Abstract
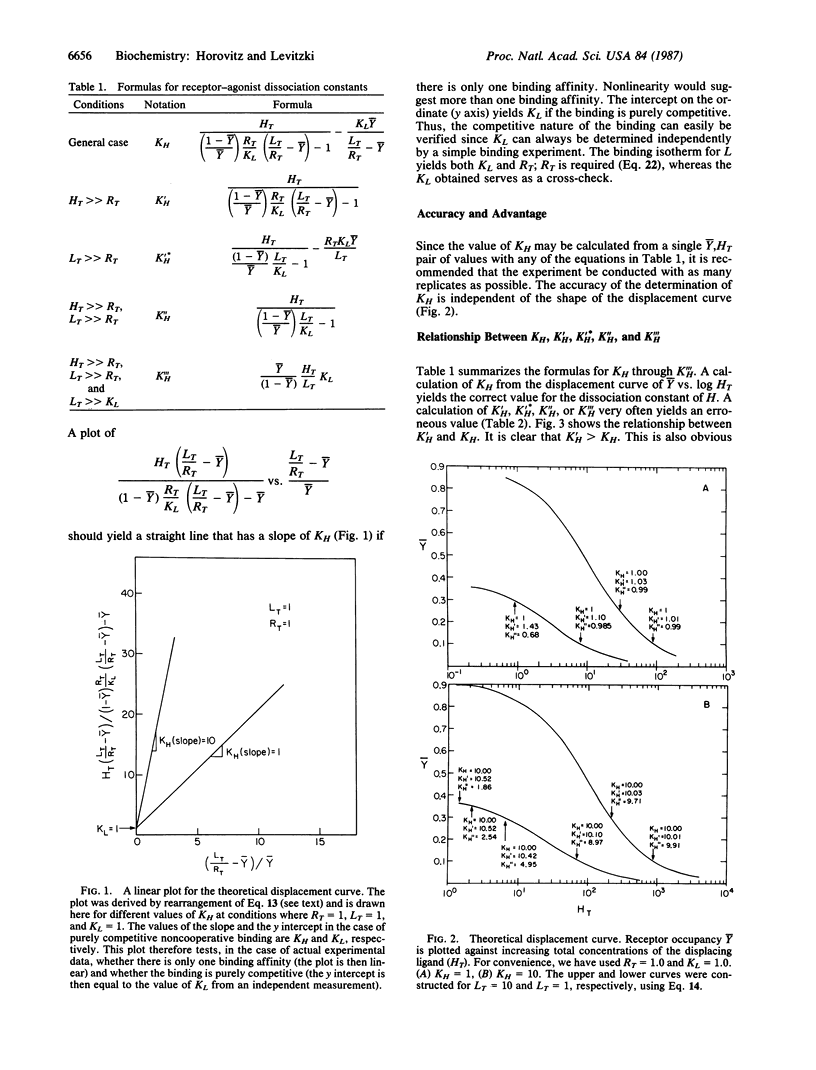
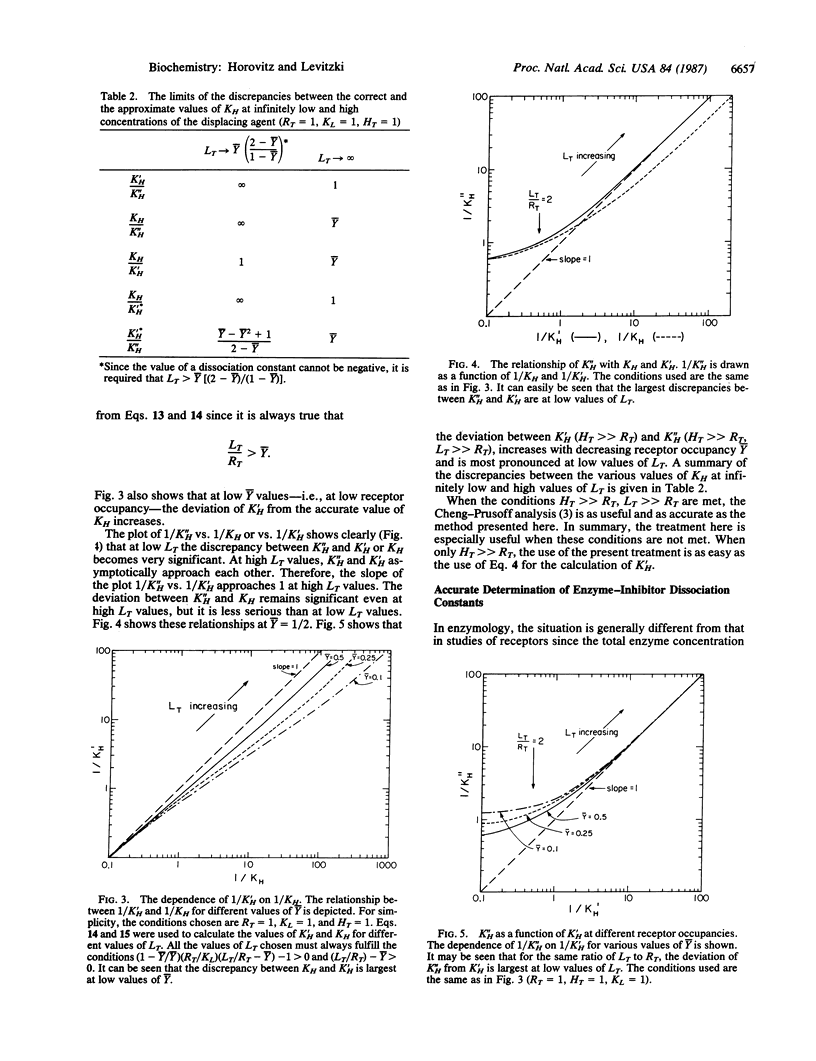
Receptor-ligand dissociation constants are usually calculated from the displacement curve of a radioactively labeled ligand bound to the receptor. The formula used is restricted to cases in which the concentration of receptor is negligible compared to the concentration of both the displacing ligand and the radioactive ligand used. In this study, we rigorously derive a simple equation that can be used for calculating receptor-ligand dissociation constants for any set of experimental conditions. A linearized form of this equation provides a convenient plot from which the dissociation constant of the displacing ligand can be directly obtained. The plot is also a test for the competitive mode of binding. This exact equation now allows us to estimate the error incurred by the conventionally used equations. Similarly, we show that for competitive inhibition in enzymology, one can derive the analogous formula. Our new formula is free of the usual restrictions--namely, that the enzyme concentration is very small compared to the concentration of both the substrate and the inhibitor. It may therefore be applied to any set of experimental conditions.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Best-Belpomme M., Dessen P. Inhibition compètitive. Relations linèaires nouvellcs et gènèrales. Biochimie. 1973;55(1):11–16. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(73)80231-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang K. J., Jacobs S., Cuatrecasas P. Quantitative aspects of hormone-receptor interactions of high affinity. Effect of receptor concentration and measurement of dissociation constants of labeled and unlabeled hormones. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Oct 6;406(2):294–303. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(75)90011-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng Y., Prusoff W. H. Relationship between the inhibition constant (K1) and the concentration of inhibitor which causes 50 per cent inhibition (I50) of an enzymatic reaction. Biochem Pharmacol. 1973 Dec 1;22(23):3099–3108. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(73)90196-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DIXON M. The determination of enzyme inhibitor constants. Biochem J. 1953 Aug;55(1):170–171. doi: 10.1042/bj0550170. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Lean A., Hancock A. A., Lefkowitz R. J. Validation and statistical analysis of a computer modeling method for quantitative analysis of radioligand binding data for mixtures of pharmacological receptor subtypes. Mol Pharmacol. 1982 Jan;21(1):5–16. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dixon M. The graphical determination of K m and K i . Biochem J. 1972 Aug;129(1):197–202. doi: 10.1042/bj1290197. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREEN N. M., WORK E. Pancreatic trypsin inhibitor. II. Reaction with trypsin. Biochem J. 1953 May;54(2):347–352. doi: 10.1042/bj0540347. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson P. J. A linear equation that describes the steady-state kinetics of enzymes and subcellular particles interacting with tightly bound inhibitors. Biochem J. 1972 Apr;127(2):321–333. doi: 10.1042/bj1270321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson P. J. Steady-state enzyme kinetics with high-affinity substrates or inhibitors. A statistical treatment of dose-response curves. Biochem J. 1973 Sep;135(1):101–107. doi: 10.1042/bj1350101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levitzki A., Sevilia N., Atlas D., Steer M. L. Ligand specificity and characteristics of the beta-adrenergic receptor in turkey erythrocyte plasma membranes. J Mol Biol. 1975 Sep 5;97(1):35–46. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison J. F. Kinetics of the reversible inhibition of enzyme-catalysed reactions by tight-binding inhibitors. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969;185(2):269–286. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(69)90420-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rang H. P. Drug receptors and their function. Nature. 1971 May 14;231(5298):91–96. doi: 10.1038/231091a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



