Abstract
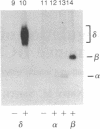
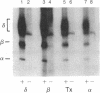
By using 32P-labeling methods and performing immunoprecipitations with specific antibodies, we have found that three subunits of the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor are phosphorylated in mouse skeletal muscle cells. In nonstimulated cells, the molar ratios of phosphate estimated in alpha, beta, and delta subunits were 0.02, 0.05, and 0.5, respectively. All three subunits contained predominantly phosphoserine with some phosphothreonine; the beta subunit also contained phosphotyrosine. Incubating cells with agents that stimulate cAMP-dependent pathways (isoproterenol, forskolin, 8-Br-cAMP) increased the phosphorylation of the delta subunit by 50%, but phosphate labeling of the beta subunit was depressed by a third. In contrast, when cells were incubated with the divalent cation ionophores A-23187 or ionomycin, phosphorylation of both the delta and beta subunits increased. The results indicate that acetylcholine receptors are phosphorylated to significant levels in skeletal muscle cells and that cAMP-dependent and Ca2+-dependent pathways exist for controlling the phosphorylation state of the receptor subunits.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Carlin B. E., Lawrence J. C., Jr, Lindstrom J. M., Merlie J. P. An acetylcholine receptor precursor alpha subunit that binds alpha-bungarotoxin but not d-tubocurare. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jan;83(2):498–502. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.2.498. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlin B. E., Lawrence J. C., Jr, Lindstrom J. M., Merlie J. P. Inhibition of acetylcholine receptor assembly by activity in primary cultures of embryonic rat muscle cells. J Biol Chem. 1986 Apr 15;261(11):5180–5186. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper J. A., Sefton B. M., Hunter T. Detection and quantification of phosphotyrosine in proteins. Methods Enzymol. 1983;99:387–402. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)99075-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- England P. J., Walsh D. A. A rapid method for the measurement of [gamma-32P]ATP specific radioactivity in tissue extracts and its application to the study of 32Pi uptake in perfused rat heart. Anal Biochem. 1976 Oct;75(2):429–435. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90096-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Froehner S. C., Douville K., Klink S., Culp W. J. Monoclonal antibodies to cytoplasmic domains of the acetylcholine receptor. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jun 10;258(11):7112–7120. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon A. S., Davis C. G., Milfay D., Diamond I. Phosphorylation of acetylcholine receptor by endogenous membrane protein kinase in receptor-enriched membranes of Torpedo californica. Nature. 1977 Jun 9;267(5611):539–540. doi: 10.1038/267539a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huganir R. L., Delcour A. H., Greengard P., Hess G. P. Phosphorylation of the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor regulates its rate of desensitization. Nature. 1986 Jun 19;321(6072):774–776. doi: 10.1038/321774a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huganir R. L., Miles K., Greengard P. Phosphorylation of the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor by an endogenous tyrosine-specific protein kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Nov;81(22):6968–6972. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.22.6968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes R. J., Boyle M. R., Brown R. D., Taylor P., Insel P. A. Characterization of coexisting alpha 1- and beta 2-adrenergic receptors on a cloned muscle cell line, BC3H-1. Mol Pharmacol. 1982 Sep;22(2):258–266. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klausner R. D., Harford J., van Renswoude J. Rapid internalization of the transferrin receptor in K562 cells is triggered by ligand binding or treatment with a phorbol ester. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 May;81(10):3005–3009. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.10.3005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levitan I. B. Phosphorylation of ion channels. J Membr Biol. 1985;87(3):177–190. doi: 10.1007/BF01871217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Logothetis D. E., Kurachi Y., Galper J., Neer E. J., Clapham D. E. The beta gamma subunits of GTP-binding proteins activate the muscarinic K+ channel in heart. Nature. 1987 Jan 22;325(6102):321–326. doi: 10.1038/325321a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- May W. S., Jacobs S., Cuatrecasas P. Association of phorbol ester-induced hyperphosphorylation and reversible regulation of transferrin membrane receptors in HL60 cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):2016–2020. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.2016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCarthy M. P., Earnest J. P., Young E. F., Choe S., Stroud R. M. The molecular neurobiology of the acetylcholine receptor. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1986;9:383–413. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.09.030186.002123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merlie J. P., Lindstrom J. Assembly in vivo of mouse muscle acetylcholine receptor: identification of an alpha subunit species that may be an assembly intermediate. Cell. 1983 Oct;34(3):747–757. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90531-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merlie J. P., Sebbane R. Acetylcholine receptor subunits transit a precursor pool before acquiring alpha-bungarotoxin binding activity. J Biol Chem. 1981 Apr 25;256(8):3605–3608. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miles K., Anthony D. T., Rubin L. L., Greengard P., Huganir R. L. Regulation of nicotinic acetylcholine receptor phosphorylation in rat myotubes by forskolin and cAMP. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Sep;84(18):6591–6595. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.18.6591. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Popot J. L., Changeux J. P. Nicotinic receptor of acetylcholine: structure of an oligomeric integral membrane protein. Physiol Rev. 1984 Oct;64(4):1162–1239. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1984.64.4.1162. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ratnam M., Sargent P. B., Sarin V., Fox J. L., Nguyen D. L., Rivier J., Criado M., Lindstrom J. Location of antigenic determinants on primary sequences of subunits of nicotinic acetylcholine receptor by peptide mapping. Biochemistry. 1986 May 6;25(9):2621–2632. doi: 10.1021/bi00357a051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salsgiver W. J., Lawrence J. C., Jr Rat skeletal muscle phosphorylase kinase: turnover and control of isozyme levels in culture. Am J Physiol. 1986 Mar;250(3 Pt 1):C365–C373. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1986.250.3.C365. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sibley D. R., Strasser R. H., Benovic J. L., Daniel K., Lefkowitz R. J. Phosphorylation/dephosphorylation of the beta-adrenergic receptor regulates its functional coupling to adenylate cyclase and subcellular distribution. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(24):9408–9412. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.24.9408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sine S. M., Steinbach J. H. Activation of acetylcholine receptors on clonal mammalian BC3H-1 cells by low concentrations of agonist. J Physiol. 1986 Apr;373:129–162. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp016039. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smilowitz H., Hadjian R. A., Dwyer J., Feinstein M. B. Regulation of acetylcholine receptor phosphorylation by calcium and calmodulin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Aug;78(8):4708–4712. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.8.4708. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith M. M., Lindstrom J., Merlie J. P. Formation of the alpha-bungarotoxin binding site and assembly of the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor subunits occur in the endoplasmic reticulum. J Biol Chem. 1987 Mar 25;262(9):4367–4376. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith M. M., Schlesinger S., Lindstrom J., Merlie J. P. The effects of inhibiting oligosaccharide trimming by 1-deoxynojirimycin on the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor. J Biol Chem. 1986 Nov 5;261(31):14825–14832. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taniuchi M., Johnson E. M., Jr, Roach P. J., Lawrence J. C., Jr Phosphorylation of nerve growth factor receptor proteins in sympathetic neurons and PC12 cells. In vitro phosphorylation by the cAMP-independent protein kinase FA/GSK-3. J Biol Chem. 1986 Oct 5;261(28):13342–13349. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teichberg V. I., Sobel A., Changeux J. P. In vitro phosphorylation of the acetylcholine receptor. Nature. 1977 Jun 9;267(5611):540–542. doi: 10.1038/267540a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tzartos S. J., Rand D. E., Einarson B. L., Lindstrom J. M. Mapping of surface structures of electrophorus acetylcholine receptor using monoclonal antibodies. J Biol Chem. 1981 Aug 25;256(16):8635–8645. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vandlen R. L., Wu W. C., Eisenach J. C., Raftery M. A. Studies of the composition of purified Torpedo californica acetylcholine receptor and of its subunits. Biochemistry. 1979 May 15;18(10):1845–1854. doi: 10.1021/bi00577a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wan K. K., Lindstrom J. M. Effects of monoclonal antibodies on the function of acetylcholine receptors purified from Torpedo californica and reconstituted into vesicles. Biochemistry. 1985 Feb 26;24(5):1212–1221. doi: 10.1021/bi00326a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]