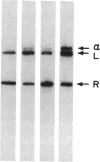
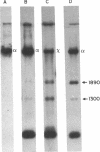
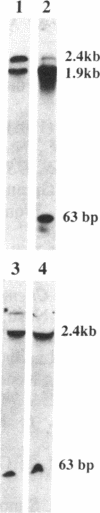
Abstract
Cre, the site-specific recombinase from bacteriophage P1, catalyzes a recombination reaction between specific DNA sequences designated as lox sites. The breakage and rejoining of partners during this recombination process must be highly concerted because it has not been possible to detect intermediates of the reaction with wild-type Cre. Several mutant Cre proteins have been isolated that produce significant amounts of a possible intermediate product of the recombination reaction. The product has been identified as a Holliday structure in which one set of the DNA strands of the recombining partners has been exchanged. Wild-type Cre protein is capable of acting on this structure to form recombinant products, which is consistent with this being an intermediate in the recombination reaction. Characterization of the Holliday structure indicated that one set of strands in the recombining partners was always exchanged preferentially before the other set. In addition, it has been found that certain Cre mutants that are unable to carry out recombination in vitro are able to resolve the intermediate. This suggests that these mutants are defective in a step in the reaction that precedes the formation of the Holliday intermediate.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abremski K., Frommer B., Hoess R. H. Linking-number changes in the DNA substrate during Cre-mediated loxP site-specific recombination. J Mol Biol. 1986 Nov 5;192(1):17–26. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90460-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Abremski K., Hoess R. Bacteriophage P1 site-specific recombination. Purification and properties of the Cre recombinase protein. J Biol Chem. 1984 Feb 10;259(3):1509–1514. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Abremski K., Hoess R., Sternberg N. Studies on the properties of P1 site-specific recombination: evidence for topologically unlinked products following recombination. Cell. 1983 Apr;32(4):1301–1311. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90311-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Abremski K., Wierzbicki A., Frommer B., Hoess R. H. Bacteriophage P1 Cre-loxP site-specific recombination. Site-specific DNA topoisomerase activity of the Cre recombination protein. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jan 5;261(1):391–396. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell L., Byers B. Occurrence of crossed strand-exchange forms in yeast DNA during meiosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jul;76(7):3445–3449. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.7.3445. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dressler D., Potter H. Molecular mechanisms in genetic recombination. Annu Rev Biochem. 1982;51:727–761. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.51.070182.003455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drew H. R. Structural specificities of five commonly used DNA nucleases. J Mol Biol. 1984 Jul 15;176(4):535–557. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90176-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Echols H., Green L. Some properties of site-specific and general recombination inferred from int-initiated exchanges by bacteriophage lambda. Genetics. 1979 Oct;93(2):297–307. doi: 10.1093/genetics/93.2.297. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enquist L. W., Nash H., Weisberg R. A. Strand exchange in site-specific recombination. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Mar;76(3):1363–1367. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.3.1363. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoess R. H., Abremski K. Mechanism of strand cleavage and exchange in the Cre-lox site-specific recombination system. J Mol Biol. 1985 Feb 5;181(3):351–362. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90224-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoess R. H., Wierzbicki A., Abremski K. The role of the loxP spacer region in P1 site-specific recombination. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Mar 11;14(5):2287–2300. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.5.2287. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoess R. H., Ziese M., Sternberg N. P1 site-specific recombination: nucleotide sequence of the recombining sites. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jun;79(11):3398–3402. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.11.3398. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu P. L., Landy A. Resolution of synthetic att-site Holliday structures by the integrase protein of bacteriophage lambda. Nature. 1984 Oct 25;311(5988):721–726. doi: 10.1038/311721a0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kikuchi Y., Nash H. A. Nicking-closing activity associated with bacteriophage lambda int gene product. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Aug;76(8):3760–3764. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.8.3760. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nash H. A., Pollock T. J. Site-specific recombination of bacteriophage lambda. The change in topological linking number associated with exchange of DNA strands. J Mol Biol. 1983 Oct 15;170(1):19–38. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80225-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radding C. M. Homologous pairing and strand exchange in genetic recombination. Annu Rev Genet. 1982;16:405–437. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.16.120182.002201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadowski P. Site-specific recombinases: changing partners and doing the twist. J Bacteriol. 1986 Feb;165(2):341–347. doi: 10.1128/jb.165.2.341-347.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sigal N., Alberts B. Genetic recombination: the nature of a crossed strand-exchange between two homologous DNA molecules. J Mol Biol. 1972 Nov 28;71(3):789–793. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(72)80039-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sternberg N. Bacteriophage P1 site-specific recombination. III. Strand exchange during recombination at lox sites. J Mol Biol. 1981 Aug 25;150(4):603–608. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90384-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wierzbicki A., Kendall M., Abremski K., Hoess R. A mutational analysis of the bacteriophage P1 recombinase Cre. J Mol Biol. 1987 Jun 20;195(4):785–794. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90484-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]