Abstract
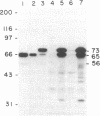
The insecticidal crystal protein gene of the coleopteran-toxic Bacillus thuringiensis var. tenebrionis has been isolated, and the nucleotide sequence has been determined. A total DNA library from var. tenebrionis was made in the plasmid vector pUC12. By using a synthetic 27-base oligonucleotide corresponding to a stretch of nine N-terminal amino acids of a tryptic fragment of purified crystal protein of var. tenebrionis as a probe, recombinant colonies were screened by in situ hybridization for the presence of the crystal protein gene. Positive clones obtained from this screening were further tested for toxicity. One recombinant, NSBP544 (which contained a 5.9-kilobase BamHI insert), was toxic to larvae of Colorado potato beetle. Immunoblot analysis revealed that this clone produces two crystal-specific antigens of 65 and 73 kDa as do sporulating var. tenebrionis cells. However, purified crystal inclusions from var. tenebrionis contain a primary peptide component of 65 kDa. A 1932-base-pair open reading frame with a coding capacity of 73,119 Da has been identified by nucleotide sequencing analysis of the cloned crystal protein. In addition, mung bean nuclease mapping indicates that transcription of the crystal protein of var. tenebrionis initiates 130 base pairs upstream from the translational start site. Southern blot analysis using an internal 0.7-kilobase EcoRI fragment of pNSBP544 as a probe revealed that the crystal protein gene is located on a 90-MDa plasmid.
Keywords: crystal toxin, coleopteran pathogen, biological insect control
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adang M. J., Staver M. J., Rocheleau T. A., Leighton J., Barker R. F., Thompson D. V. Characterized full-length and truncated plasmid clones of the crystal protein of Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. kurstaki HD-73 and their toxicity to Manduca sexta. Gene. 1985;36(3):289–300. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90184-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eckhardt T. A rapid method for the identification of plasmid desoxyribonucleic acid in bacteria. Plasmid. 1978 Sep;1(4):584–588. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(78)90016-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- González J. M., Jr, Carlton B. C. Patterns of plasmid DNA in crystalliferous and acrystalliferous strains of Bacillus thuringiensis. Plasmid. 1980 Jan;3(1):92–98. doi: 10.1016/s0147-619x(80)90038-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson W. C., Moran C. P., Jr, Losick R. Two RNA polymerase sigma factors from Bacillus subtilis discriminate between overlapping promoters for a developmentally regulated gene. Nature. 1983 Apr 28;302(5911):800–804. doi: 10.1038/302800a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klier A., Fargette F., Ribier J., Rapoport G. Cloning and expression of the crystal protein genes from Bacillus thuringiensis strain berliner 1715. EMBO J. 1982;1(7):791–799. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01249.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kronstad J. W., Schnepf H. E., Whiteley H. R. Diversity of locations for Bacillus thuringiensis crystal protein genes. J Bacteriol. 1983 Apr;154(1):419–428. doi: 10.1128/jb.154.1.419-428.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyte J., Doolittle R. F. A simple method for displaying the hydropathic character of a protein. J Mol Biol. 1982 May 5;157(1):105–132. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90515-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsh J. L., Erfle M., Wykes E. J. The pIC plasmid and phage vectors with versatile cloning sites for recombinant selection by insertional inactivation. Gene. 1984 Dec;32(3):481–485. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90022-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray M. G. Use of sodium trichloroacetate and mung bean nuclease to increase sensitivity and precision during transcript mapping. Anal Biochem. 1986 Oct;158(1):165–170. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(86)90605-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnepf H. E., Whiteley H. R. Cloning and expression of the Bacillus thuringiensis crystal protein gene in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 May;78(5):2893–2897. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.5.2893. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnepf H. E., Whiteley H. R. Delineation of a toxin-encoding segment of a Bacillus thuringiensis crystal protein gene. J Biol Chem. 1985 May 25;260(10):6273–6280. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnepf H. E., Wong H. C., Whiteley H. R. The amino acid sequence of a crystal protein from Bacillus thuringiensis deduced from the DNA base sequence. J Biol Chem. 1985 May 25;260(10):6264–6272. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sekar V. Biochemical and immunological characterization of the cloned crystal toxin of Bacillus thuringiensis var. israelensis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Jun 13;137(2):748–751. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(86)91142-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sekar V., Carlton B. C. Molecular cloning of the delta-endotoxin gene of Bacillus thuringiensis var. israelensis. Gene. 1985;33(2):151–158. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90089-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torczynski R. M., Fuke M., Bollon A. P. Human genomic library screened with 17-base oligonucleotide probes yields a novel interferon gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Oct;81(20):6451–6455. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.20.6451. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waalwijk C., Dullemans A. M., van Workum M. E., Visser B. Molecular cloning and the nucleotide sequence of the Mr 28 000 crystal protein gene of Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. israelensis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Nov 25;13(22):8207–8217. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.22.8207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward E. S., Ellar D. J. Bacillus thuringiensis var. israelensis delta-endotoxin. Nucleotide sequence and characterization of the transcripts in Bacillus thuringiensis and Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1986 Sep 5;191(1):1–11. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90417-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong H. C., Chang S. Identification of a positive retroregulator that stabilizes mRNAs in bacteria. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 May;83(10):3233–3237. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.10.3233. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong H. C., Schnepf H. E., Whiteley H. R. Transcriptional and translational start sites for the Bacillus thuringiensis crystal protein gene. J Biol Chem. 1983 Feb 10;258(3):1960–1967. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanisch-Perron C., Vieira J., Messing J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene. 1985;33(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]