Abstract
Nicotinic acid adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NAADP) is a ubiquitous messenger proposed to stimulate Ca2+ release from acidic organelles via two-pore channels (TPCs). It has been difficult to resolve this trigger event from its amplification via endoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ stores, fuelling speculation that archetypal intracellular Ca2+ channels are the primary targets of NAADP. Here, we redirect TPC2 from lysosomes to the plasma membrane and show that NAADP evokes Ca2+ influx independent of ryanodine receptors and that it activates a Ca2+-permeable channel whose conductance is reduced by mutation of a residue within a putative pore. We therefore uncouple TPC2 from amplification pathways and prove that it is a pore-forming subunit of an NAADP-gated Ca2+ channel.
Keywords: Biophysics, Calcium Channels, Calcium Intracellular Release, Lysosomes, Ryanodine, Trafficking, NAADP, Two-pore Channels
Introduction
Nicotinic acid adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NAADP) 7 is a potent Ca2+-mobilizing messenger in many cells, where it regulates processes as diverse as fertilization and neuronal growth (1). Recent studies suggest that ubiquitous but poorly characterized ion channels, the two-pore channels (TPCs), are credible candidates for the NAADP receptor (2–7). Localization of TPCs to the endo-lysosomal system and modification of NAADP-evoked Ca2+ signals after changes in TPC expression (2–6) support the idea that TPCs mediate NAADP-evoked Ca2+ signals from acidic organelles (8–12). But the Ca2+ signals evoked by NAADP are often attenuated when Ca2+ release from the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is inhibited (11–16), leading some to suggest that the initial NAADP-evoked Ca2+ signal is amplified by ryanodine or inositol trisphosphate receptors (Fig. 1A, i and ii) (10–14) and others to conclude that ryanodine receptors are the primary targets of NAADP (Fig. 1Aiii) (15, 17–19). It has proven difficult to observe NAADP-mediated Ca2+ signals free of their presumed interactions with conventional intracellular Ca2+ channels in the ER. The inaccessibility of intracellular NAADP-sensitive channels to patch clamp recording has further limited opportunities to resolve directly their biophysical properties. Here, we address these issues by mutating a lysosomal targeting sequence in TPC2. This redirects TPC2 to the plasma membrane, where it is both uncoupled from ryanodine receptors and accessible to electrophysiological analysis.
FIGURE 1.
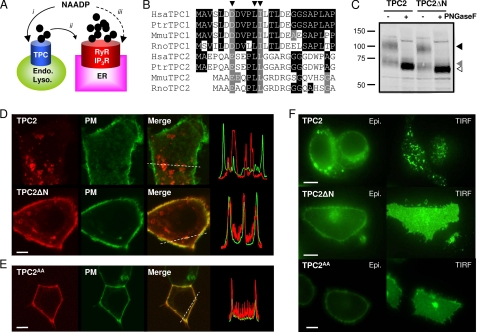
Removal of the N terminus redirects TPC2 from lysosomes to the plasma membrane. A, possible actions of NAADP. NAADP is proposed to activate TPCs on the endo-lysosomal system (i) followed by amplification of these trigger signals by ER Ca2+ channels (ii) such as ryanodine receptors (RyR) and inositol trisphosphate receptors (IP3R). Alternatively, NAADP has been proposed to activate Ca2+ release from the ER directly (iii). B, sequence alignments of Human (Hsa), chimpanzee (Ptr), mouse (Mmu) and rat (Rno) TPC N-terminal sequences highlighting a conserved dileucine endo-lysosomal targeting motif conforming to the consensus sequence (DE)XXXL(L/I) (arrowheads). C, Western blot analysis of SKBR3 cell extracts expressing GFP-tagged TPC2 or TPC2ΔN (10 μg/lane). Samples were incubated with (+) or without (−) peptide:N-glycosidase F (PNGaseF) prior to analysis. Arrowheads mark the positions of fully glycosylated (black arrowhead), core glycosylated (gray arrowhead), and deglycosylated (white arrowhead) TPC2 or TPC2ΔN. Results are representative of three experiments. D, confocal fluorescence images of SKBR3 cells coexpressing GFP-tagged human reduced folate carrier to delineate the plasma membrane (PM) and either mRFP-tagged TPC2 (top) or mRFP-tagged TPC2 lacking residues 3–25 (TPC2ΔN; bottom). Merged images are overlays of the plasma membrane marker (green) and TPC constructs (red). Transect analyses of red and green fluorescence intensities across the regions marked by dotted lines are shown on the right. E, confocal fluorescence images of HEK cells coexpressing the plasma membrane marker and mRFP-tagged TPC2 in which Leu-11 and Leu-12 were replaced with Ala (TPC2AA). F, epifluorescence (Epi.) and TIRF images of HEK cells expressing C-terminally GFP-tagged TPC2, TPC2ΔN, or TPC2AA. Images (D–F) are typical examples from samples of 15–20 cells. All scale bars, 5 μm.
EXPERIMENTAL PROCEDURES
Plasmids
Plasmids encoding wild-type mRFP- and GFP-tagged TPC1 and TPC2 were described previously (4). A construct encoding human TPC1 lacking residues 3–12 (TPC1ΔN) was generated by PCR using the primers 1F and 1R and IMAGE clone 40148827 (accession number BC150203) as template. Primer sequences are presented in supplemental Table S1. The product was cloned into pCS2+GFP or pCS2+mRFP (described in Ref. 4) at the ClaI and EcoRI sites to introduce the fluorescent tag at the C terminus. TPC2 lacking residues 3–25 (TPC2ΔN) was generated using the primers 2F and 2R and IMAGE clone 5214862 (accession number: BC063008). The product was cloned into the EcoRI and XhoI sites. Constructs in which Leu-740 and Leu-741 of TPC1 were replaced by Ala were generated by sequence overlap extension using the mutagenic primers 3F and 3R and the outer primers 4F and 1R. The cassette was digested with BspEI and EcoRI and cloned into the corresponding sites of pCS2+TPC1 mRFP or pCS2+TPC1ΔN mRFP to generate constructs encoding mRFP-tagged TPC1AA or TPC1ΔNAA. Constructs in which Leu-11 and Leu-12 of GFP-tagged or mRFP-tagged TPC2 were replaced by Ala (TPC2AA) were generated using the QuikChange® Site-directed Mutagenesis kit (Stratagene) and mutagenic primers 5F and 5R. Constructs in which Leu-265 of GFP-tagged TPC2 or TPC2ΔN was replaced by Pro (TPC2L265P and TPC2ΔNL265P) were generated similarly using mutagenic primers 6F and 6R. The coding sequences of all plasmids were fully sequenced to confirm that only the desired mutations were introduced.
Cells and Transfection
SKBR3 human breast cancer cells and HEK cells were cultured as described (4). For Western blot analyses, confocal microscopy, and patch clamp recording, cells were transiently transfected with plasmids using LipofectamineTM 2000 transfection reagent (Invitrogen) according to the manufacturer's instructions. For total internal reflection fluorescence (TIRF) microscopy, cells were transfected using either the Neon transfection device (Invitrogen) for SKBR3 cells or by nucleofection (Amaxa) for HEK cells. Plasmid DNA was used at a concentration of 5 μg/100 μl of cells, and cells were then plated onto polylysine-coated glass-bottomed culture dishes (no. 0 coverglass; MatTek Corp.). Cells were used 1–2 days after transfection.
Western Blotting
Cells expressing GFP-tagged TPC2 constructs were harvested by scraping, washed by centrifugation (500 × g, 5 min), and resuspended in solubilization buffer (10 μl/cm2 adherent cells) comprising 20 mm Tris (pH 7.2), 50 mm NaCl, 10 mm magnesium acetate, 1% Surfact-Amps X-100 (Pierce), and a EDTA-free protease inhibitor mixture (Roche Applied Sciences). The suspension was rotated for 60 min at 4 °C, then centrifuged (90,000 × g, 60 min, 4 °C), and the supernatant was incubated with or without peptide:N-glycosidase F (50,000 units/ml; New England Biolabs) for 60 min at 37 °C according to the manufacturer's instructions except that the denaturation step was omitted. Samples (10 μg) were resuspended in NuPAGE® LDS-sample buffer (Invitrogen) supplemented with 100 mm DTT and incubated at 20 °C for 60 min prior to SDS-PAGE using NuPAGE® Novex 4–12% BisTris gels (Invitrogen). Proteins were transferred to nitrocellulose, and Western blotting was performed as described in Ref. 20 using a mouse anti-GFP primary antibody (1:1000; Roche Applied Sciences) and an anti-mouse horseradish peroxidase-conjugated secondary antibody (1:1000; Invitrogen).
Microscopy
Confocal microscopy was performed as described previously (4). For TIRF microscopy, an Olympus IX81 microscope equipped with a 150×/1.45NA TIRF objective was used. Images were acquired with an Andor iXON 897 camera (512 × 512 pixels). Cells were illuminated with either a 488-nm laser (TIRF) or a xenon arc lamp via a GFP (488-nm) filter set (wide-field). All settings were identical for images of TPC2, TPC2ΔN, and TPC2AA. Yellow-green FluoSpheres (100-nm diameter; Invitrogen) were used to establish the angle of reflection for TIRF.
Cytosolic Ca2+ Measurements
Free cytosolic Ca2+ concentrations of single fura-2-loaded SKBR3 cells were measured, and microinjection was performed as described (4). All microinjected cells were included in the analysis.
Patch Clamp Recording
The whole-cell or excised inside-out configurations were used for patch clamp recording at 20 °C from transiently transfected HEK cells (21). Unless stated otherwise, both bath and pipette solutions contained 200 mm CsSO3CH3, 2 mm CsCl, 10 mm HEPES (pH 7.2 with CsOH). For determination of the single-channel Ca2+ conductance (γCa), the solutions contained 140 mm calcium gluconate, 2 mm CaCl2, 10 mm HEPES (pH 7.2 with CsOH). For determination of ionic selectivity, the solutions contained 140 mm NMDG gluconate, 2 mm NMDG-Cl, 10 mm HEPES (pH 7.2) with NMDG. The pipette tip resistance when filled with pipette solution was 8–15 megohms (excised patch clamp recordings) and 5–8 megohms (whole-cell recordings). The methods used for recording and analyzing currents were reported previously (22). Briefly, currents were analyzed using the 50% threshold crossing criterion. Openings briefer than 700 μs (twice the filter rise time) were excluded from the analysis (23). Because it is difficult to establish the number of active channels when Po (the single-channel open probability) is low, we use NPo to report channel activity (22). Currents were filtered at 1 kHz and sampled at 10 kHz. For presentation only, traces were further filtered with a Gaussian digital filter at a cut-off frequency of 500 Hz.
Materials
NAADP, ryanodine, and cyclic ADP-ribose were from Sigma. Bafilomycin A1 was from Calbiochem. Trans-NED19 was from Enzo Life Sciences.
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
Targeting of TPC2 to Endo-lysosomes by a Dileucine Motif
The N terminus of several mammalian TPCs includes a conserved dileucine-based motif (Fig. 1B). This sequence targets other trans-membrane proteins to endosomes and lysosomes (24). We expressed human TPC1 and TPC2 with and without their native N termini and used C-terminal mRFP or GFP tags to determine their subcellular distributions. After removal of the N terminus from TPC1 (TPC1ΔN), mutation of another dileucine motif near the C terminus (TPC1AA) or combining both modifications (TPC1ΔNAA), the expressed protein retained an intracellular distribution similar to that of TPC1 (supplemental Fig. S1). These results suggest that targeting of TPC1 does not require its dileucine motifs and may instead involve other sequences, possibly tyrosine-based motifs (24) that are also present in TPC1.
In contrast, TPC2ΔN localized to the plasma membrane although its level of expression and glycosylation were similar to those of TPC2 (Fig. 1C and supplemental Fig. S2A). In confocal images of SKBR3 breast cancer cells (Fig. 1D) and HEK cells (supplemental Fig. S2B), most TPC2ΔN was peripherally located and colocalized with a plasma membrane marker. The small amount of nonperipheral TPC2ΔN also colocalized with the plasma membrane marker (Fig. 1D and supplemental Fig. S2B), suggesting that it represents either TPC2ΔN in transit or invaginations of the plasma membrane. Similar plasma membrane targeting was obtained with TPC2 in which the dileucine motif was mutated by substitution of Leu-11 and Leu-12 with alanine (TPC2AA, Fig. 1E and supplemental Fig. S2C). Additionally, despite similar levels of expression of TPC2, TPC2ΔN, and TPC2AA in HEK (Fig. 1F) and SKBR3 (supplemental Fig. S2D) cells determined using epifluorescence microscopy, TPC2ΔN and TPC2AA were much more evident within the plasma membrane region as revealed by TIRF microscopy. The small punctate TIRF signals from TPC2-expressing cells (Fig. 1F and supplemental Fig. S2D) probably arise from TPC2 in lysosomes lying within 100 nm of the plasma membrane, consistent with our detection of similar signals from cells labeled with Lysotracker Red (data not shown). Together, these results demonstrate that loss of the N-terminal dileucine motif prevents the normal trafficking of TPC2 to lysosomes. TPC2ΔN and TPC2AA are instead localized at the plasma membrane. Mouse TPC2 has been reported to remain intracellular after deletion of its N terminus (3), suggesting either that this truncated protein was misfolded or that mouse TPC2 has an additional lysosomal targeting motif.
Uncoupling of NAADP-evoked Ca2+ Signals from Activation of Ryanodine Receptors
We measured cytosolic Ca2+ signals after microinjection of NAADP into fura-2-loaded SKBR3 cells transiently transfected with plasmids encoding TPC2. NAADP increased the cytosolic Ca2+ concentration in cells expressing TPC2 (Fig. 2A and supplemental Fig. S3A), but not in GFP-transfected cells, nor was there any response from TPC2-expressing cells microinjected with buffer (Fig. 2B). The latter demonstrates that responses to microinjected NAADP are not, as some have suggested (6), a consequence of TPC2 causing increased mechanosensitivity. The selective NAADP antagonist, trans-NED19 (25), blocked the Ca2+ signals evoked by microinjected NAADP (Fig. 2B), further demonstrating the specificity of the NAADP-evoked Ca2+ signals in TPC2-expressing cells.
FIGURE 2.
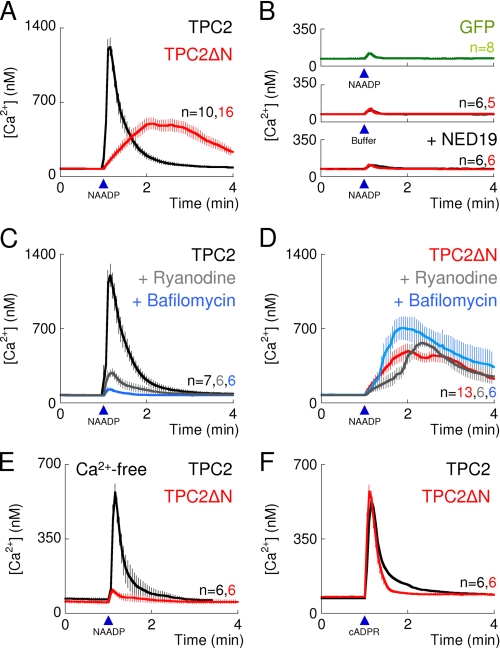
TPC2 targeted to the plasma membrane is uncoupled from ryanodine receptors. A–F, cytosolic Ca2+ signals from individual fura-2-loaded SKBR3 cells transiently transfected with C-terminally GFP-tagged TPC2 (black traces), TPC2ΔN (red traces), or GFP alone (green). A and B, responses to microinjection (arrowheads) with NAADP (10 nm) or buffer. Cells were incubated with trans-NED19 (100 nm, 15 min) as indicated. C and D, responses to microinjection of NAADP (10 nm) from untreated cells or cells incubated with ryanodine (10 μm, 15 min) or bafilomycin A1 (1 μm, 60 min) as indicated. E, extracellular Ca2+ was removed 2–3 min before injection of NAADP. F, cells injected with cyclic ADP-ribose (cADPR, 500 nm). Results are means ± S.E. of the indicated number (n) of cells.
In cells expressing TPC2, the peak Ca2+ signals evoked by NAADP were substantially inhibited after treatment with ryanodine (Fig. 2C), indicating a requirement for ryanodine receptors, which are expressed in the ER. The responses were abolished after treatment with bafilomycin A1, an inhibitor of V-type ATPases, confirming the involvement of acidic organelles (Fig. 2C). These results show that NAADP mobilizes Ca2+ from intracellular Ca2+ stores and involves activation of both TPC2 and ryanodine receptors.
In similar experiments with cells expressing TPC2ΔN, microinjection of NAADP, but not buffer, also evoked Ca2+ signals (Fig. 2, A and B, and supplemental Fig. S3B), and these too were abolished by trans-NED19 (Fig. 2B). In contrast to the results with TPC2, ryanodine had no effect on the amplitude of the Ca2+ signals in TPC2ΔN-expressing cells, although the rising phase of the response was slightly slower (Fig. 2D). Bafilomycin A1, which abolished responses to NAADP in TPC2-expressing cells, modestly enhanced responses to NAADP in TPC2ΔN-expressing cells (Fig. 2D), perhaps reflecting the reduced ability of acidic stores to sequester Ca2+ (discussed in Ref. 26). Furthermore, the Ca2+ signals evoked by NAADP in TPC2ΔN-expressing cells were abolished by removal of extracellular Ca2+ whereas they persisted in TPC2-expressing cells (Fig. 2E). Although even in the latter, responses to NAADP were attenuated, probably because the associated stimulation of ryanodine receptors depletes the ER of Ca2+ and thereby normally stimulates store-operated Ca2+ entry. These results demonstrate that TPC2ΔN mediates NAADP-evoked Ca2+ entry, consistent with its plasma membrane distribution (Fig. 1, D–F, and supplemental Fig. S2, B–D). Together, these results (supplemental Fig. S4, A–C) show that targeting of TPC2 to the plasma membrane dissociates activation of TPC2 from activation of ryanodine receptors. This uncoupling is not caused by impaired function of ryanodine receptors because responses to cyclic ADP-ribose, which activates ryanodine receptors (27), were similar in cells expressing TPC2 and TPC2ΔN (Fig. 2F and supplemental Fig. S4C). We conclude that inhibition of NAADP-evoked Ca2+ signals by ryanodine in cells expressing TPC2 (Fig. 2C) results from disruption of an amplification pathway rather than a direct effect of NAADP on ryanodine receptors. Other Ca2+-permeable channels can also amplify NAADP-evoked Ca2+ signals, for example inositol trisphosphate receptors in HEK cells (2) or nonselective cation channels in medulla neurons (28). The lack of such amplification in TPC2ΔN-expressing cells probably explains the smaller amplitude and modestly slower rise times of their NAADP-evoked Ca2+ signals (Fig. 2A and supplemental Fig. S4D), although we note that in TPC2-expressing cells (Fig. 2B), ryanodine appeared to affect only the amplitude of the Ca2+ signals. Differences in the pH and/or Ca2+ concentration of the extracellular medium compared with the lumen of the lysosome may also contribute to the different kinetics.
Single-channel Properties of TPC2
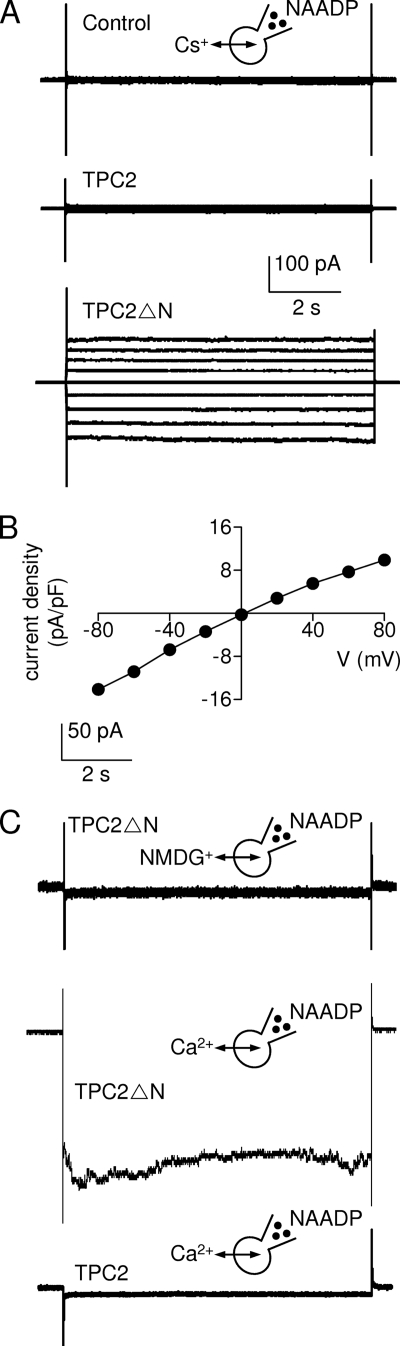
Targeting of functional TPC2 to the plasma membrane provided the first opportunity to examine its single-channel behavior in a native membrane. In whole-cell recordings from HEK cells expressing TPC2ΔN and using Cs+ as the charge-carrier, intracellular NAADP (500 nm) evoked currents that were slightly inwardly rectifying (Fig. 3, A and B). We detected no such currents in either control cells or in cells expressing full-length TPC2 (Fig. 3A). In media containing symmetrical calcium gluconate, NAADP evoked whole-cell currents in cells expressing TPC2ΔN, but not in those expressing TPC2 (Fig. 3C). There were no currents in the TPC2ΔN-expressing cells when the Ca2+ was replaced with an impermeant cation (NMDG+) (Fig. 3C). These results demonstrate that NAADP activates a Ca2+-permeable cation channel in the plasma membrane of cells expressing TPC2ΔN.
FIGURE 3.
TPC2 is an NAADP-gated Ca2+-permeable cation channel. A, whole-cell recordings were performed from nontransfected HEK cells or after transient transfection with C-terminally GFP-tagged TPC2 or TPC2ΔN. With 500 nm NAADP in the pipette solution, and from a holding potential of 0 mV, the potential was switched in 20-mV increments from −80 to +80 mV, and the whole-cell currents were recorded. Results typical of 8 experiments are shown. B, from experiments similar to those in A, the current density-voltage (V) relationship for the NAADP-activated whole-cell current is shown. Results are means ± S.E., n = 6 (error bars are smaller than the symbols). C, whole-cell recordings are similar to those shown in A, but using either symmetrical Ca2+ gluconate or NMDG gluconate-based solutions as indicated. With 500 nm NAADP in the pipette solution, the inward whole-cell current was recorded in response to stepping to −140 mV from a holding potential of 0 mV. Results typical of five or three (middle trace) experiments are shown.
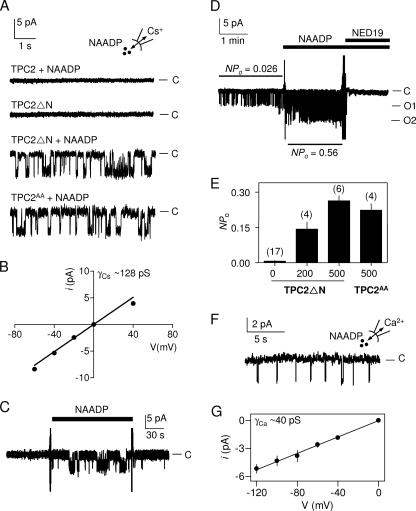
In 17 of 38 recordings from inside-out patches from the plasma membrane of cells expressing TPC2ΔN, NAADP (200–500 nm, in the bathing solution) stimulated bursts of channel openings (Fig. 4A). Detection of channels in ∼40% of patches suggests an average of ∼0.5 randomly distributed channels/patch and is consistent with the relative scarcity (∼8%) of patches in which we detected more than one channel (supplemental text). The current-voltage relationship for these single-channel openings was, like the whole-cell currents (Fig. 3B), slightly inwardly rectifying. The unitary Cs+ conductance (γCs, measured between 0 and −60 mV) was 128 ± 4 pS (Fig. 4B). In continuous recordings, NAADP rapidly and reversibly stimulated this channel activity (Fig. 4C), and trans-NED19 rapidly reversed the activity (Fig. 4D). Channels with indistinguishable conductance (γCs = 138 ± 15 pS, n = 4, data not shown) and NPo (Fig. 4, A and E) were detected in excised patches from cells expressing TPC2AA. We detected no such channels in parallel recordings from either mock-transfected cells (n = 20; data not shown) or from cells expressing TPC2 (Fig. 4A). Some patches from TPC2ΔN-expressing cells (3 of 17 recordings) had detectable activity in the absence of added NAADP, although most were quiescent. In each, the activity was massively increased by addition of 200 or 500 nm NAADP (Fig. 4E).
FIGURE 4.
Activation of single Ca2+-permeable TPC2 channels by NAADP. A, typical recordings from excised inside-out patches from the plasma membrane of HEK cells expressing TPC2, TPC2ΔN, or TPC2AA and stimulated as indicated with NAADP (500 nm in the bathing solution). Cs+ was the charge carrier, and the holding potential was −60 mV; C denotes the closed state. Results are typical (from top to bottom) of 15, 17, 17, and 4 experiments, respectively. B, current (i)-voltage (V) relationship for the NAADP-activated channels in TPC2ΔN-expressing cells. Results are means ± S.E., n = 8. C, recording, typical of three experiments, from an excised inside-out patch from the plasma membrane of HEK cells expressing TPC2ΔN. NAADP (500 nm) was added and removed as indicated. C denotes the closed state. D, recording, typical of three similar records, from a patch excised from the plasma membrane of HEK cells expressing TPC2ΔN and treated with NAADP (500 nm) and trans-NED19 (100 nm) as indicated. Cs+ was the charge carrier, and the holding potential was −40 mV; C, O1, and O2 denote the closed state and openings of one and two channels, respectively. Note the presence of basal activity (NPo), which is increased ∼20-fold by the addition of NAADP; trans-NED19 inhibits both the basal and NAADP-evoked activity. In both C and D changes of media are accompanied by brief electrical spike artifacts. E, summary results showing NPo for excised patches of cells expressing TPC2ΔN or TPC2AA and stimulated with the indicated concentrations of NAADP (nanomolar) in the bathing solution. Results are means ± S.E., with n shown above each bar. F, record, typical of five similar records, from an excised patch expressing TPC2ΔN and with Ca2+ as the charge carrier. Pipette solution contained 500 nm NAADP, and the holding potential was −100 mV. C denotes the closed state. G, current-voltage relationship from records similar to those shown in F. Recordings were restricted to negative holding potentials to avoid activation of voltage-gated Ca2+ channels that may be endogenously expressed in HEK cells (34). Results are means ± S.E., n = 5.
TPC2 is a Pore-forming Subunit of the Ca2+-permeable NAADP-activated Channel
To determine the Ca2+ permeability of the NAADP-activated channel, we recorded currents in excised patches from TPC2ΔN-expressing cells in symmetrical Ca2+ at negative holding potentials (Fig. 4F). From the slopes of the linear current-voltage relationships, the unitary Ca2+ conductance (γCa) of the NAADP-activated channel was 40 ± 1.3 pS (Fig. 4G). NAADP did not activate Ca2+-permeable channels in cells expressing full-length TPC2 (n = 8; data not shown). We note that whereas bursts of openings are common with Cs+ as the charge carrier (Fig. 2, A, C, and D), they are less common with Ca2+ as the charge carrier (Fig. 4F and supplemental Fig. S5). Such effects of permeating ions on channel gating kinetics are also observed for other channels (29–31). These results establish that TPC2 is an essential component of the Ca2+-permeable cation channel activated by NAADP.
An outstanding question is whether TPC2 is itself the pore-forming subunit of the channel. To address this issue, we mutated a conserved residue (Leu-265) within a putative pore region (4) of TPC2 and TPC2ΔN (Fig. 5A). The mutant, TPC2L265P, showed an intracellular distribution similar to that of TPC2, whereas TPC2ΔNL265P, like TPC2ΔN, localized to the plasma membrane in both SKBR3 (Fig. 5B) and HEK (supplemental Fig. S2E) cells. Microinjection of NAADP into SKBR3 cells expressing either TPC2L265P or TPC2ΔNL265P failed to evoke Ca2+ signals (Fig. 5C). We recorded Cs+ currents in excised patches from cells expressing TPC2ΔNL265P. NAADP (500 nm) activated channels in these patches (Fig. 5D) that had similar activity (NPo = 0.32 ± 0.04, n = 3) to those of TPC2ΔN, but their γCs was massively reduced to 9.5 ± 0.41 pS (Fig. 5E). These results, showing that a mutation within the putative pore of TPC2 affects the conductance of the NAADP-activated channel, establish that TPC2 is a pore-forming subunit of the NAADP-activated cation channel. While our work was under review, others reported NAADP-evoked Ca2+ currents from enlarged lysosomes of cells overexpressing mouse TPC2 (32) and single-channel recordings from immunopurified human TPC2 incorporated into artificial lipid bilayers (33). Both studies reported dramatic effects of luminal pH on channel activity (32, 33). Our study is consistent with that of Pitt et al. (33) in demonstrating NAADP-stimulated channel activity at neutral pH, although in our experiments the effects of NAADP were more rapid in onset, reversible, and blocked by lower concentrations of trans-NED19. Our results and those from Pitt et al. (33) differ, however, from the study of Scheider et al. (32), who detected NAADP-mediated currents only at acidic luminal pH.
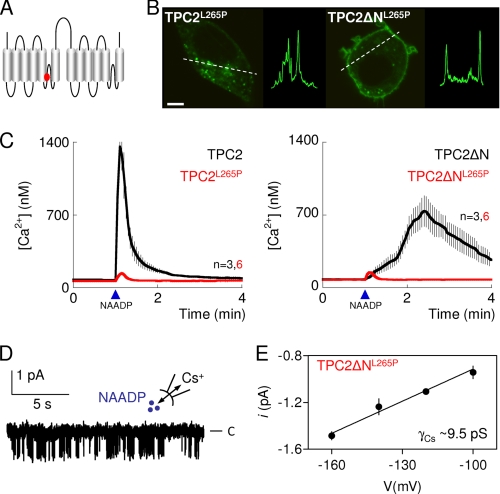
FIGURE 5.
TPC2 is the pore-forming subunit of an NAADP-gated channel. A, depiction of TPC2 showing location of a putative pore residue (Leu-265, red). B, confocal fluorescence images of SKBR3 cells expressing GFP-tagged TPC2 in which Leu-265 was replaced by proline (TPC2L265P, left) or in which this was combined with removal of the N terminus (TPC2ΔNL265P, right). Images are typical of those from 6–10 cells. Scale bar, 5 μm. Similar results with HEK cells are shown in supplemental Fig. S2E. C, cytosolic Ca2+ signals from individual fura-2-loaded SKBR3 cells transiently transfected with the indicated C-terminally GFP-tagged TPC2 constructs and microinjected with NAADP (10 nm, arrowheads). Results are means ± S.E. of the indicated number (n) of cells. D, recording, typical of four similar records, from excised inside-out patches from the plasma membrane of HEK cells expressing TPC2ΔNL265P and stimulated with 500 nm NAADP in the bathing solution with Cs+ as the charge carrier. C denotes the closed state. E, current-voltage relationship from records similar to those shown in D. Results are means ± S.E., n = 4.
CONCLUSIONS
By manipulating an endogenous endo-lysosomal targeting sequence near the N terminus of TPC2, we succeeded in expressing TPC2 in the plasma membrane. This allowed us to dissociate activation of TPC2 by NAADP from amplification of the initial Ca2+ signal by Ca2+ release from the ER, thereby demonstrating that ryanodine receptors are not the primary targets of NAADP. Our single-channel recordings and mutagenesis demonstrate that TPC2 is a pore-forming subunit of a Ca2+-permeable channel activated by NAADP.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgment
We thank Chi Li for useful discussion.
This work was supported, in whole or in part, by National Institutes of Health Grant HL90804 (to E. B.). This work was also supported by the Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council Grants BB/G013721/1 (to S. P.) and BB/H009736/1 (to C. W. T.), the Wellcome Trust Grant 085295 (to C. W. T.), and an equipment grant from the Isaac Newton Trust, Cambridge (to C. W. T).

The on-line version of this article (available at http://www.jbc.org) contains supplemental text, Table S1, and Figs. S1–S5.
- NAADP
- nicotinic acid adenine dinucleotide phosphate
- BisTris
- bis(2-hydroxyethyl)iminotris(hydroxymethyl)methane
- ER
- endoplasmic reticulum
- γ
- single-channel conductance
- HEK
- human embryonic kidney
- NMDG
- N-methyl-d-glucamine
- NPo
- mean channel activity
- NPo
- basal activity
- Po
- single-channel open probability
- pS
- picosiemens
- RFP
- red fluorescent protein
- TIRF
- total internal reflection fluorescence
- TPC
- two-pore channel.
REFERENCES
- 1.Guse A. H., Lee H. C. (2008) Sci. Signal. 1, re10. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Calcraft P. J., Ruas M., Pan Z., Cheng X., Arredouani A., Hao X., Tang J., Rietdorf K., Teboul L., Chuang K. T., Lin P., Xiao R., Wang C., Zhu Y., Lin Y., Wyatt C. N., Parrington J., Ma J., Evans A. M., Galione A., Zhu M. X. (2009) Nature 459, 596–600 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Zong X., Schieder M., Cuny H., Fenske S., Gruner C., Rötzer K., Griesbeck O., Harz H., Biel M., Wahl-Schott C. (2009) Pflugers Arch. 458, 891–899 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Brailoiu E., Churamani D., Cai X., Schrlau M. G., Brailoiu G. C., Gao X., Hooper R., Boulware M. J., Dun N. J., Marchant J. S., Patel S. (2009) J. Cell Biol. 186, 201–209 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Brailoiu E., Hooper R., Cai X., Brailoiu G. C., Keebler M. V., Dun N. J., Marchant J. S., Patel S. (2010) J. Biol. Chem. 285, 2897–2901 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Ruas M., Rietdorf K., Arredouani A., Davis L. C., Lloyd-Evans E., Koegel H., Funnell T. M., Morgan A. J., Ward J. A., Watanabe K., Cheng X., Churchill G. C., Zhu M. X., Platt F. M., Wessel G. M., Parrington J., Galione A. (2010) Curr. Biol. 20, 703–709 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Patel S., Marchant J. S., Brailoiu E. (2010) Cell Calcium 47, 480–490 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Churchill G. C., Okada Y., Thomas J. M., Genazzani A. A., Patel S., Galione A. (2002) Cell 111, 703–708 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Mitchell K. J., Lai F. A., Rutter G. A. (2003) J. Biol. Chem. 278, 11057–11064 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Yamasaki M., Masgrau R., Morgan A. J., Churchill G. C., Patel S., Ashcroft S. J., Galione A. (2004) J. Biol. Chem. 279, 7234–7240 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Kinnear N. P., Boittin F. X., Thomas J. M., Galione A., Evans A. M. (2004) J. Biol. Chem. 279, 54319–54326 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Brailoiu E., Hoard J. L., Filipeanu C. M., Brailoiu G. C., Dun S. L., Patel S., Dun N. J. (2005) J. Biol. Chem. 280, 5646–5650 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Cancela J. M., Churchill G. C., Galione A. (1999) Nature 398, 74–76 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Churchill G. C., Galione A. (2001) EMBO J. 20, 2666–2671 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Gerasimenko J. V., Maruyama Y., Yano K., Dolman N. J., Tepikin A. V., Petersen O. H., Gerasimenko O. V. (2003) J. Cell Biol. 163, 271–282 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Langhorst M. F., Schwarzmann N., Guse A. H. (2004) Cell. Signal. 16, 1283–1289 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Mojzisová A., Krizanová O., Záciková L., Komínková V., Ondrias K. (2001) Pflugers Arch. 441, 674–677 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Hohenegger M., Suko J., Gscheidlinger R., Drobny H., Zidar A. (2002) Biochem. J. 367, 423–431 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Dammermann W., Zhang B., Nebel M., Cordiglieri C., Odoardi F., Kirchberger T., Kawakami N., Dowden J., Schmid F., Dornmair K., Hohenegger M., Flügel A., Guse A. H., Potter B. V. (2009) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 106, 10678–10683 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Churamani D., Boulware M. J., Geach T. J., Martin A. C., Moy G. W., Su Y. H., Vacquier V. D., Marchant J. S., Dale L., Patel S. (2007) PLoS ONE 2, e797. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Hamill O. P., Marty A., Neher E., Sakmann B., Sigworth F. J. (1981) Pflugers Arch. 391, 85–100 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Taufiq-Ur-Rahman, Skupin A., Falcke M., Taylor C. W. (2009) Nature 458, 655–659 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Sakmann B., Neher E. (1995) Single-Channel Recording, 2nd Ed., Plenum Press, New York [Google Scholar]
- 24.Bonifacino J. S., Traub L. M. (2003) Annu. Rev. Biochem. 72, 395–447 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Naylor E., Arredouani A., Vasudevan S. R., Lewis A. M., Parkesh R., Mizote A., Rosen D., Thomas J. M., Izumi M., Ganesan A., Galione A., Churchill G. C. (2009) Nat. Chem. Biol. 5, 220–226 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Patel S., Docampo R. (2010) Trends Cell Biol. 20, 277–286 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Galione A., Churchill G. C. (2000) Sci. STKE 2000, pe1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Brailoiu G. C., Brailoiu E., Parkesh R., Galione A., Churchill G. C., Patel S., Dun N. J. (2009) Biochem. J. 419, 91–97 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Bezprozvanny I., Ehrlich B. E. (1994) J. Gen. Physiol. 104, 821–856 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Lu T., Wu L., Xiao J., Yang J. (2001) J. Gen. Physiol. 118, 509–522 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Kusch J., Nache V., Benndorf K. (2004) J. Physiol 560, 605–616 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Schieder M., Rötzer K., Brüggemann A., Biel M., Wahl-Schott C. A. (2010) J. Biol. Chem. 285, 21219–21222 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Pitt S. J., Funnell T., Sitsapesan M., Venturi E., Rietdorf K., Ruas M., Ganesan A., Gosain R., Churchill G. C., Zhu M. X., Parrington J., Galione A., Sitsapesan R. (2010) J. Biol. Chem. 285, in press [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Thomas P., Smart T. G. (2005) J. Pharmacol. Toxicol. Methods 51, 187–200 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.