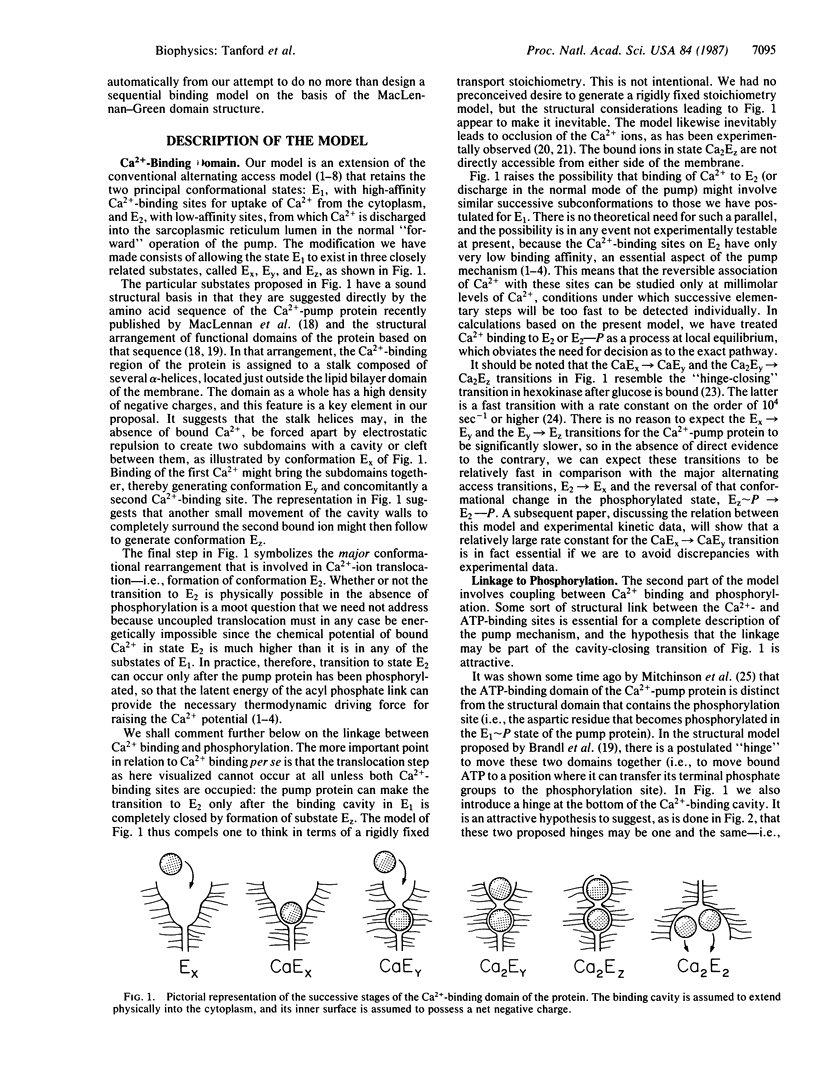
Abstract
The conventional alternating access model for Ca2+ transport by the sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ pump is modified, partly on the basis of the proposed MacLennan-Green domain structure for the Ca2+-pump protein. The present model divides the uptake state (E1) of the protein into three substates, differing in the condition of the Ca2+-binding domain. The domain is an open cavity in the first substate and can bind only a single Ca2+ ion. A fast "jaw-closing" (or "hinge-bending") step then partially closes the cavity to generate the second substate that has a second Ca2+-binding site. Occupation of this site is followed by another jaw-closing step that closes the binding cavity and occludes the bound ions. The subsequent translocation step (to form E2) remains unchanged from previous models. The modified model predicts a constant transport stoichiometry of two Ca2+ per pump reaction cycle. It suggests a plausible mechanism for coupling between Ca2+ binding and ATP utilization: the model predicts (in agreement with experiment) that Ca2+ binding should be a mandatory requirement for phosphorylation of the pump protein, though ATP binding per se does not require Ca2+. The model is consistent with high cooperativity in equilibrium binding of Ca2+, both in the absence and presence of ATP.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bennett W. S., Jr, Steitz T. A. Glucose-induced conformational change in yeast hexokinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Oct;75(10):4848–4852. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.10.4848. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandl C. J., Green N. M., Korczak B., MacLennan D. H. Two Ca2+ ATPase genes: homologies and mechanistic implications of deduced amino acid sequences. Cell. 1986 Feb 28;44(4):597–607. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90269-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Champeil P., Gingold M. P., Guillain F., Inesi G. Effect of magnesium on the calcium-dependent transient kinetics of sarcoplasmic reticulum ATPase, studied by stopped flow fluorescence and phosphorylation. J Biol Chem. 1983 Apr 10;258(7):4453–4458. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dupont Y. Low-temperature studies of the sarcoplasmic reticulum calcium pump. Mechanisms of calcium binding. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 May 21;688(1):75–87. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(82)90580-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dupont Y. Occlusion of divalent cations in the phosphorylated calcium pump of sarcoplasmic reticulum. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Aug;109(1):231–238. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb04788.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dutton A., Rees E. D., Singer S. J. An experiment eliminating the rotating carrier mechanism for the active transport of Ca ion in sarcoplasmic reticulum membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 May;73(5):1532–1536. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.5.1532. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernandez-Belda F., Kurzmack M., Inesi G. A comparative study of calcium transients by isotopic tracer, metallochromic indicator, and intrinsic fluorescence in sarcoplasmic reticulum ATPase. J Biol Chem. 1984 Aug 10;259(15):9687–9698. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Froud R. J., Lee A. G. A model for the phosphorylation of the Ca2+ + Mg2+-activated ATPase by phosphate. Biochem J. 1986 Jul 1;237(1):207–215. doi: 10.1042/bj2370207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gafni A., Boyer P. D. Modulation of stoichiometry of the sarcoplasmic reticulum calcium pump may enhance thermodynamic efficiency. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(1):98–101. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.1.98. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hasselbach W. The sarcoplasmic calcium pump. A model of energy transduction in biological membranes. Top Curr Chem. 1979;78:1–56. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill T. L., Inesi G. Equilibrium cooperative binding of calcium and protons by sarcoplasmic reticulum ATPase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jul;79(13):3978–3982. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.13.3978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inesi G., Hill T. L. Calcium and proton dependence of sarcoplasmic reticulum ATPase. Biophys J. 1983 Nov;44(2):271–280. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(83)84299-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inesi G., Kurzmack M., Coan C., Lewis D. E. Cooperative calcium binding and ATPase activation in sarcoplasmic reticulum vesicles. J Biol Chem. 1980 Apr 10;255(7):3025–3031. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inesi G. Mechanism of calcium transport. Annu Rev Physiol. 1985;47:573–601. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.47.030185.003041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jardetzky O. Simple allosteric model for membrane pumps. Nature. 1966 Aug 27;211(5052):969–970. doi: 10.1038/211969a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson E. A., Tanford C., Reynolds J. A. Variable stoichiometry in active ion transport: theoretical analysis of physiological consequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Aug;82(16):5352–5356. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.16.5352. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MONOD J., WYMAN J., CHANGEUX J. P. ON THE NATURE OF ALLOSTERIC TRANSITIONS: A PLAUSIBLE MODEL. J Mol Biol. 1965 May;12:88–118. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(65)80285-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacLennan D. H., Brandl C. J., Korczak B., Green N. M. Amino-acid sequence of a Ca2+ + Mg2+-dependent ATPase from rabbit muscle sarcoplasmic reticulum, deduced from its complementary DNA sequence. Nature. 1985 Aug 22;316(6030):696–700. doi: 10.1038/316696a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meltzer S., Berman M. C. Effects of pH, temperature, and calcium concentration on the stoichiometry of the calcium pump of sarcoplasmic reticulum. J Biol Chem. 1984 Apr 10;259(7):4244–4253. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchinson C., Wilderspin A. F., Trinnaman B. J., Green N. M. Identification of a labelled peptide after stoicheiometric reaction of fluorescein isothiocyanate with the Ca2+ -dependent adenosine triphosphatase of sarcoplasmic reticulum. FEBS Lett. 1982 Sep 6;146(1):87–92. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(82)80710-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pick U., Karlish S. J. Regulation of the conformation transition in the Ca-ATPase from sarcoplasmic reticulum by pH, temperature, and calcium ions. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jun 10;257(11):6120–6126. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds J. A., Johnson E. A., Tanford C. Application of the principle of linked functions to ATP-driven ion pumps: kinetics of activation by ATP. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jun;82(11):3658–3661. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.11.3658. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takisawa H., Makinose M. Occlusion of calcium in the ADP-sensitive phosphoenzyme of the adenosine triphosphatase of sarcoplasmic reticulum. J Biol Chem. 1983 Mar 10;258(5):2986–2992. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanford C., Martin D. W. Equilibrium constants for some steps of the reaction cycle of the sarcoplasmic reticulum calcium pump. Z Naturforsch C. 1982 May-Jun;37(5-6):522–526. doi: 10.1515/znc-1982-5-626. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanford C. Mechanism of active transport: free energy dissipation and free energy transduction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(21):6527–6531. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.21.6527. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanford C., Reynolds J. A., Johnson E. A. Thermodynamic and kinetic cooperativity in ligand binding to multiple sites on a protein: Ca2+ activation of an ATP-driven Ca pump. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jul;82(14):4688–4692. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.14.4688. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanford C. Simple model for the chemical potential change of a transported ion in active transport. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 May;79(9):2882–2884. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.9.2882. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanford C. Translocation pathway in the catalysis of active transport. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(12):3701–3705. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.12.3701. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WYMAN J., Jr LINKED FUNCTIONS AND RECIPROCAL EFFECTS IN HEMOGLOBIN: A SECOND LOOK. Adv Protein Chem. 1964;19:223–286. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3233(08)60190-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson K. D., Rose I. A. Study of crystalline hexokinase-glucose complexes by isotope trapping. J Biol Chem. 1981 Oct 10;256(19):9890–9894. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Meis L., Vianna A. L. Energy interconversion by the Ca2+-dependent ATPase of the sarcoplasmic reticulum. Annu Rev Biochem. 1979;48:275–292. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.48.070179.001423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



