Abstract
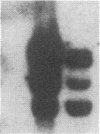
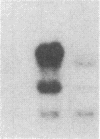
A probe derived from the 3' region of the BCR gene (breakpoint cluster region gene) detects four distinct loci in the human genome. One of the loci corresponds to the complete BCR gene, whereas the others contain a 3' segment of the gene. After HindIII cleavage of human DNA, these four loci are detected as 23-, 19-, 13-, and 9-kilobase-pair fragments, designated BCR4, BCR3, BCR2, and BCR1, respectively, with BCR1 deriving from the original complete BCR gene. All four BCR loci segregate 100% concordantly with human chromosome 22 in a rodent-human somatic cell hybrid panel and are located at chromosome region 22q11.2 by chromosomal in situ hybridization. The BCR2 and BCR4 loci are amplified in leukemia cell line K562 cells, indicating that they fall within the amplification unit that includes immunoglobulin lambda light chain locus (IGL) and ABL locus on the K562 Philadelphia chromosome (Ph1); additionally, in chronic myelogenous leukemia-derived mouse-human hybrids retaining a Ph1 chromosome in the absence of the 9q+ and normal chromosome 22, BCR2 and BCR4 loci are retained, whereas the 3' region of BCR1 and the BCR3 locus are lost, indicating that BCR3 is distal to BCR1 on chromosome 22. Similarly, in mouse-human hybrids retaining a Ph1 chromosome derived from an acute lymphoblastic leukemia-in the absence of the 9q+ and 22, only BCR2 and BCR4 loci are retained, indicating that the breakpoint in this acute lymphoblastic leukemia, as in chronic myelogenous leukemia, is proximal to the BCR1 3' region, but distal to the IGLC locus and the BCR2 and BCR4 3' loci. Thus, the order of loci on chromosome 22 is centromere----BCR2, BCR4, and IGL----BCR1----BCR3----SIS, possibly eliminating BCR2 and BCR4 loci as candidate targets for juxtaposition to the ABL gene in the acute lymphoblastic leukemia Ph1 chromosome.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bartram C. R., de Klein A., Hagemeijer A., van Agthoven T., Geurts van Kessel A., Bootsma D., Grosveld G., Ferguson-Smith M. A., Davies T., Stone M. Translocation of c-ab1 oncogene correlates with the presence of a Philadelphia chromosome in chronic myelocytic leukaemia. Nature. 1983 Nov 17;306(5940):277–280. doi: 10.1038/306277a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cannizzaro L. A., Emanuel B. S. An improved method for G-banding chromosomes after in situ hybridization. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1984;38(4):308–309. doi: 10.1159/000132079. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catovsky D. Ph1-positive acute leukaemia and chronic granulocytic leukaemia: one or two diseases? Br J Haematol. 1979 Aug;42(4):493–498. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1979.tb01161.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan L. C., Karhi K. K., Rayter S. I., Heisterkamp N., Eridani S., Powles R., Lawler S. D., Groffen J., Foulkes J. G., Greaves M. F. A novel abl protein expressed in Philadelphia chromosome positive acute lymphoblastic leukaemia. Nature. 1987 Feb 12;325(6105):635–637. doi: 10.1038/325635a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark S. S., McLaughlin J., Crist W. M., Champlin R., Witte O. N. Unique forms of the abl tyrosine kinase distinguish Ph1-positive CML from Ph1-positive ALL. Science. 1987 Jan 2;235(4784):85–88. doi: 10.1126/science.3541203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Croce C. M., Isobe M., Palumbo A., Puck J., Ming J., Tweardy D., Erikson J., Davis M., Rovera G. Gene for alpha-chain of human T-cell receptor: location on chromosome 14 region involved in T-cell neoplasms. Science. 1985 Mar 1;227(4690):1044–1047. doi: 10.1126/science.3919442. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Croce C. M. Role of chromosome translocations in human neoplasia. Cell. 1987 Apr 24;49(2):155–156. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90552-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Croce C. M., Thierfelder W., Erikson J., Nishikura K., Finan J., Lenoir G. M., Nowell P. C. Transcriptional activation of an unrearranged and untranslocated c-myc oncogene by translocation of a C lambda locus in Burkitt. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Nov;80(22):6922–6926. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.22.6922. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalla-Favera R., Bregni M., Erikson J., Patterson D., Gallo R. C., Croce C. M. Human c-myc onc gene is located on the region of chromosome 8 that is translocated in Burkitt lymphoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(24):7824–7827. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.24.7824. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalla-Favera R., Gallo R. C., Giallongo A., Croce C. M. Chromosomal localization of the human homolog (c-sis) of the simian sarcoma virus onc gene. Science. 1982 Nov 12;218(4573):686–688. doi: 10.1126/science.6291150. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Klein A., Hagemeijer A., Bartram C. R., Houwen R., Hoefsloot L., Carbonell F., Chan L., Barnett M., Greaves M., Kleihauer E. bcr rearrangement and translocation of the c-abl oncogene in Philadelphia positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Blood. 1986 Dec;68(6):1369–1375. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dürst M., Croce C. M., Gissmann L., Schwarz E., Huebner K. Papillomavirus sequences integrate near cellular oncogenes in some cervical carcinomas. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Feb;84(4):1070–1074. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.4.1070. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erikson J., Finger L., Sun L., ar-Rushdi A., Nishikura K., Minowada J., Finan J., Emanuel B. S., Nowell P. C., Croce C. M. Deregulation of c-myc by translocation of the alpha-locus of the T-cell receptor in T-cell leukemias. Science. 1986 May 16;232(4752):884–886. doi: 10.1126/science.3486470. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erikson J., Griffin C. A., ar-Rushdi A., Valtieri M., Hoxie J., Finan J., Emanuel B. S., Rovera G., Nowell P. C., Croce C. M. Heterogeneity of chromosome 22 breakpoint in Philadelphia-positive (Ph+) acute lymphocytic leukemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(6):1807–1811. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.6.1807. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gale R. P., Canaani E. An 8-kilobase abl RNA transcript in chronic myelogenous leukemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Sep;81(18):5648–5652. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.18.5648. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groffen J., Stephenson J. R., Heisterkamp N., de Klein A., Bartram C. R., Grosveld G. Philadelphia chromosomal breakpoints are clustered within a limited region, bcr, on chromosome 22. Cell. 1984 Jan;36(1):93–99. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90077-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harper M. E., Saunders G. F. Localization of single copy DNA sequences of G-banded human chromosomes by in situ hybridization. Chromosoma. 1981;83(3):431–439. doi: 10.1007/BF00327364. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heisterkamp N., Stam K., Groffen J., de Klein A., Grosveld G. Structural organization of the bcr gene and its role in the Ph' translocation. 1985 Jun 27-Jul 3Nature. 315(6022):758–761. doi: 10.1038/315758a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konopka J. B., Watanabe S. M., Witte O. N. An alteration of the human c-abl protein in K562 leukemia cells unmasks associated tyrosine kinase activity. Cell. 1984 Jul;37(3):1035–1042. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90438-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozbor D., Giallongo A., Sierzega M. E., Konopka J. B., Witte O. N., Showe L. C., Croce C. M. Expression of a translocated c-abl gene in hybrids of mouse fibroblasts and chronic myelogenous leukaemia cells. Nature. 1986 Jan 23;319(6051):331–333. doi: 10.1038/319331a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurzrock R., Shtalrid M., Romero P., Kloetzer W. S., Talpas M., Trujillo J. M., Blick M., Beran M., Gutterman J. U. A novel c-abl protein product in Philadelphia-positive acute lymphoblastic leukaemia. Nature. 1987 Feb 12;325(6105):631–635. doi: 10.1038/325631a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawn R. M., Fritsch E. F., Parker R. C., Blake G., Maniatis T. The isolation and characterization of linked delta- and beta-globin genes from a cloned library of human DNA. Cell. 1978 Dec;15(4):1157–1174. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90043-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lozzio C. B., Lozzio B. B. Human chronic myelogenous leukemia cell-line with positive Philadelphia chromosome. Blood. 1975 Mar;45(3):321–334. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McBride O. W., Hieter P. A., Hollis G. F., Swan D., Otey M. C., Leder P. Chromosomal location of human kappa and lambda immunoglobulin light chain constant region genes. J Exp Med. 1982 May 1;155(5):1480–1490. doi: 10.1084/jem.155.5.1480. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pegoraro L., Matera L., Ritz J., Levis A., Palumbo A., Biagini G. Establishment of a Ph1-positive human cell line (BV173). J Natl Cancer Inst. 1983 Mar;70(3):447–453. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowley J. D. Letter: A new consistent chromosomal abnormality in chronic myelogenous leukaemia identified by quinacrine fluorescence and Giemsa staining. Nature. 1973 Jun 1;243(5405):290–293. doi: 10.1038/243290a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selden J. R., Emanuel B. S., Wang E., Cannizzaro L., Palumbo A., Erikson J., Nowell P. C., Rovera G., Croce C. M. Amplified C lambda and c-abl genes are on the same marker chromosome in K562 leukemia cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Dec;80(23):7289–7292. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.23.7289. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Showe L. C., Moore R. C., Erikson J., Croce C. M. MYC oncogene involved in a t(8;22) chromosome translocation is not altered in its putative regulatory regions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(9):2824–2828. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.9.2824. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]