):471–474. doi: 10.1038/293471a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pennefather P., Lancaster B., Adams P. R., Nicoll R. A. Two distinct Ca-dependent K currents in bullfrog sympathetic ganglion cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(9):3040–3044. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.9.3040. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfaffinger P. J., Martin J. M., Hunter D. D., Nathanson N. M., Hille B. GTP-binding proteins couple cardiac muscarinic receptors to a K channel. Nature. 1985 Oct 10;317(6037):536–538. doi: 10.1038/317536a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roy G., Sauvé R. Stable membrane potentials and mechanical K+ responses activated by internal Ca2+ in HeLa cells. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1983 Feb;61(2):144–148. doi: 10.1139/y83-021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salkoff L. Drosophila mutants reveal two components of fast outward current. Nature. 1983 Mar 17;302(5905):249–251. doi: 10.1038/302249a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegelbaum S. A., Tsien R. W. Calcium-activated transient outward current in calf cardiac Purkinje fibres. J Physiol. 1980 Feb;299:485–506. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013138. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spitzer N. C., Lamborghini J. E. The development of the action potential mechanism of amphibian neurons isolated in culture. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 May;73(5):1641–1645. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.5.1641. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Standen N. B., Stanfield P. R. A potential- and time-dependent blockade of inward rectification in frog skeletal muscle fibres by barium and strontium ions. J Physiol. 1978 Jul;280:169–191. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012379. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson S. H. Three pharmacologically distinct potassium channels in molluscan neurones. J Physiol. 1977 Feb;265(2):465–488. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trautmann A., Marty A. Activation of Ca-dependent K channels by carbamoylcholine in rat lacrimal glands. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jan;81(2):611–615. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.2.611. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vassort G. Voltage-clamp analysis of transmembrane ionic currents in guinea-pig myometrium: evidence for an initial potassium activation triggered by calcium influx. J Physiol. 1975 Nov;252(3):713–734. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp011167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vergara C., Latorre R. Kinetics of Ca2+-activated K+ channels from rabbit muscle incorporated into planar bilayers. Evidence for a Ca2+ and Ba2+ blockade. J Gen Physiol. 1983 Oct;82(4):543–568. doi: 10.1085/jgp.82.4.543. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vergara C., Moczydlowski E., Latorre R. Conduction, Blockade and Gating in a Ca -activated K Channel Incorporated into Planar Lipid Bilayers. Biophys J. 1984 Jan;45(1):73–76. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(84)84114-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woll K. H. The effect of internal barium on the K current of the node of Ranvier. Pflugers Arch. 1982 Jun;393(4):318–321. doi: 10.1007/BF00581417. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong B. S., Lecar H., Adler M. Single calcium-dependent potassium channels in clonal anterior pituitary cells. Biophys J. 1982 Sep;39(3):313–317. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(82)84522-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zbicz K. L., Weight F. F. Transient voltage and calcium-dependent outward currents in hippocampal CA3 pyramidal neurons. J Neurophysiol. 1985 Apr;53(4):1038–1058. doi: 10.1152/jn.1985.53.4.1038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


