Abstract
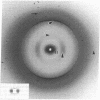
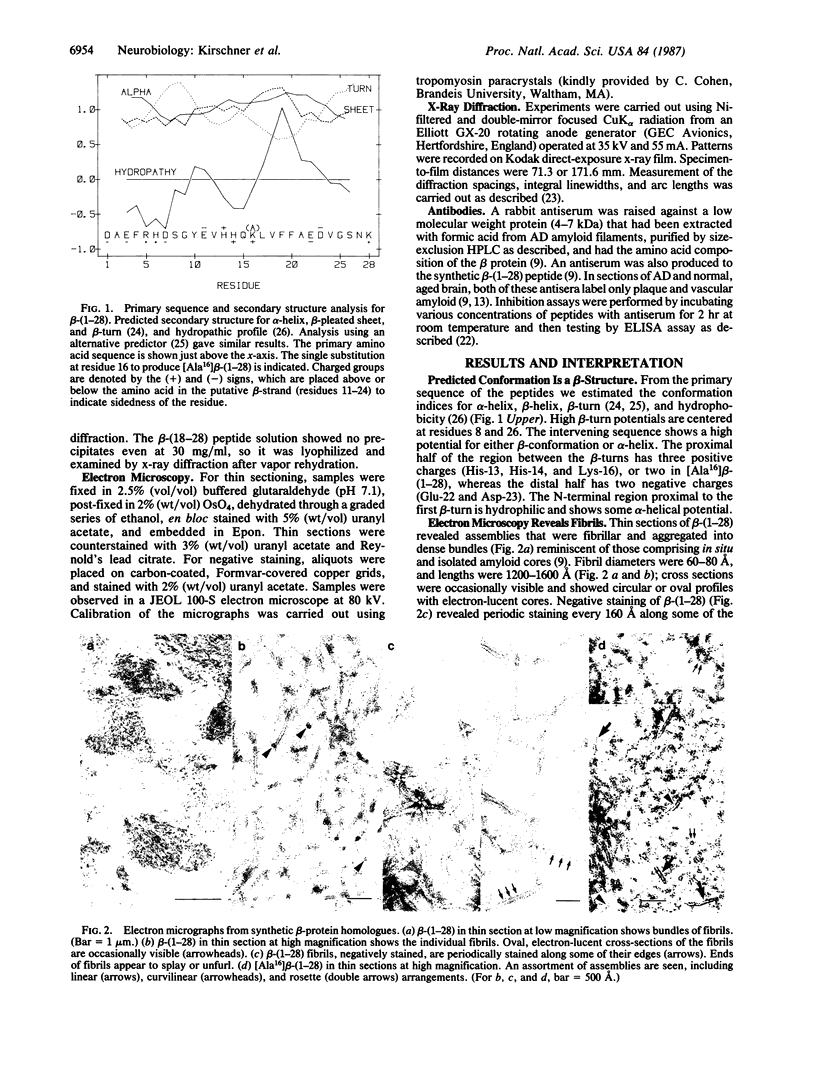
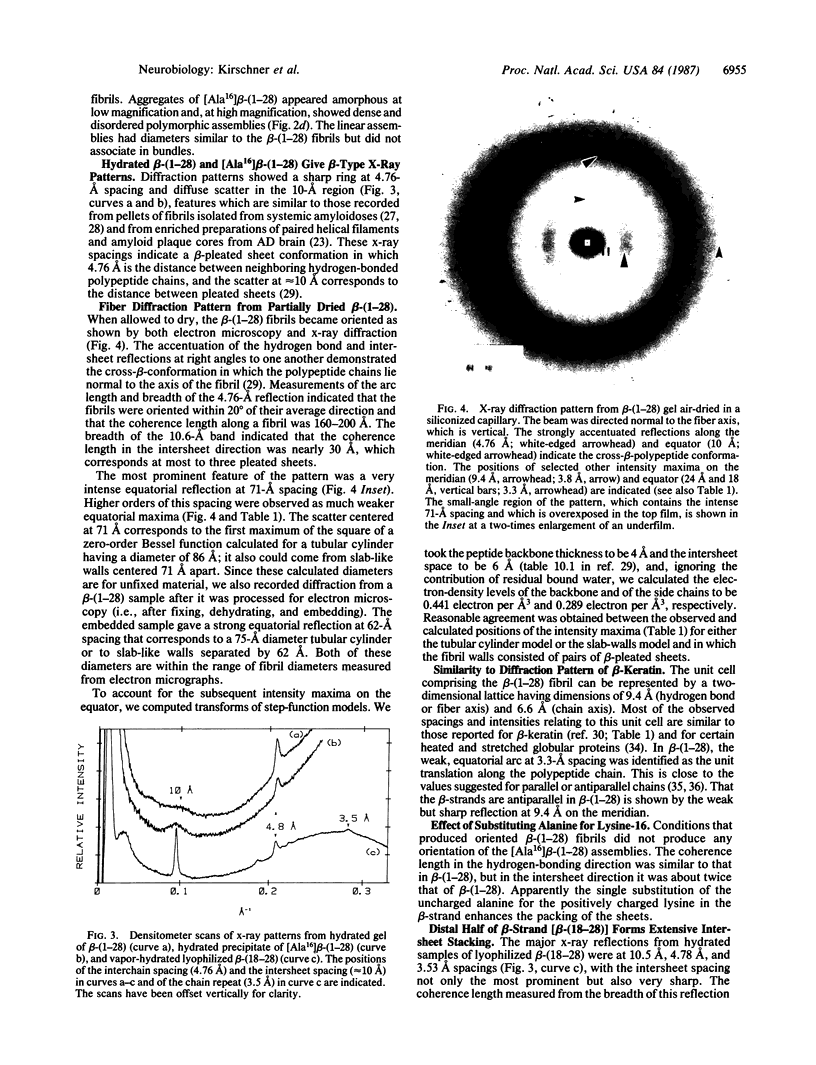
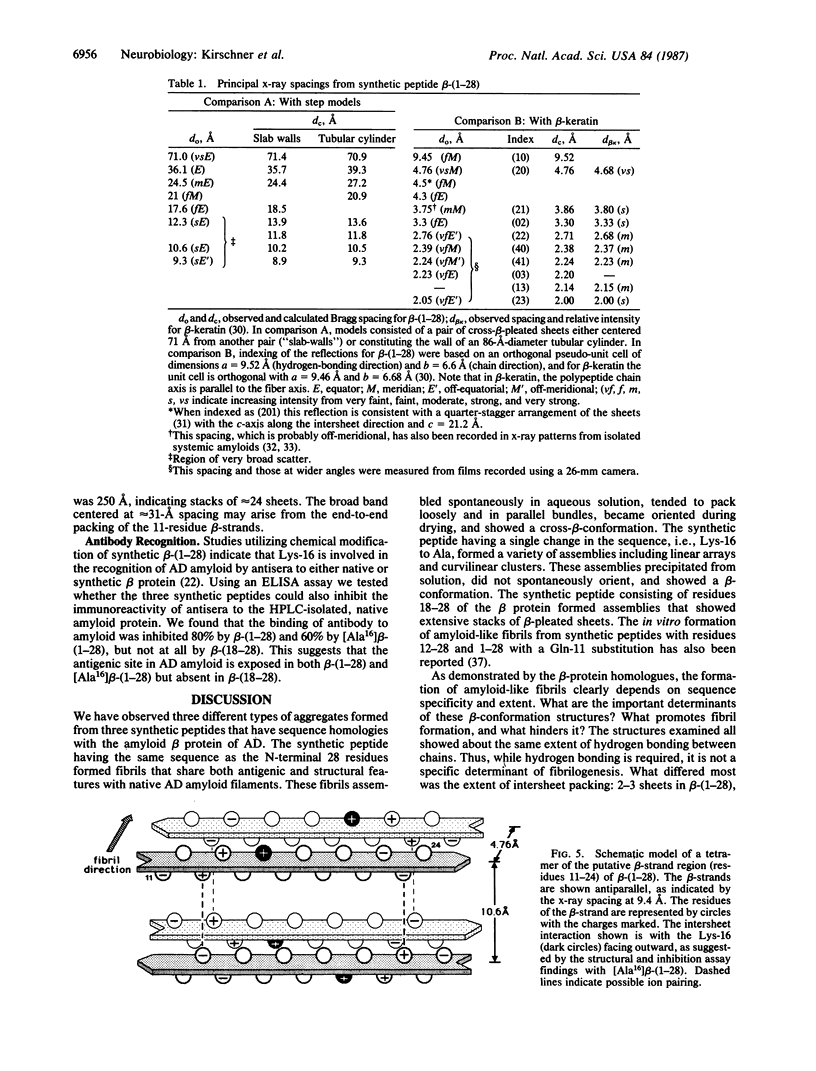
Progressive amyloid deposition in senile plaques and cortical blood vessels may play a central role in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer disease. We have used x-ray diffraction and electron microscopy to study the molecular organization and morphology of macromolecular assemblies formed by three synthetic peptides homologous to beta protein of brain amyloid: beta-(1-28), residues 1-28 of the beta protein; [Ala16]beta-(1-28), beta-(1-28) with alanine substituted for lysine at position 16; and beta-(18-28), residues 18-28 of the beta protein. beta-(1-28) readily formed fibrils in vitro that were similar in ultrastructure to the in vivo amyloid and aggregated into large bundles resembling those of senile plaque cores. X-ray patterns from partially dried, oriented pellets showed a cross-beta-conformation. A series of small-angle, equatorial maxima were consistent with a tubular fibril having a mean diameter of 86 A and a wall composed of pairs of cross-beta-pleated sheets. The data may also be consistent with pairs of cross-beta-sheets that are centered 71-A apart. [Ala16]beta-(1-28) formed beta-pleated sheet assemblies that were dissimilar to in vivo fibrils. The width of the 10-A spacing indicated stacks of about six sheets. Thus, substitution of the uncharged alanine for the positively charged lysine in the beta-strand region enhances the packing of the sheets and dramatically alters the type of macromolecular aggregate formed. beta-(18-28) formed assemblies that had even a greater number of stacked sheets, approximately equal to 24 per diffracting domain as indicated by the sharp intersheet reflection. Our findings on these homologous synthetic assemblies help to define the specific sequence that is required to form Alzheimer-type amyloid fibrils, thus providing an in vitro model of age-related cerebral amyloidogenesis.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bonar L., Cohen A. S., Skinner M. M. Characterization of the amyloid fibril as a cross-beta protein. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1969 Sep;131(4):1373–1375. doi: 10.3181/00379727-131-34110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castaño E. M., Ghiso J., Prelli F., Gorevic P. D., Migheli A., Frangione B. In vitro formation of amyloid fibrils from two synthetic peptides of different lengths homologous to Alzheimer's disease beta-protein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Dec 15;141(2):782–789. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(86)80241-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou P. Y., Fasman G. D. Empirical predictions of protein conformation. Annu Rev Biochem. 1978;47:251–276. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.47.070178.001343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eanes E. D., Glenner G. G. X-ray diffraction studies on amyloid filaments. J Histochem Cytochem. 1968 Nov;16(11):673–677. doi: 10.1177/16.11.673. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg D., Schwarz E., Komaromy M., Wall R. Analysis of membrane and surface protein sequences with the hydrophobic moment plot. J Mol Biol. 1984 Oct 15;179(1):125–142. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90309-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRASER R. D., MACRAE T. P. An investigation of the structure of beta-keratin. J Mol Biol. 1962 Nov;5:457–466. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(62)80118-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garnier J., Osguthorpe D. J., Robson B. Analysis of the accuracy and implications of simple methods for predicting the secondary structure of globular proteins. J Mol Biol. 1978 Mar 25;120(1):97–120. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90297-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geddes A. J., Parker K. D., Atkins E. D., Beighton E. "Cross-beta" conformation in proteins. J Mol Biol. 1968 Mar 14;32(2):343–358. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90014-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glenner G. G., Henry J. H., Fujihara S. Congophilic angiopathy in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer's degeneration. Ann Pathol. 1981;1(2):120–129. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glenner G. G., Wong C. W. Alzheimer's disease and Down's syndrome: sharing of a unique cerebrovascular amyloid fibril protein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Aug 16;122(3):1131–1135. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)91209-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glenner G. G., Wong C. W. Alzheimer's disease: initial report of the purification and characterization of a novel cerebrovascular amyloid protein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 May 16;120(3):885–890. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(84)80190-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldgaber D., Lerman M. I., McBride O. W., Saffiotti U., Gajdusek D. C. Characterization and chromosomal localization of a cDNA encoding brain amyloid of Alzheimer's disease. Science. 1987 Feb 20;235(4791):877–880. doi: 10.1126/science.3810169. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kang J., Lemaire H. G., Unterbeck A., Salbaum J. M., Masters C. L., Grzeschik K. H., Multhaup G., Beyreuther K., Müller-Hill B. The precursor of Alzheimer's disease amyloid A4 protein resembles a cell-surface receptor. Nature. 1987 Feb 19;325(6106):733–736. doi: 10.1038/325733a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirschner D. A., Abraham C., Selkoe D. J. X-ray diffraction from intraneuronal paired helical filaments and extraneuronal amyloid fibers in Alzheimer disease indicates cross-beta conformation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jan;83(2):503–507. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.2.503. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masters C. L., Multhaup G., Simms G., Pottgiesser J., Martins R. N., Beyreuther K. Neuronal origin of a cerebral amyloid: neurofibrillary tangles of Alzheimer's disease contain the same protein as the amyloid of plaque cores and blood vessels. EMBO J. 1985 Nov;4(11):2757–2763. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04000.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masters C. L., Simms G., Weinman N. A., Multhaup G., McDonald B. L., Beyreuther K. Amyloid plaque core protein in Alzheimer disease and Down syndrome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jun;82(12):4245–4249. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.12.4245. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merz P. A., Wisniewski H. M., Somerville R. A., Bobin S. A., Masters C. L., Iqbal K. Ultrastructural morphology of amyloid fibrils from neuritic and amyloid plaques. Acta Neuropathol. 1983;60(1-2):113–124. doi: 10.1007/BF00685355. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Narang H. K. High-resolution electron microscopic analysis of the amyloid fibril in Alzheimer's disease. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1980 Nov;39(6):621–631. doi: 10.1097/00005072-198011000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robakis N. K., Wisniewski H. M., Jenkins E. C., Devine-Gage E. A., Houck G. E., Yao X. L., Ramakrishna N., Wolfe G., Silverman W. P., Brown W. T. Chromosome 21q21 sublocalisation of gene encoding beta-amyloid peptide in cerebral vessels and neuritic (senile) plaques of people with Alzheimer disease and Down syndrome. Lancet. 1987 Feb 14;1(8529):384–385. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(87)91754-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selkoe D. J., Abraham C. R., Podlisny M. B., Duffy L. K. Isolation of low-molecular-weight proteins from amyloid plaque fibers in Alzheimer's disease. J Neurochem. 1986 Jun;46(6):1820–1834. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1986.tb08501.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selkoe D. J., Bell D. S., Podlisny M. B., Price D. L., Cork L. C. Conservation of brain amyloid proteins in aged mammals and humans with Alzheimer's disease. Science. 1987 Feb 20;235(4791):873–877. doi: 10.1126/science.3544219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanzi R. E., Gusella J. F., Watkins P. C., Bruns G. A., St George-Hyslop P., Van Keuren M. L., Patterson D., Pagan S., Kurnit D. M., Neve R. L. Amyloid beta protein gene: cDNA, mRNA distribution, and genetic linkage near the Alzheimer locus. Science. 1987 Feb 20;235(4791):880–884. doi: 10.1126/science.2949367. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Termine J. D., Eanes E. D., Ein D., Glenner G. G. Infrared spectroscopy of human amyloid fibrils and immunoglobulin proteins. Biopolymers. 1972;11(5):1103–1113. doi: 10.1002/bip.1972.360110512. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomlinson B. E., Blessed G., Roth M. Observations on the brains of non-demented old people. J Neurol Sci. 1968 Sep-Oct;7(2):331–356. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(68)90154-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vanley C. T., Aguilar M. J., Kleinhenz R. J., Lagios M. D. Cerebral amyloid angiopathy. Hum Pathol. 1981 Jul;12(7):609–616. doi: 10.1016/s0046-8177(81)80044-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong C. W., Quaranta V., Glenner G. G. Neuritic plaques and cerebrovascular amyloid in Alzheimer disease are antigenically related. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(24):8729–8732. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.24.8729. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]