Abstract
We have constructed a respiring yeast strain devoid of mitochondrial introns to screen nuclear pet- mutants for those that play a direct role in mitochondrial intron excision. Intron-less mitochondria are introduced by cytoduction into pet- strains that have been made rho0; cytoductants therefrom recover respiratory competency if the original pet- mutation is required only for mitochondrial splicing. By this means, we have identified 11 complementation groups of such genes. Their total number may be estimated as about 18.
Full text
PDF


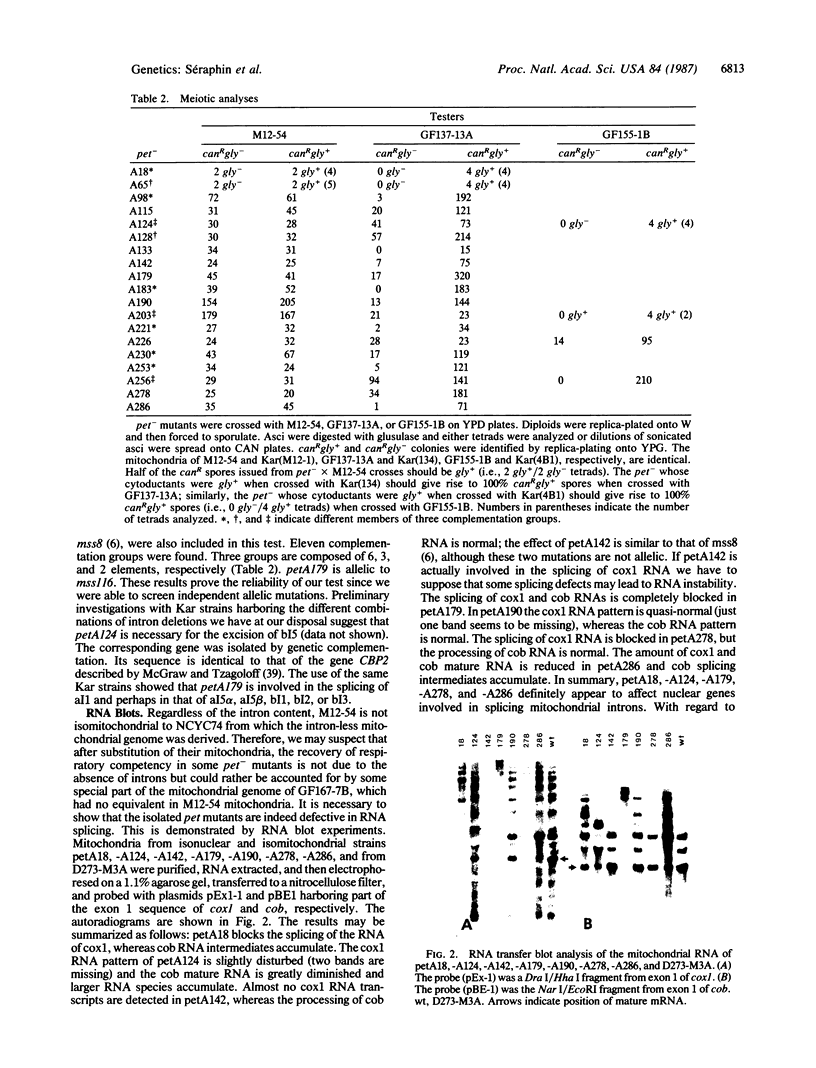

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Boeke J. D., LaCroute F., Fink G. R. A positive selection for mutants lacking orotidine-5'-phosphate decarboxylase activity in yeast: 5-fluoro-orotic acid resistance. Mol Gen Genet. 1984;197(2):345–346. doi: 10.1007/BF00330984. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolotin-Fukuhara M., Fay G., Fukuhara H. Temperature-sensitive respiratory-deficient mitochondrial mutations: isolation and genetic mapping. Mol Gen Genet. 1977 Apr 29;152(3):295–305. doi: 10.1007/BF00693083. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cech T. R., Bass B. L. Biological catalysis by RNA. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:599–629. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.003123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chattoo B. B., Sherman F., Azubalis D. A., Fjellstedt T. A., Mehnert D., Ogur M. Selection of lys2 Mutants of the Yeast SACCHAROMYCES CEREVISIAE by the Utilization of alpha-AMINOADIPATE. Genetics. 1979 Sep;93(1):51–65. doi: 10.1093/genetics/93.1.51. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colleaux L., d'Auriol L., Betermier M., Cottarel G., Jacquier A., Galibert F., Dujon B. Universal code equivalent of a yeast mitochondrial intron reading frame is expressed into E. coli as a specific double strand endonuclease. Cell. 1986 Feb 28;44(4):521–533. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90262-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conde J., Fink G. R. A mutant of Saccharomyces cerevisiae defective for nuclear fusion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Oct;73(10):3651–3655. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.10.3651. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costanzo M. C., Seaver E. C., Fox T. D. At least two nuclear gene products are specifically required for translation of a single yeast mitochondrial mRNA. EMBO J. 1986 Dec 20;5(13):3637–3641. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04693.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies R. W., Waring R. B., Ray J. A., Brown T. A., Scazzocchio C. Making ends meet: a model for RNA splicing in fungal mitochondria. Nature. 1982 Dec 23;300(5894):719–724. doi: 10.1038/300719a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis R. W., Thomas M., Cameron J., St John T. P., Scherer S., Padgett R. A. Rapid DNA isolations for enzymatic and hybridization analysis. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):404–411. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65051-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dieckmann C. L., Tzagoloff A. Assembly of the mitochondrial membrane system. CBP6, a yeast nuclear gene necessary for synthesis of cytochrome b. J Biol Chem. 1985 Feb 10;260(3):1513–1520. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faye G., Simon M. Analysis of a yeast nuclear gene involved in the maturation of mitochondrial pre-messenger RNA of the cytochrome oxidase subunit I. Cell. 1983 Jan;32(1):77–87. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90498-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foury F., Tzagloff A. Assembly of the mitochondrial membrane system. XIX. Genetic characterization of mit- mutants with deficiencies in cytochrome oxidase and coenzyme qh2-cytochrome c reductase. Mol Gen Genet. 1976 Nov 24;149(1):43–50. doi: 10.1007/BF00275959. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukuhara H., Rabinowitz M. Yeast petite mutants for DNA gene amplification. Methods Enzymol. 1979;56:154–163. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)56017-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill J., McGraw P., Tzagoloff A. A mutation in yeast mitochondrial DNA results in a precise excision of the terminal intron of the cytochrome b gene. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 25;260(6):3235–3238. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreike J., Schulze M., Pillar T., Körte A., Rödel G. Cloning of a nuclear gene MRS1 involved in the excision of a single group I intron (bI3) from the mitochondrial COB transcript in S. cerevisiae. Curr Genet. 1986;11(3):185–191. doi: 10.1007/BF00420605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kutzleb R., Schweyen R. J., Kaudewitz F. Extrachromosomal inheritance of paromomycin resistance in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetic and biochemical characterization of mutants. Mol Gen Genet. 1973 Sep 5;125(1):91–98. doi: 10.1007/BF00292984. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labouesse M., Slonimski P. P. Construction of novel cytochrome b genes in yeast mitochondria by subtraction or addition of introns. EMBO J. 1983;2(2):269–276. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01416.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lancashire W. E., Mattoon J. R. Cytoduction: a tool for mitochondrial genetic studies in yeast. Utilization of the nuclear-fusion mutation kar 1-1 for transfer of drug r and mit genomes in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Gen Genet. 1979 Mar 5;170(3):333–344. doi: 10.1007/BF00267067. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGraw P., Tzagoloff A. Assembly of the mitochondrial membrane system. Characterization of a yeast nuclear gene involved in the processing of the cytochrome b pre-mRNA. J Biol Chem. 1983 Aug 10;258(15):9459–9468. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michel F., Dujon B. Conservation of RNA secondary structures in two intron families including mitochondrial-, chloroplast- and nuclear-encoded members. EMBO J. 1983;2(1):33–38. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01376.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers A. M., Pape L. K., Tzagoloff A. Mitochondrial protein synthesis is required for maintenance of intact mitochondrial genomes in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. EMBO J. 1985 Aug;4(8):2087–2092. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03896.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Padgett R. A., Grabowski P. J., Konarska M. M., Seiler S., Sharp P. A. Splicing of messenger RNA precursors. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:1119–1150. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.005351. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perea J., Jacq C. Role of the 5' hairpin structure in the splicing accuracy of the fourth intron of the yeast cob-box gene. EMBO J. 1985 Dec 1;4(12):3281–3288. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04078.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Putrament A., Baranowska H., Prazmo W. Induction by manganese of mitochondrial antibiotic resistance mutations in yeast. Mol Gen Genet. 1973 Nov 22;126(4):357–366. doi: 10.1007/BF00269445. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rödel G., Michaelis U., Forsbach V., Kreike J., Kaudewitz F. Molecular cloning of the yeast nuclear genes CBS1 and CBS2. Curr Genet. 1986;11(1):47–53. doi: 10.1007/BF00389425. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiestl R., Wintersberger U. X-ray enhances mating type switching in heterothallic strains of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Gen Genet. 1982;186(4):512–517. doi: 10.1007/BF00337958. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmelzer C., Schweyen R. J. Self-splicing of group II introns in vitro: mapping of the branch point and mutational inhibition of lariat formation. Cell. 1986 Aug 15;46(4):557–565. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90881-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon M., Faye G. Steps in processing of the mitochondrial cytochrome oxidase subunit I pre-mRNA affected by a nuclear mutation in yeast. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jan;81(1):8–12. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.1.8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Séraphin B., Simon M., Faye G. The mitochondrial reading frame RF3 is a functional gene in Saccharomyces uvarum. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jul 25;262(21):10146–10153. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA and small DNA fragments transferred to nitrocellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5201–5205. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tzagoloff A., Akai A., Needleman R. B. Assembly of the mitochondrial membrane system: isolation of nuclear and cytoplasmic mutants of Saccharomyces cerevisiae with specific defects in mitochondrial functions. J Bacteriol. 1975 Jun;122(3):826–831. doi: 10.1128/jb.122.3.826-831.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tzagoloff A., Myers A. M. Genetics of mitochondrial biogenesis. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:249–285. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.001341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ten Berge A. M. Genes for the fermentation of maltose and -methylglucoside in Saccharomyces carlsbergensis. Mol Gen Genet. 1972;115(1):80–88. doi: 10.1007/BF00272220. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Veen R., Arnberg A. C., van der Horst G., Bonen L., Tabak H. F., Grivell L. A. Excised group II introns in yeast mitochondria are lariats and can be formed by self-splicing in vitro. Cell. 1986 Jan 31;44(2):225–234. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90756-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]